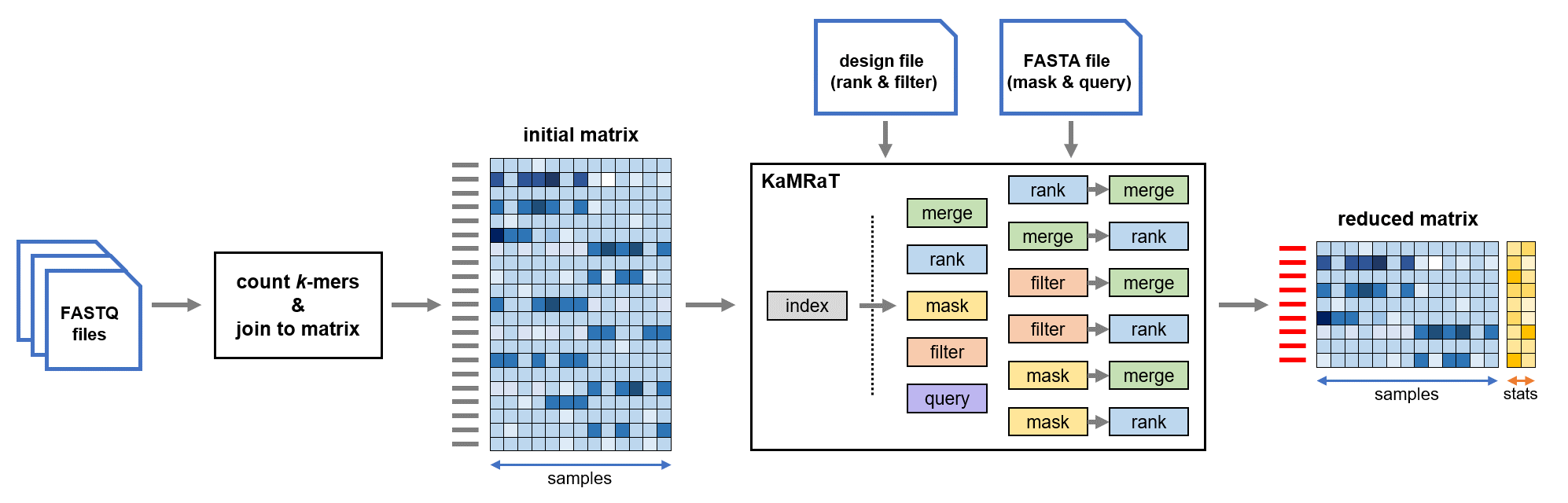
KaMRaT is a C++ tool for finding substrings with interesting properties in large NGS datasets.
KaMRaT requires a k-mer count matrix extracted from the NGS files (e.g. with Jellyfish), and potential design table or FASTA file (see below for more information).
KaMRaT then provides a set of tools for reducing the k-mer matrix and extending k-mers to longer contigs. The main modules are:
-
kamrat index: index feature* count table on disk
-
kamrat filter: remove/retain features* by expression level
-
kamrat mask: remove/retain k-mers matching given fasta sequences
-
kamrat merge: merge k-mers into contigs
-
kamrat score (or kamrat rank as an alias): score features* by classification performance, statistical significance, correlation, or variability
-
kamrat query: estimate count vectors of given list of contigs
Note: * features can be not only k-mers or k-mer contigs, but also general features such as genes or transcripts.
KaMRaT means "k-mer Matrix Reduction Toolkit", or "k-mer Matrix, Really Tremendous !".
Variables
indir="demo-data/inputs"
outdir="demo-data/outputs"
sample_list=(sample1 sample2)
dsgnfile=$indir/rank-design.txt
kmer_tab_path=$outdir/kmer-counts.tsv.gzk-mer matrix preparation
mkdir $outdir
# Step 1: jellyfish count & dump
for s in ${sample_list[@]} # $sample_list contains list of considered sample names
do
jellyfish count -m 31 -s 1000000 -C -o $outdir/$s.jf -F 2 <(zcat $indir/$s.R1.fastq.gz) <(zcat $indir/$s.R2.fastq.gz)
jellyfish dump -c $outdir/$s.jf | sort -k 1 > $outdir/$s.txt # <= here sort is important !
done
# Step 2: joinCounts
echo -n "tag" | gzip -c > $kmer_tab_path
for s in ${sample_list[@]} # $sample_list contains list of considered sample names
do
echo -ne "\t"$s | gzip -c >> $kmer_tab_path
done
echo "" | gzip -c >> $kmer_tab_path
apptainer exec --bind /src:/des kamrat.sif joinCounts -r 1 -a 1 $outdir/*.txt | gzip -c >> $kmer_tab_path # no filter of recurrenceNote: please keep in mind that the sort after jellyfish dump is important for joinCounts.
KaMRaT index
mkdir $outdir/kamrat.idx
# Make index for k-mer matrix with k=31, unstranded mode, and with a count per billion normalization
apptainer exec --bind /src:/des kamrat.sif kamrat index -intab $kmer_tab_path -outdir $outdir/kamrat.idx -klen 31 -unstrand -nfbase 1000000000KaMRaT score-merge approach
# Select top 50% of relevant k-mers using ttest pi-value
apptainer exec --bind /src:/des kamrat.sif kamrat score -idxdir $outdir/kamrat.idx -scoreby ttest.pi -design $indir/rank-design.txt -outpath $outdir/top-ranked-kmers.ttest-pi.bin -seltop 0.5
# Extend k-mers by tolerating overlap from 30nc to 15nc, intervened by Pearson distance <= 0.20, and with mean contig count
apptainer exec --bind /src:/des kamrat.sif kamrat merge -idxdir $outdir/kamrat.idx -overlap 30-15 -with $outdir/top-ranked-kmers.ttest-pi.bin -interv pearson:0.20 -outpath $outdir/contig-counts.ttest-pi.pearson20.tsv -withcounts meanKaMRaT merge-score approach
# Extend k-mers by tolerating overlap from 30nc to 15nc, intervened by Pearson distance <= 0.20, and with mean contig count
apptainer exec --bind /src:/des kamrat.sif kamrat merge -idxdir $outdir/kamrat.idx -overlap 30-15 -interv pearson:0.20 -outpath $outdir/contigs.pearson20.bin
# Select top 50% of relevant contigs using ttest pi-value
apptainer exec --bind /src:/des kamrat.sif kamrat score -idxdir $outdir/kamrat.idx -scoreby ttest.pi -design $indir/rank-design.txt -seltop 0.5 -with $outdir/contigs.pearson20.bin -outpath $outdir/top-ranked-contigs.pearson20.ttest-pi.tsv -withcountsKaMRaT per se is shown at the center of the workflow. It is a C++ program that takes as input a count matrix and produces another reduced matrix as output.
In the shown workflow, KaMRaT is used for reducing a count matrix produced from a set of FASTQ files and producing a reduced matrix with features of interest with respect to information given in the design or the FASTA file.
The feature count matrix contains features in row and samples in column. Features can be k-mers (for all modules) as well as other general features such as genes/transcripts (only for KaMRaT index, filter, and score). The feature counts can be either normalized or non-normalized.
The matrix should be in .tsv or .tsv.gz format, in which fields are separated by tabulations. The first column in matrix should always be the feature column (sequences or feature names).
Features of k-mers or contigs are represented by their own sequence.
The k-mer feature matrix can be constructed with the following possibilities:
- The Snakefile provided with the project + DE-kupl joinCounts
- DE-kupl's raw-counts.tsv or masked-counts.tsv matrices
The final output count matrix is also .tsv format table, where fields are separated by tabulations.
In the matrix, the features are presented as rows, and the columns are in same order as the input.
This final output of count matrix is generated when -withcounts option is given to the module.
KaMRaT index is always the first module of workflow. In a typical use case, it only needs to be done once for different applications of other functional modules. However, because currently KaMRaT only supports up to two-layer chaining of functional modules, advanced users may want to reindex the final output matrix. In this situation, please ensure that the matrix to reindex only contains feature column and sample count columns.
The functional modules of KaMRaT include filter, mask, merge, score, and query. They are always applied on the constructed KaMRaT index. As indicated in the workflow figure, some functional modules like merge and score can follow others as a second layer. In these cases, the intermediate output of the first module and the final output of the second module are controlled by the -withcounts and -with arguments (described below).
The design file is indicated by the -design option in the modules filter and score.
The design file is formed by two columns:
- the first column indicates samples (i.e., columns of the input count matrix);
- the second column indicates the associated values considered to filter or score.
In KaMRaT filter, the second column can be either "UP" or "DOWN", indicating whether the sample should be considered as up-regulated or down-regulated for filtering.
In KaMRaT score, the second column can be:
- a string indicating sample's condition for the classification methods;
- a real value for correlation evaluation.
Please note that this file should not contain any header row.
The FASTA file is indicated by the -fasta option in the modules mask and query, giving the sequences to mask or query.
As indicated by the workflow figure, some functional modules may follow others in the workflow. In this situation, the -withcounts option is supposed to be given to the second module rather than to the first. For example in the merge-score workflow, -withcounts should be given to score but not to merge.
The first functional module in the workflow without -withcounts option genrates binary intermediate files as the second module's input (taken by the -with argument of the second module).
A set of auxiliary tools to be used for upstream and downstream of kamrat are provided:
- Upstream tools:
- A matrix generating module controlled by Snakemake which applies jellyfish and DE-kupl joinCounts module
- A bash script for generating a submatrix by selecting from it a set of columns
- Downstream tools:
- A feature selection model with an R script applying ridge/lasso regressions and random forest classifier
- A contig counting module implemented in C++ for estimating the counts of a list of contigs in an independent dataset; it also supports evaluation of sample count coherence among contig's compositional k-mers
- A model evaluation module written in R taking a trained model and evaluating it with a feature count matrix and feature conditions
Build from source
- CMake
- MLPack >=4.0.0
- Armadillo
- Boost-iostreams
MLPack can be installed on Linux/Mac, Windows, or via conda by following the corresponding links.
If you are installing MLPack with conda, please add the following line into your .bashrc file in the home/ directory before compiling KaMRaT:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/path_to_conda_env/mlpack/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATHFirstly, clone the repository:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/Transipedia/KaMRaT.git
cd KaMRaT
cmake . && make -jFinally, an executable binary file is available as apps/kamrat.
Use apptainer (previously singularity)
You can build the container from docker hub:
apptainer build KaMRaT.sif docker://xuehl/kamrat:latestNote: if you use KaMRaT in command line, please remember to indicate the full path to KaMRaT binary file.
We recommande using KaMRaT within apptainer(previously singularity):
apptainer exec -B /bind_src:/bind_des kamrat <CMD> [options] input_table
# <CMD> can be one of filter, mask, merge, scoreThe -B option is for binding disk partitions to apptainer image, please check apptainer helper for details:
apptainer exec -hIt's also executable directly on command line:
/path_to_KaMRaT_bin_dir/kamrat <CMD> [options] input_table
# <CMD> can be index, filter, mask, merge, score, queryIn the following sections, we present under the situation of using KaMRaT in apptainer.
For running it directly on command line, please replace the leading apptainer exec -B /bind_src:/bind_des by the path to KaMRaT binary file.
KaMRaT's top-level helper is accessible by typing one of these commands:
apptainer exec kamrat
apptainer exec kamrat -h
apptainer exec kamrat -helpHelpers of each KaMRaT modules are accessible via:
# <CMD> can be one from filter, mask, merge, score #
apptainer exec kamrat <CMD> -h
apptainer exec kamrat <CMD> -helpindex: index feature count table on disk
[USAGE] kamrat index -intab STR -outdir STR [-klen INT -unstrand -nfbase INT]
[OPTION] -h, -help Print the helper
-intab STR Input table for index, mandatory
-outdir STR Output index directory, mandatory
-klen k-mer length, mandatory if features are k-mer
if present, indexation will be switched to k-mer mode
-unstrand Unstranded mode, indexation with canonical k-mers
if present, indexation will be switched to k-mer mode
-nfbase INT Base for calculating normalization factor
normCount_ij <- INT * rawCount_ij / sum_i{rawCount_ij}
if not provided, input counts will not be normalized
filter: filter feature by expression level
[USAGE] kamrat filter -idxdir STR -design STR [-upmin INT1:INT2 -downmax INT1:INT2 -reverse -outpath STR -withcounts]
[OPTION] -h,-help Print the helper
-idxdir STR Indexing folder by KaMRaT index, mandatory
-design STR Path to filter design file, a table of two columns, mandatory
the first column indicate sample names
the second column should be either UP or DOWN (capital letters)
samples with UP will be considered as up-regulated samples
samples with DOWN will be considered as down-regulated samples
samples not given will be neutral (not considered for filter)
samples can also be all UP or all DOWN
-upmin INT1:INT2 Up feature lower bound, [1:1, meaning no filter]
output features counting >= INT1 in >= INT2 UP-samples
-downmax INT1:INT2 Down feature upper bound [inf:1, meaning no filter]
output features counting <= INT1 in >= INT2 DOWN-samples
-reverse Reverse filter, to remove eligible features [false]
-outpath STR Path to results after filter
if not provided, output to screen
-withcounts Output sample count vectors [false]
mask: mask k-mers from matrix
[USAGE] kamrat mask -idxdir STR -fasta STR [-reverse -outpath STR -withcounts]
[OPTION] -h,-help Print the helper
-idxdir STR Indexing folder by KaMRaT index, mandatory
-fasta STR Sequence fasta file as the mask, mandatory;
-reverse Reverse mask, to select the k-mers in sequence fasta file [false];
-outpath STR Path to extension results
if not provided, output to screen
-withcounts Output sample count vectors [false]
merge: extend k-mers into contigs
[USAGE] kamrat merge -idxdir STR -overlap MAX-MIN [-with STR1[:STR2] -interv STR[:FLOAT] -min-nbkmer INT -outpath STR -withcounts STR]
[OPTION] -h,-help Print the helper;
-idxdir STR Indexing folder by KaMRaT index, mandatory;
-overlap MAX-MIN Overlap range for extension, mandatory
MIN and MAX are integers, MIN <= MAX < k-mer length;
-with STR1[:STR2] File indicating k-mers to be extended (STR1) and rep-mode (STR2)
if not provided, all indexed k-mers are used for extension
in the file STR1, a supplementary column of rep-value can be provided
STR2 can be one of {min, minabs, max, maxabs} [min];
-interv STR[:FLOAT] Intervention method for extension [pearson:0.20]
can be one of {none, pearson, spearman, mac}
the threshold may follow a ':' symbol;
-min-nbkmer INT Minimal length of extended contigs [0];
-outpath STR Path to extension results
if not provided, output to screen;
-withcounts STR Output sample count vectors, STR can be one of [mean, median]
if not provided, output without count vector
Three intervention methods are available for choice:
pearson: Pearson distance, i.e., 0.5 * [1 - pearson.correlation(x, y)]spearman: Spearman distance, i.e., 0.5 * [1 - spearman.correlation(x, y)]mac: mean absolute contrast, as described in Nguyen, H.T., et al. 2021
The threshold controlling these distances can be given between [0, 1], where 0 indicates the most strict case and 1 indicates the most permissive case (equivalent to none).
score: score features* by classification performance, statistical significance, correlation, or variability
[USAGE] kamrat score -idxdir STR -count-mode STR -scoreby STR -design STR [-with STR1[:STR2] -seltop NUM -outpath STR -withcounts] # kamrat rank as an alias
[OPTION] -h,-help Print the helper
-idxdir STR Indexing folder by KaMRaT index, mandatory
-scoreby STR Scoring method, mandatory, can be one of:
ttest.padj adjusted p-value of t-test between conditions
ttest.pi \u03C0-value of t-test between conditions
snr signal-to-noise ratio between conditions
dids DIDS score
lr:nfold accuracy by logistic regression classifier
bayes:nfold accuracy by naive Bayes classifier
svm:nfold accuracy on SVM classifier
-design STR Path to file indicating sample-condition design
without header line, each row can be either:
sample name, sample condition
sample name, sample condition, sample batch (only for lrc, nbc, and svm)
-with STR1[:STR2] File indicating features to score (STR1) and counting mode (STR2)
if not provided, all indexed features are used for scoring
STR2 can be one of [rep, mean, median]
-seltop NUM Select top scored features
if NUM > 1, number of top features to select (should be integer)
if 0 < NUM <= 1, ratio of top features to select
if absent or NUM <= 0, output all features
-outpath STR Path to scoring result
if not provided, output to screen
-withcounts Output sample count vectors [false]
[NOTE] For scoring methods lrc, nbc, and svm, a univariate CV fold number (nfold) can be provided
if nfold = 0, leave-one-out cross-validation
if nfold = 1, without cross-validation, training and testing on the whole datset
if nfold > 1, n-fold cross-validation
For t-test scoring methods, a transformation log2(x + 1) is applied to sample counts
For SVM scoring, sample counts standardization is applied feature by feature
query: query sequences
[USAGE] kamrat query -idxdir STR -fasta STR -toquery STR [-withabsent -outpath STR]
[OPTION] -h,-help Print the helper
-idxdir STR Indexing folder by KaMRaT index, mandatory
-fasta STR Sequence fasta file, mandatory
-toquery STR Query method, mandatory, can be one of:
mean mean count among all composite k-mers for each sample
median median count among all composite k-mers for each sample
-withabsent Output also absent queries (count vector all 0) [default: false]
-outpath STR Path to extension results
if not provided, output to screen
Armadillo:
- Conrad Sanderson and Ryan Curtin. Armadillo: a template-based C++ library for linear algebra. Journal of Open Source Software, Vol. 1, pp. 26, 2016.
- Conrad Sanderson and Ryan Curtin. A User-Friendly Hybrid Sparse Matrix Class in C++. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS), Vol. 10931, pp. 422-430, 2018.
DE-kupl: Audoux, J., Philippe, N., Chikhi, R. et al. DE-kupl: exhaustive capture of biological variation in RNA-seq data through k-mer decomposition. Genome Biol 18, 243 (2017).
MLPack: R.R. Curtin, M. Edel, M. Lozhnikov, Y. Mentekidis, S. Ghaisas, S. Zhang. mlpack 3: a fast, flexible machine learning library. Journal of Open Source Software 3:26, 2018.
glmnet: Friedman, Jerome, Trevor Hastie, and Rob Tibshirani. "Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent." Journal of statistical software 33.1 (2010): 1.
randomForest: Liaw, Andy, and Matthew Wiener. "Classification and regression by randomForest." R news 2.3 (2002): 18-22.