Simplified, monocycle version of the LEGv8 processor designed by the Department of Computer and Digital Systems Engineering (PCS) at Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo (Poli-USP) and implemented in VHDL for Digital Systems II (PCS3225) in 2021.
The build process once hdlmake is installed is straightforward:
- Clone this repository
git clone https://github.com/tomaz-suller/PoliLEG.git- Enter the
simulationdirectory and build with hdlmake
cd simulation
hdlmake makefile
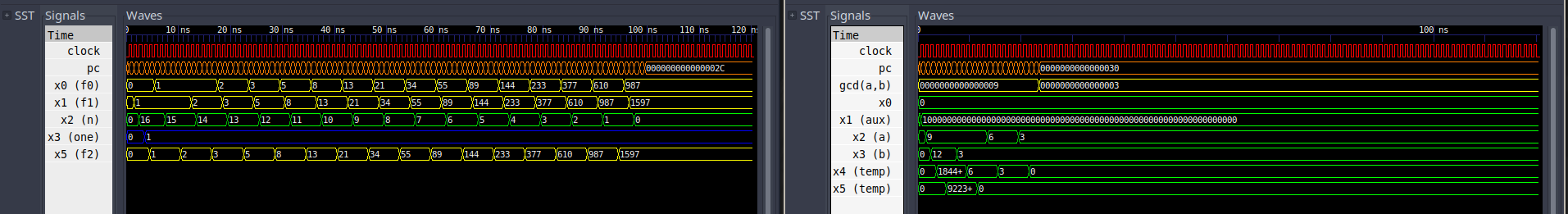
makeThe default options will run fibonacci and automatically
open GTKWave to show the generated waveform using the
configuration file supplied (fibonacci.gtkw). This behaviour
can be altered by editing simulation/Manifest.py and by then
recreating the Makefile as described previously.
PoliLEG can only execute a small subset of the ARMv8 instructions. Namely, it can only execute the following functions, with their respective formats and opcodes for reference. More detailed information can be found in the Green Card of LEGv8.
| Instruction | Format | opcode |
|---|---|---|
| LDUR | D | 11111000010 |
| STUR | D | 11111000000 |
| CBZ | CB | 10110100 |
| B | B | 000101 |
| ADD | R | 10001011000 |
| SUB | R | 11001011000 |
| AND | R | 10001010000 |
| ORR | R | 10101010000 |
Therefore, any software must be specifically designed to only
use these instructions. As this processor was developed for
educational purposes, the supplied software (fibonacci and
gcd) were handwritten in LEGv8 Assembly and then manually
converted to machine code.
Any component is avaliable for use in other projects if and only if these projects comply with this software's LICENSE. Most importantly, it is work noting that your work must disclose its full source if it uses any part whatsoever of this software.
It is also worth noting this repository is NOT meant to provide ready-made implementations for the course's projects. Therefore, this software cannot be submitted as proof of your own work, and any known attempts to do so will be reported immediately without exception.
Directories were set up according to hdlmake's example setup.
github: media content used in the README;modules: hardware descriptions of components used to build the processor, including a dummy toplevel implementation for testing purposes;simulation: files related to simulation with GHDL ( hdlmake'sManifest.pyand GTKWave configuration files);software: content of both the instruction memory (rom.dat) and the data memory (ram.dat). A GCD calculator using Euclides' Algorithm (gcd) and a Fibonacci sequence generator (fibonacci) are supplied;testbenches: testbenches for hardware descriptions following the directory structure ofmodules. Note that all components have testbenches with assertions (i.e. automatically produce a pass or fail message on execution) except forpolilegsc,datapathandtoplevel.
D. Patterson and J. Hennessy. Computer Organization and Design ARM Edition: The Hardware Software Interface. The Morgan Kaufmann Series in Computer Architecture and Design. Elsevier Science, 2016.