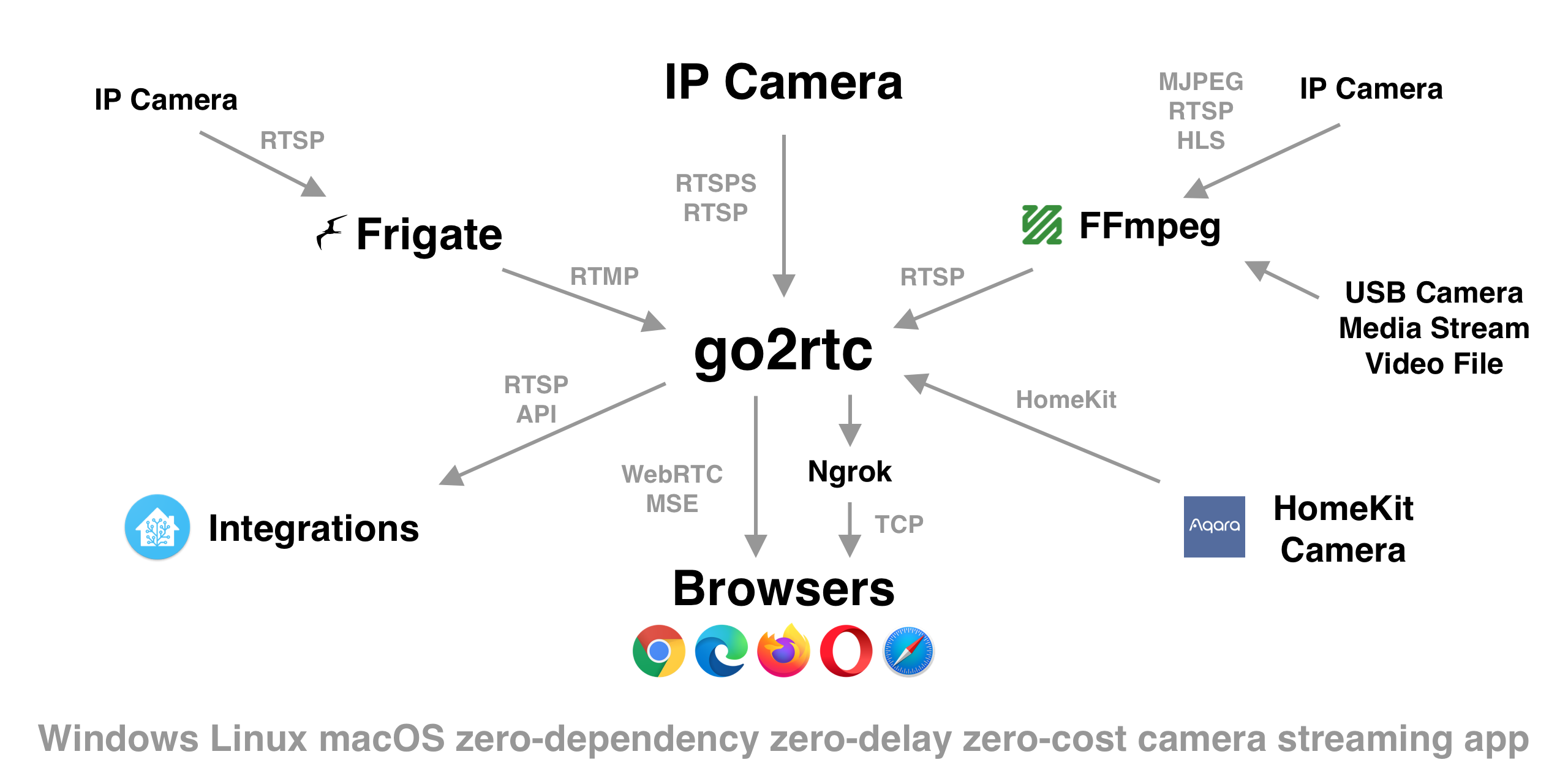
Ultimate camera streaming application with support RTSP, WebRTC, HomeKit, FFmpeg, RTMP, etc.
- zero-dependency and zero-config small app for all OS (Windows, macOS, Linux, ARM)
- zero-delay for many supported protocols (lowest possible streaming latency)
- streaming from RTSP, RTMP, DVRIP, HTTP (FLV/MJPEG/JPEG/TS), USB Cameras and other sources
- streaming from any sources, supported by FFmpeg
- streaming to RTSP, WebRTC, MSE/MP4, HLS or MJPEG
- first project in the World with support streaming from HomeKit Cameras
- first project in the World with support H265 for WebRTC in browser (Safari only, read more)
- on the fly transcoding for unsupported codecs via FFmpeg
- play audio files and live streams on some cameras with speaker
- multi-source 2-way codecs negotiation
- mixing tracks from different sources to single stream
- auto match client supported codecs
- 2-way audio for some cameras
- streaming from private networks via Ngrok
- can be integrated to any smart home platform or be used as standalone app
Inspired by:
- series of streaming projects from @deepch
- webrtc go library and whole @pion team
- rtsp-simple-server idea from @aler9
- GStreamer framework pipeline idea
- MediaSoup framework routing idea
- HomeKit Accessory Protocol from @brutella
- Fast start
- Configuration
- Module: Streams
- Two way audio
- Source: RTSP
- Source: RTMP
- Source: HTTP
- Source: ONVIF
- Source: FFmpeg
- Source: FFmpeg Device
- Source: Exec
- Source: Echo
- Source: HomeKit
- Source: DVRIP
- Source: Tapo
- Source: Ivideon
- Source: Hass
- Source: ISAPI
- Source: Roborock
- Source: WebRTC
- Source: WebTorrent
- Incoming sources
- Stream to camera
- Module: API
- Module: RTSP
- Module: WebRTC
- Module: WebTorrent
- Module: Ngrok
- Module: Hass
- Module: MP4
- Module: HLS
- Module: MJPEG
- Module: Log
- Module: Streams
- Security
- Codecs filters
- Codecs madness
- Codecs negotiation
- Projects using go2rtc
- Camera experience
- TIPS
- FAQ
- Download binary or use Docker or Home Assistant Add-on or Integration
- Open web interface:
http://localhost:1984/
Optionally:
- add your streams to config file
- setup external access to webrtc
Developers:
- write your own web interface
- integrate web api into your smart home platform
Download binary for your OS from latest release:
go2rtc_win64.zip- Windows 64-bitgo2rtc_win32.zip- Windows 32-bitgo2rtc_win_arm64.zip- Windows ARM 64-bitgo2rtc_linux_amd64- Linux 64-bitgo2rtc_linux_i386- Linux 32-bitgo2rtc_linux_arm64- Linux ARM 64-bit (ex. Raspberry 64-bit OS)go2rtc_linux_arm- Linux ARM 32-bit (ex. Raspberry 32-bit OS)go2rtc_linux_armv6- Linux ARMv6 (for old Raspberry 1 and Zero)go2rtc_linux_mipsel- Linux MIPS (ex. Xiaomi Gateway 3)go2rtc_mac_amd64.zip- Mac Intel 64-bitgo2rtc_mac_arm64.zip- Mac ARM 64-bit
Don't forget to fix the rights chmod +x go2rtc_xxx_xxx on Linux and Mac.
Container alexxit/go2rtc with support amd64, 386, arm64, arm. This container is the same as Home Assistant Add-on, but can be used separately from Home Assistant. Container has preinstalled FFmpeg, Ngrok and Python.
- Install Add-On:
- Settings > Add-ons > Plus > Repositories > Add
https://github.com/AlexxIT/hassio-addons - go2rtc > Install > Start
- Settings > Add-ons > Plus > Repositories > Add
- Setup Integration
WebRTC Camera custom component can be used on any Home Assistant installation, including HassWP on Windows. It can automatically download and use the latest version of go2rtc. Or it can connect to an existing version of go2rtc. Addon installation in this case is optional.
- by default go2rtc will search
go2rtc.yamlin the current work dirrectory apiserver will start on default 1984 port (TCP)rtspserver will start on default 8554 port (TCP)webrtcwill use port 8555 (TCP/UDP) for connectionsffmpegwill use default transcoding options
Configuration options and a complete list of settings can be found in the wiki.
Available modules:
- streams
- api - HTTP API (important for WebRTC support)
- rtsp - RTSP Server (important for FFmpeg support)
- webrtc - WebRTC Server
- mp4 - MSE, MP4 stream and MP4 shapshot Server
- hls - HLS TS or fMP4 stream Server
- mjpeg - MJPEG Server
- ffmpeg - FFmpeg integration
- ngrok - Ngrok integration (external access for private network)
- hass - Home Assistant integration
- log - logs config
go2rtc support different stream source types. You can config one or multiple links of any type as stream source.
Available source types:
- rtsp -
RTSPandRTSPScameras with two way audio support - rtmp -
RTMPstreams - http -
HTTP-FLV,MPEG-TS,JPEG(snapshots),MJPEGstreams - onvif - get camera
RTSPlink and snapshot link usingONVIFprotocol - ffmpeg - FFmpeg integration (
HLS,filesand many others) - ffmpeg:device - local USB Camera or Webcam
- exec - get media from external app output
- echo - get stream link from bash or python
- homekit - streaming from HomeKit Camera
- dvrip - streaming from DVR-IP NVR
- tapo - TP-Link Tapo cameras with two way audio support
- ivideon - public cameras from Ivideon service
- hass - Home Assistant integration
- isapi - two way audio for Hikvision (ISAPI) cameras
- roborock - Roborock vacuums with cameras
- webrtc - WebRTC/WHEP sources
- webtorrent - WebTorrent source from another go2rtc
Read more about incoming sources
Supported for sources:
- RTSP cameras with ONVIF Profile T (back channel connection)
- TP-Link Tapo cameras
- Hikvision ISAPI cameras
- Roborock vacuums models with cameras
- Any Browser as IP-camera
Two way audio can be used in browser with WebRTC technology. The browser will give access to the microphone only for HTTPS sites (read more).
go2rtc also support play audio files and live streams on this cameras.
streams:
sonoff_camera: rtsp://rtsp:12345678@192.168.1.123/av_stream/ch0
dahua_camera:
- rtsp://admin:password@192.168.1.123/cam/realmonitor?channel=1&subtype=0&unicast=true&proto=Onvif
- rtsp://admin:password@192.168.1.123/cam/realmonitor?channel=1&subtype=1
amcrest_doorbell:
- rtsp://username:password@192.168.1.123:554/cam/realmonitor?channel=1&subtype=0#backchannel=0
unify_camera: rtspx://192.168.1.123:7441/fD6ouM72bWoFijxK
glichy_camera: ffmpeg:rstp://username:password@192.168.1.123/live/ch00_1 Recommendations
- Amcrest Doorbell users may want to disable two way audio, because with an active stream you won't have a call button working. You need to add
#backchannel=0to the end of your RTSP link in YAML config file - Dahua Doorbell users may want to change backchannel audio codec
- Unify users may want to disable HTTPS verification. Use
rtspx://prefix instead ofrtsps://. And don't use?enableSrtpsuffix - TP-Link Tapo users may skip login and password, because go2rtc support login without them
- If your camera has two RTSP links - you can add both of them as sources. This is useful when streams has different codecs, as example AAC audio with main stream and PCMU/PCMA audio with second stream
- If the stream from your camera is glitchy, try using ffmpeg source. It will not add CPU load if you won't use transcoding
- If the stream from your camera is very glitchy, try to use transcoding with ffmpeg source
You can get stream from RTMP server, for example Frigate.
streams:
rtmp_stream: rtmp://192.168.1.123/live/camera1Support Content-Type:
- HTTP-FLV (
video/x-flv) - same as RTMP, but over HTTP - HTTP-JPEG (
image/jpeg) - camera snapshot link, can be converted by go2rtc to MJPEG stream - HTTP-MJPEG (
multipart/x) - simple MJPEG stream over HTTP - MPEG-TS (
video/mpeg) - legacy streaming format
Source also support HTTP and TCP streams with autodetection for different formats: MJPEG, H.264/H.265 bitstream, MPEG-TS.
streams:
# [HTTP-FLV] stream in video/x-flv format
http_flv: http://192.168.1.123:20880/api/camera/stream/780900131155/657617
# [JPEG] snapshots from Dahua camera, will be converted to MJPEG stream
dahua_snap: http://admin:password@192.168.1.123/cgi-bin/snapshot.cgi?channel=1
# [MJPEG] stream will be proxied without modification
http_mjpeg: https://mjpeg.sanford.io/count.mjpeg
# [MJPEG or H.264/H.265 bitstream or MPEG-TS]
tcp_magic: tcp://192.168.1.123:12345PS. Dahua camera has bug: if you select MJPEG codec for RTSP second stream - snapshot won't work.
The source is not very useful if you already know RTSP and snapshot links for your camera. But it can be useful if you don't.
WebUI > Add webpage support ONVIF autodiscovery. Your server must be on the same subnet as the camera. If you use docker, you must use "network host".
streams:
dahua1: onvif://admin:password@192.168.1.123
reolink1: onvif://admin:password@192.168.1.123:8000
tapo1: onvif://admin:password@192.168.1.123:2020You can get any stream or file or device via FFmpeg and push it to go2rtc. The app will automatically start FFmpeg with the proper arguments when someone starts watching the stream.
- FFmpeg preistalled for Docker and Hass Add-on users
- Hass Add-on users can target files from /media folder
Format: ffmpeg:{input}#{param1}#{param2}#{param3}. Examples:
streams:
# [FILE] all tracks will be copied without transcoding codecs
file1: ffmpeg:/media/BigBuckBunny.mp4
# [FILE] video will be transcoded to H264, audio will be skipped
file2: ffmpeg:/media/BigBuckBunny.mp4#video=h264
# [FILE] video will be copied, audio will be transcoded to pcmu
file3: ffmpeg:/media/BigBuckBunny.mp4#video=copy#audio=pcmu
# [HLS] video will be copied, audio will be skipped
hls: ffmpeg:https://devstreaming-cdn.apple.com/videos/streaming/examples/bipbop_16x9/gear5/prog_index.m3u8#video=copy
# [MJPEG] video will be transcoded to H264
mjpeg: ffmpeg:http://185.97.122.128/cgi-bin/faststream.jpg#video=h264
# [RTSP] video with rotation, should be transcoded, so select H264
rotate: ffmpeg:rtsp://rtsp:12345678@192.168.1.123/av_stream/ch0#video=h264#rotate=90All trascoding formats has built-in templates: h264, h265, opus, pcmu, pcmu/16000, pcmu/48000, pcma, pcma/16000, pcma/48000, aac, aac/16000.
But you can override them via YAML config. You can also add your own formats to config and use them with source params.
ffmpeg:
bin: ffmpeg # path to ffmpeg binary
h264: "-codec:v libx264 -g:v 30 -preset:v superfast -tune:v zerolatency -profile:v main -level:v 4.1"
mycodec: "-any args that support ffmpeg..."
myinput: "-fflags nobuffer -flags low_delay -timeout 5000000 -i {input}"- You can use
videoandaudioparams multiple times (ex.#video=copy#audio=copy#audio=pcmu) - You can use go2rtc stream name as ffmpeg input (ex.
ffmpeg:camera1#video=h264) - You can use
rotateparams with90,180,270or-90values, important with transcoding (ex.#video=h264#rotate=90) - You can use
widthand/orheightparams, important with transcoding (ex.#video=h264#width=1280) - You can use
rawparam for any additional FFmpeg arguments (ex.#raw=-vf transpose=1) - You can use
inputparam to override default input template (ex.#input=rtsp/udpwill change RTSP transport from TCP to UDP+TCP)- You can use raw input value (ex.
#input=-timeout 5000000 -i {input}) - You can add your own input templates
- You can use raw input value (ex.
Read more about encoding hardware acceleration.
You can get video from any USB-camera or Webcam as RTSP or WebRTC stream. This is part of FFmpeg integration.
- check available devices in Web interface
video_sizeandframeratemust be supported by your camera!- for Linux supported only video for now
- for macOS you can stream Facetime camera or whole Desktop!
- for macOS important to set right framerate
Format: ffmpeg:device?{input-params}#{param1}#{param2}#{param3}
streams:
linux_usbcam: ffmpeg:device?video=0&video_size=1280x720#video=h264
windows_webcam: ffmpeg:device?video=0#video=h264
macos_facetime: ffmpeg:device?video=0&audio=1&video_size=1280x720&framerate=30#video=h264#audio=pcmaExec source can run any external application and expect data from it. Two transports are supported - pipe and RTSP.
If you want to use RTSP transport - the command must contain the {output} argument in any place. On launch, it will be replaced by the local address of the RTSP server.
pipe reads data from app stdout in different formats: MJPEG, H.264/H.265 bitstream, MPEG-TS.
The source can be used with:
- FFmpeg - go2rtc ffmpeg source just a shortcut to exec source
- GStreamer
- Raspberry Pi Cameras
- any your own software
streams:
stream: exec:ffmpeg -re -i /media/BigBuckBunny.mp4 -c copy -rtsp_transport tcp -f rtsp {output}
picam_h264: exec:libcamera-vid -t 0 --inline -o -
picam_mjpeg: exec:libcamera-vid -t 0 --codec mjpeg -o -Some sources may have a dynamic link. And you will need to get it using a bash or python script. Your script should echo a link to the source. RTSP, FFmpeg or any of the supported sources.
Docker and Hass Add-on users has preinstalled python3, curl, jq.
Check examples in wiki.
streams:
apple_hls: echo:python3 hls.py https://developer.apple.com/streaming/examples/basic-stream-osx-ios5.htmlImportant:
- You can use HomeKit Cameras without Apple devices (iPhone, iPad, etc.), it's just a yet another protocol
- HomeKit device can be paired with only one ecosystem. So, if you have paired it to an iPhone (Apple Home) - you can't pair it with Home Assistant or go2rtc. Or if you have paired it to go2rtc - you can't pair it with iPhone
- HomeKit device should be in same network with working mDNS between device and go2rtc
go2rtc support import paired HomeKit devices from Home Assistant. So you can use HomeKit camera with Hass and go2rtc simultaneously. If you using Hass, I recommend pairing devices with it, it will give you more options.
You can pair device with go2rtc on the HomeKit page. If you can't see your devices - reload the page. Also try reboot your HomeKit device (power off). If you still can't see it - you have a problems with mDNS.
If you see a device but it does not have a pair button - it is paired to some ecosystem (Apple Home, Home Assistant, HomeBridge etc). You need to delete device from that ecosystem, and it will be available for pairing. If you cannot unpair device, you will have to reset it.
Important:
- HomeKit audio uses very non-standard AAC-ELD codec with very non-standard params and specification violation
- Audio can be transcoded by ffmpeg source with
#asyncoption - Audio can be played by
ffplaywith-use_wallclock_as_timestamps 1 -async 1options - Audio can't be played in
VLCand probably any other player
Recommended settings for using HomeKit Camera with WebRTC, MSE, MP4, RTSP:
streams:
aqara_g3:
- hass:Camera-Hub-G3-AB12
- ffmpeg:aqara_g3#audio=aac#audio=opus#async
RTSP link with "normal" audio for any player: rtsp://192.168.1.123:8554/aqara_g3?video&audio=aac
This source is in active development! Tested only with Aqara Camera Hub G3 (both EU and CN versions).
Other names: DVR-IP, NetSurveillance, Sofia protocol (NETsurveillance ActiveX plugin XMeye SDK).
- you can skip
username,password,port,channelandsubtypeif they are default - setup separate streams for different channels
- use
subtype=0for Main stream, andsubtype=1for Extra1 stream - only the TCP protocol is supported
streams:
camera1: dvrip://username:password@192.168.1.123:34567?channel=0&subtype=0TP-Link Tapo proprietary camera protocol with two way audio support.
- stream quality is the same as RTSP protocol
- use the cloud password, this is not the RTSP password! you do not need to add a login!
- you can also use UPPERCASE MD5 hash from your cloud password with
adminusername
streams:
# cloud password without username
camera1: tapo://cloud-password@192.168.1.123
# admin username and UPPERCASE MD5 cloud-password hash
camera2: tapo://admin:MD5-PASSWORD-HASH@192.168.1.123Support public cameras from service Ivideon.
streams:
quailcam: ivideon:100-tu5dkUPct39cTp9oNEN2B6/0Support import camera links from Home Assistant config files:
- Generic Camera, setup via GUI
- HomeKit Camera
- ONVIF
- Roborock vacuums with camera
hass:
config: "/config" # skip this setting if you Hass Add-on user
streams:
generic_camera: hass:Camera1 # Settings > Integrations > Integration Name
aqara_g3: hass:Camera-Hub-G3-AB12More cameras, like Tuya, and possibly others can also be imported by using this method.
This source type support only backchannel audio for Hikvision ISAPI protocol. So it should be used as second source in addition to the RTSP protocol.
streams:
hikvision1:
- rtsp://admin:password@192.168.1.123:554/Streaming/Channels/101
- isapi://admin:password@192.168.1.123:80/This source type support Roborock vacuums with cameras. Known working models:
- Roborock S6 MaxV - only video (the vacuum has no microphone)
- Roborock S7 MaxV - video and two way audio
Source support load Roborock credentials from Home Assistant custom integration. Otherwise, you need to log in to your Roborock account (MiHome account is not supported). Go to: go2rtc WebUI > Add webpage. Copy roborock://... source for your vacuum and paste it to go2rtc.yaml config.
If you have graphic pin for your vacuum - add it as numeric pin (lines: 123, 456, 678) to the end of the roborock-link.
This source type support two connection formats:
- WebRTC/WHEP - is an unapproved standard for WebRTC video/audio viewers. But it may already be supported in some third-party software. It is supported in go2rtc.
go2rtc/WebSocket- This format is only supported in go2rtc. Unlike WHEP it supports asynchronous WebRTC connection and two way audio.
streams:
webrtc1: webrtc:http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/webrtc?src=dahua1
webrtc2: webrtc:ws://192.168.1.123:1984/api/ws?src=dahua1This source can get a stream from another go2rtc via WebTorrent protocol.
streams:
webtorrent1: webtorrent:?share=huofssuxaty00izc&pwd=k3l2j9djeg8v8r7eBy default, go2rtc establishes a connection to the source when any client requests it. Go2rtc drops the connection to the source when it has no clients left.
- Go2rtc also can accepts incoming sources in RTSP, HTTP and WebRTC/WHIP formats
- Go2rtc won't stop such a source if it has no clients
- You can push data only to existing stream (create stream with empty source in config)
- You can push multiple incoming sources to same stream
- You can push data to non empty stream, so it will have additional codecs inside
Examples
- RTSP with any codec
ffmpeg -re -i BigBuckBunny.mp4 -c copy -rtsp_transport tcp -f rtsp rtsp://localhost:8554/camera1 - HTTP-MJPEG with MJPEG codec
ffmpeg -re -i BigBuckBunny.mp4 -c mjpeg -f mpjpeg http://localhost:1984/api/stream.mjpeg?dst=camera1 - HTTP-FLV with H264, AAC codecs
ffmpeg -re -i BigBuckBunny.mp4 -c copy -f flv http://localhost:1984/api/stream.flv?dst=camera1 - MPEG-TS with H264 codec
ffmpeg -re -i BigBuckBunny.mp4 -c copy -f mpegts http://localhost:1984/api/stream.ts?dst=camera1
You can turn the browser of any PC or mobile into an IP-camera with support video and two way audio. Or even broadcast your PC screen:
- Create empty stream in the
go2rtc.yaml - Go to go2rtc WebUI
- Open
linkspage for you stream - Select
camera+microphoneordisplay+speakeroption - Open
webrtclocal page (your go2rtc should work over HTTPS!) orshare linkvia WebTorrent technology (work over HTTPS by default)
You can use OBS Studio or any other broadcast software with WHIP protocol support. This standard has not yet been approved. But you can download OBS Studio dev version:
- Settings > Stream > Service: WHIP > http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/webrtc?dst=camera1
go2rtc support play audio files (ex. music or TTS) and live streams (ex. radio) on cameras with two way audio support (RTSP/ONVIF cameras, TP-Link Tapo, Hikvision ISAPI, Roborock vacuums, any Browser).
API example:
POST http://localhost:1984/api/streams?dst=camera1&src=ffmpeg:http://example.com/song.mp3#audio=pcma#input=file
- you can stream: local files, web files, live streams or any format, supported by FFmpeg
- you should use ffmpeg source for transcoding audio to codec, that your camera supports
- you can check camera codecs on the go2rtc WebUI info page when the stream is active
- some cameras support only low quality
PCMA/8000codec (ex. Tapo) - it is recommended to choose higher quality formats if your camera supports them (ex.
PCMA/48000for some Dahua cameras) - if you play files over http-link, you need to add
#input=fileparams for transcoding, so file will be transcoded and played in real time - if you play live streams, you should skip
#inputparam, because it is already in real time - you can stop active playback by calling the API with the empty
srcparameter - you will see one active producer and one active consumer in go2rtc WebUI info page during streaming
The HTTP API is the main part for interacting with the application. Default address: http://127.0.0.1:1984/.
go2rtc has its own JS video player (video-rtc.js) with:
- support technologies:
- WebRTC over UDP or TCP
- MSE or MP4 or MJPEG over WebSocket
- automatic selection best technology according on:
- codecs inside your stream
- current browser capabilities
- current network configuration
- automatic stop stream while browser or page not active
- automatic stop stream while player not inside page viewport
- automatic reconnection
Technology selection based on priorities:
- Video and Audio better than just Video
- H265 better than H264
- WebRTC better than MSE, than MP4, than MJPEG
go2rtc has simple HTML page (stream.html) with support params in URL:
- multiple streams on page
src=camera1&src=camera2... - stream technology autoselection
mode=webrtc,mse,mp4,mjpeg - stream technology comparison
src=camera1&mode=webrtc&mode=mse&mode=mp4 - player width setting in pixels
width=320pxor percentswidth=50%
Module config
- you can disable HTTP API with
listen: ""and use, for example, only RTSP client/server protocol - you can enable HTTP API only on localhost with
listen: "127.0.0.1:1984"setting - you can change API
base_pathand host go2rtc on your main app webserver suburl - all files from
static_dirhosted on root path:/
api:
listen: ":1984" # default ":1984", HTTP API port ("" - disabled)
username: "admin" # default "", Basic auth for WebUI
password: "pass" # default "", Basic auth for WebUI
base_path: "/rtc" # default "", API prefix for serve on suburl (/api => /rtc/api)
static_dir: "www" # default "", folder for static files (custom web interface)
origin: "*" # default "", allow CORS requests (only * supported)PS:
- go2rtc doesn't provide HTTPS. Use Nginx or Ngrok or Home Assistant Add-on for this tasks
- MJPEG over WebSocket plays better than native MJPEG because Chrome bug
- MP4 over WebSocket was created only for Apple iOS because it doesn't support MSE and native MP4
You can get any stream as RTSP-stream: rtsp://192.168.1.123:8554/{stream_name}
You can enable external password protection for your RTSP streams. Password protection always disabled for localhost calls (ex. FFmpeg or Hass on same server).
rtsp:
listen: ":8554" # RTSP Server TCP port, default - 8554
username: "admin" # optional, default - disabled
password: "pass" # optional, default - disabled
default_query: "video&audio" # optional, default codecs filters By default go2rtc provide RTSP-stream with only one first video and only one first audio. You can change it with the default_query setting:
default_query: "mp4"- MP4 compatible codecs (H264, H265, AAC)default_query: "video=all&audio=all"- all tracks from all source (not all players can handle this)default_query: "video=h264,h265"- only one video track (H264 or H265)default_query: "video&audio=all"- only one first any video and all audio as separate tracks
Read more about codecs filters.
In most cases WebRTC uses direct peer-to-peer connection from your browser to go2rtc and sends media data via UDP. It can't pass media data through your Nginx or Cloudflare or Nabu Casa HTTP TCP connection! It can automatically detects your external IP via public STUN server. It can establish a external direct connection via UDP hole punching technology even if you not open your server to the World.
But about 10-20% of users may need to configure additional settings for external access if mobile phone or go2rtc server behing Symmetric NAT.
- by default, WebRTC uses both TCP and UDP on port 8555 for connections
- you can use this port for external access
- you can change the port in YAML config:
webrtc:
listen: ":8555" # address of your local server and port (TCP/UDP)Static public IP
- forward the port 8555 on your router (you can use same 8555 port or any other as external port)
- add your external IP-address and external port to YAML config
webrtc:
candidates:
- 216.58.210.174:8555 # if you have static public IP-addressDynamic public IP
- forward the port 8555 on your router (you can use same 8555 port or any other as the external port)
- add
stunword and external port to YAML config- go2rtc automatically detects your external address with STUN-server
webrtc:
candidates:
- stun:8555 # if you have dynamic public IP-addressPrivate IP
- setup integration with Ngrok service
ngrok:
command: ...Hard tech way 1. Own TCP-tunnel
If you have personal VPS, you can create TCP-tunnel and setup in the same way as "Static public IP". But use your VPS IP-address in YAML config.
Hard tech way 2. Using TURN-server
If you have personal VPS, you can install TURN server (e.g. coturn, config example).
webrtc:
ice_servers:
- urls: [stun:stun.l.google.com:19302]
- urls: [turn:123.123.123.123:3478]
username: your_user
credential: your_passThis module support:
- Share any local stream via WebTorrent technology
- Get any incoming stream from PC or mobile via WebTorrent technology
- Get any remote go2rtc source via WebTorrent technology
Securely and free. You do not need to open a public access to the go2rtc server. But in some cases (Symmetric NAT) you may need to set up external access to WebRTC module.
To generate sharing link or incoming link - goto go2rtc WebUI (stream links page). This link is temporary and will stop working after go2rtc is restarted!
You can create permanent external links in go2rtc config:
webtorrent:
shares:
super-secret-share: # share name, should be unique among all go2rtc users!
pwd: super-secret-password
src: rtsp-dahua1 # stream name from streams sectionLink example: https://alexxit.github.io/go2rtc/#share=02SNtgjKXY&pwd=wznEQqznxW&media=video+audio
TODO: article how it works...
With Ngrok integration you can get external access to your streams in situation when you have Internet with private IP-address.
- Ngrok preistalled for Docker and Hass Add-on users
- you may need external access for two different things:
- WebRTC stream, so you need tunnel WebRTC TCP port (ex. 8555)
- go2rtc web interface, so you need tunnel API HTTP port (ex. 1984)
- Ngrok support authorization for your web interface
- Ngrok automatically adds HTTPS to your web interface
Ngrok free subscription limitations:
- you will always get random external address (not a problem for webrtc stream)
- you can forward multiple ports but use only one Ngrok app
go2rtc will automatically get your external TCP address (if you enable it in ngrok config) and use it with WebRTC connection (if you enable it in webrtc config).
You need manually download Ngrok agent app for your OS and register in Ngrok service.
Tunnel for only WebRTC Stream
You need to add your Ngrok token and WebRTC TCP port to YAML:
ngrok:
command: ngrok tcp 8555 --authtoken eW91IHNoYWxsIG5vdCBwYXNzCnlvdSBzaGFsbCBub3QgcGFzcwTunnel for WebRTC and Web interface
You need to create ngrok.yaml config file and add it to go2rtc config:
ngrok:
command: ngrok start --all --config ngrok.yamlNgrok config example:
version: "2"
authtoken: eW91IHNoYWxsIG5vdCBwYXNzCnlvdSBzaGFsbCBub3QgcGFzcw
tunnels:
api:
addr: 1984 # use the same port as in go2rtc config
proto: http
basic_auth:
- admin:password # you can set login/pass for your web interface
webrtc:
addr: 8555 # use the same port as in go2rtc config
proto: tcpThe best and easiest way to use go2rtc inside the Home Assistant is to install the custom integration WebRTC Camera and custom lovelace card.
But go2rtc is also compatible and can be used with RTSPtoWebRTC built-in integration.
You have several options on how to add a camera to Home Assistant:
- Camera RTSP source => Generic Camera
- Camera any source => go2rtc config => Generic Camera
- Install any go2rtc
- Add your stream to go2rtc config
- Hass > Settings > Integrations > Add Integration > ONVIF > Host:
127.0.0.1, Port:1984 - Hass > Settings > Integrations > Add Integration > Generic Camera >
rtsp://127.0.0.1:8554/camera1(change to your stream name)
You have several options on how to watch the stream from the cameras in Home Assistant:
Camera Entity=>Picture Entity Card=> TechnologyHLS, codecs:H264/H265/AAC, poor latency.Camera Entity=> RTSPtoWebRTC =>Picture Entity Card=> TechnologyWebRTC, codecs:H264/PCMU/PCMA/OPUS, best latency.- Install any go2rtc
- Hass > Settings > Integrations > Add Integration > RTSPtoWebRTC >
http://127.0.0.1:1984/ - RTSPtoWebRTC > Configure > STUN server:
stun.l.google.com:19302 - Use Picture Entity or Picture Glance lovelace card
Camera EntityorCamera URL=> WebRTC Camera => Technology:WebRTC/MSE/MP4/MJPEG, codecs:H264/H265/AAC/PCMU/PCMA/OPUS, best latency, best compatibility.- Install and add WebRTC Camera custom integration
- Use WebRTC Camera custom lovelace card
You can add camera entity_id to go2rtc config if you need transcoding:
streams:
"camera.hall": ffmpeg:{input}#video=copy#audio=opusPS. Default Home Assistant lovelace cards don't support 2-way audio. You can use 2-way audio from Add-on Web UI. But you need use HTTPS to access the microphone. This is a browser restriction and cannot be avoided.
Provides several features:
- MSE stream (fMP4 over WebSocket)
- Camera snapshots in MP4 format (single frame), can be sent to Telegram
- HTTP progressive streaming (MP4 file stream) - bad format for streaming because of high start delay. This format doesn't work in all Safari browsers, but go2rtc will automatically redirect it to HLS/fMP4 it this case.
API examples:
- MP4 snapshot:
http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/frame.mp4?src=camera1(H264, H265) - MP4 stream:
http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/stream.mp4?src=camera1(H264, H265, AAC)
Read more about codecs filters.
HLS is the worst technology for real-time streaming. It can only be useful on devices that do not support more modern technology, like WebRTC, MSE/MP4.
The go2rtc implementation differs from the standards and may not work with all players.
API examples:
- HLS/TS stream:
http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/stream.m3u8?src=camera1(H264) - HLS/fMP4 stream:
http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/stream.m3u8?src=camera1&mp4(H264, H265, AAC)
Read more about codecs filters.
Important. For stream as MJPEG format, your source MUST contain the MJPEG codec. If your stream has a MJPEG codec - you can receive MJPEG stream or JPEG snapshots via API.
You can receive an MJPEG stream in several ways:
- some cameras support MJPEG codec inside RTSP stream (ex. second stream for Dahua cameras)
- some cameras has HTTP link with MJPEG stream
- some cameras has HTTP link with snapshots - go2rtc can convert them to MJPEG stream
- you can convert H264/H265 stream from your camera via FFmpeg integraion
With this example, your stream will have both H264 and MJPEG codecs:
streams:
camera1:
- rtsp://rtsp:12345678@192.168.1.123/av_stream/ch0
- ffmpeg:camera1#video=mjpegAPI examples:
- MJPEG stream:
http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/stream.mjpeg?src=camera1 - JPEG snapshots:
http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/frame.jpeg?src=camera1
You can set different log levels for different modules.
log:
level: info # default level
api: trace
exec: debug
ngrok: info
rtsp: warn
streams: error
webrtc: fatalBy default go2rtc starts the Web interface on port 1984 and RTSP on port 8554, as well as use port 8555 for WebRTC connections. The three ports are accessible from your local network. So anyone on your local network can watch video from your cameras without authorization. The same rule applies to the Home Assistant Add-on.
This is not a problem if you trust your local network as much as I do. But you can change this behaviour with a go2rtc.yaml config:
api:
listen: "127.0.0.1:1984" # localhost
rtsp:
listen: "127.0.0.1:8554" # localhost
webrtc:
listen: ":8555" # external TCP/UDP port- local access to RTSP is not a problem for FFmpeg integration, because it runs locally on your server
- local access to API is not a problem for Home Assistant Add-on, because Hass runs locally on same server and Add-on Web UI protected with Hass authorization (Ingress feature)
- external access to WebRTC TCP port is not a problem, because it used only for transmit encrypted media data
- anyway you need to open this port to your local network and to the Internet in order for WebRTC to work
If you need Web interface protection without Home Assistant Add-on - you need to use reverse proxy, like Nginx, Caddy, Ngrok, etc.
PS. Additionally WebRTC will try to use the 8555 UDP port for transmit encrypted media. It works without problems on the local network. And sometimes also works for external access, even if you haven't opened this port on your router (read more). But for stable external WebRTC access, you need to open the 8555 port on your router for both TCP and UDP.
go2rtc can automatically detect which codecs your device supports for WebRTC and MSE technologies.
But it cannot be done for RTSP, HTTP progressive streaming, HLS technologies. You can manually add a codec filter when you create a link to a stream. The filters work the same for all three technologies. Filters do not create a new codec. They only select the suitable codec from existing sources. You can add new codecs to the stream using the FFmpeg transcoding.
Without filters:
- RTSP will provide only the first video and only the first audio (any codec)
- MP4 will include only compatible codecs (H264, H265, AAC)
- HLS will output in the legacy TS format (H264 without audio)
Some examples:
rtsp://192.168.1.123:8554/camera1?mp4- useful for recording as MP4 files (e.g. Hass or Frigate)rtsp://192.168.1.123:8554/camera1?video=h264,h265&audio=aac- full version of the filter abovertsp://192.168.1.123:8554/camera1?video=h264&audio=aac&audio=opus- H264 video codec and two separate audio tracksrtsp://192.168.1.123:8554/camera1?video&audio=all- any video codec and all audio codecs as separate trackshttp://192.168.1.123:1984/api/stream.m3u8?src=camera1&mp4- HLS stream with MP4 compatible codecs (HLS/fMP4)http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/stream.m3u8?src=camera1&mp4=flac- HLS stream with PCMA/PCMU/PCM audio support (HLS/fMP4), won't work on old deviceshttp://192.168.1.123:1984/api/stream.mp4?src=camera1&mp4=flac- MP4 file with PCMA/PCMU/PCM audio support, won't work on old devices (ex. iOS 12)http://192.168.1.123:1984/api/stream.mp4?src=camera1&mp4=all- MP4 file with non standard audio codecs, won't work on some players
AVC/H.264 video can be played almost anywhere. But HEVC/H.265 has a lot of limitations in supporting with different devices and browsers. It's all about patents and money, you can't do anything about it.
| Device | WebRTC | MSE | HTTP Progressive Streaming |
|---|---|---|---|
| latency | best | medium | bad |
| Desktop Chrome 107+ | H264, OPUS, PCMU, PCMA | H264, H265*, AAC, FLAC*, OPUS | H264, H265*, AAC, FLAC*, OPUS, MP3 |
| Desktop Edge | H264, OPUS, PCMU, PCMA | H264, H265*, AAC, FLAC*, OPUS | H264, H265*, AAC, FLAC*, OPUS, MP3 |
| Android Chrome 107+ | H264, OPUS, PCMU, PCMA | H264, H265*, AAC, FLAC*, OPUS | H264, H265*, AAC, FLAC*, OPUS, MP3 |
| Desktop Firefox | H264, OPUS, PCMU, PCMA | H264, AAC, FLAC*, OPUS | H264, AAC, FLAC*, OPUS |
| Desktop Safari | H264, H265*, OPUS, PCMU, PCMA | H264, H265, AAC, FLAC* | no! |
| iPad Safari 13+ | H264, H265*, OPUS, PCMU, PCMA | H264, H265, AAC, FLAC* | no! |
| iPhone Safari 13+ | H264, H265*, OPUS, PCMU, PCMA | no! | no! |
| masOS Hass App | no | no | no |
- Chrome H265: read this and read this
- Edge H265: read this
- Desktop Safari H265: Menu > Develop > Experimental > WebRTC H265
- iOS Safari H265: Settings > Safari > Advanced > Experimental > WebRTC H265
Audio
- Go2rtc support automatic repack
PCMA/PCMU/PCMcodecs toFLACfor MSE/MP4/HLS so they will work almost anywhere - WebRTC audio codecs:
PCMU/8000,PCMA/8000,OPUS/48000/2 OPUSandMP3inside MP4 is part of the standard, but some players do not support them anyway (especially Apple)
Apple devices
- all Apple devices don't support HTTP progressive streaming
- iPhones don't support MSE technology because it competes with the HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) technology, invented by Apple
- HLS is the worst technology for live streaming, it still exists only because of iPhones
Codec names
- H264 = H.264 = AVC (Advanced Video Coding)
- H265 = H.265 = HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding)
- PCMU = G.711 PCM (A-law) = PCM A-law (
alaw) - PCMA = G.711 PCM (µ-law) = PCM mu-law (
mulaw) - PCM = L16 = PCM signed 16-bit big-endian (
s16be) - AAC = MPEG4-GENERIC
- MP3 = MPEG-1 Audio Layer III or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III
There are no plans to embed complex transcoding algorithms inside go2rtc. FFmpeg source does a great job with this. Including hardware acceleration support.
But go2rtc has some simple algorithms. They are turned on automatically, you do not need to set them up additionally.
PCM for MSE/MP4/HLS
Go2rtc can pack PCMA, PCMU and PCM codecs into an MP4 container so that they work in all browsers and all built-in players on modern devices. Including Apple QuickTime:
PCMA/PCMU => PCM => FLAC => MSE/MP4/HLS
Resample PCMA/PCMU for WebRTC
By default WebRTC support only PCMA/8000 and PCMU/8000. But go2rtc can automatically resample PCMA and PCMU codec with with a different sample rate. Also go2rtc can transcode PCM codec to PCMA/8000, so WebRTC can play it:
PCM/xxx => PCMA/8000 => WebRTC
PCMA/xxx => PCMA/8000 => WebRTC
PCMU/xxx => PCMU/8000 => WebRTC
Important
- FLAC codec not supported in a RTSP stream. If you using Frigate or Hass for recording MP4 files with PCMA/PCMU/PCM audio - you should setup transcoding to AAC codec.
- PCMA and PCMU are VERY low quality codecs. Them support only 256! different sounds. Use them only when you have no other options.
For example, you want to watch RTSP-stream from Dahua IPC-K42 camera in your Chrome browser.
- this camera support 2-way audio standard ONVIF Profile T
- this camera support codecs H264, H265 for send video, and you select
H264in camera settings - this camera support codecs AAC, PCMU, PCMA for send audio (from mic), and you select
AAC/16000in camera settings - this camera support codecs AAC, PCMU, PCMA for receive audio (to speaker), you don't need to select them
- your browser support codecs H264, VP8, VP9, AV1 for receive video, you don't need to select them
- your browser support codecs OPUS, PCMU, PCMA for send and receive audio, you don't need to select them
- you can't get camera audio directly, because its audio codecs doesn't match with your browser codecs
- so you decide to use transcoding via FFmpeg and add this setting to config YAML file
- you have chosen
OPUS/48000/2codec, because it is higher quality than thePCMU/8000orPCMA/8000
Now you have stream with two sources - RTSP and FFmpeg:
streams:
dahua:
- rtsp://admin:password@192.168.1.123/cam/realmonitor?channel=1&subtype=0&unicast=true&proto=Onvif
- ffmpeg:rtsp://admin:password@192.168.1.123/cam/realmonitor?channel=1&subtype=0#audio=opusgo2rtc automatically match codecs for you browser and all your stream sources. This called multi-source 2-way codecs negotiation. And this is one of the main features of this app.
PS. You can select PCMU or PCMA codec in camera setting and don't use transcoding at all. Or you can select AAC codec for main stream and PCMU codec for second stream and add both RTSP to YAML config, this also will work fine.
- Frigate 12+ - open source NVR built around real-time AI object detection
- ring-mqtt - Ring devices to MQTT Bridge
- EufyP2PStream - A small project that provides a Video/Audio Stream from Eufy cameras that don't directly support RTSP
- Proxmox Helper Scripts
- Unraid
- Dahua - reference implementation streaming protocols, a lot of settings, high stream quality, multiple streaming clients
- Hikvision - a lot of proprietary streaming technologies
- Reolink - some models has awful unusable RTSP realisation and not best HTTP-FLV alternative (I recommend that you contact Reolink support for new firmware), few settings
- Sonoff - very low stream quality, no settings, not best protocol implementation
- TP-Link - few streaming clients, packet loss?
- Chinese cheap noname cameras, Wyze Cams, Xiaomi cameras with hacks (usual has
/live/ch00_1in RTSP URL) - awful but usable RTSP protocol realisation, low stream quality, few settings, packet loss?
Using apps for low RTSP delay
ffplay -fflags nobuffer -flags low_delay "rtsp://192.168.1.123:8554/camera1"- VLC > Preferences > Input / Codecs > Default Caching Level: Lowest Latency
Snapshots to Telegram
Q. What's the difference between go2rtc, WebRTC Camera and RTSPtoWebRTC?
go2rtc is a new version of the server-side WebRTC Camera integration, completely rewritten from scratch, with a number of fixes and a huge number of new features. It is compatible with native Home Assistant RTSPtoWebRTC integration. So you can use default lovelace Picture Entity or Picture Glance.
Q. Should I use go2rtc addon or WebRTC Camera integration?
go2rtc is more than just viewing your stream online with WebRTC/MSE/HLS/etc. You can use it all the time for your various tasks. But every time the Hass is rebooted - all integrations are also rebooted. So your streams may be interrupted if you use them in additional tasks.
Basic users can use WebRTC Camera integration. Advanced users can use go2rtc addon or Frigate 12+ addon.
Q. Which RTSP link should I use inside Hass?
You can use direct link to your cameras there (as you always do). go2rtc support zero-config feature. You may leave streams config section empty. And your streams will be created on the fly on first start from Hass. And your cameras will have multiple connections. Some from Hass directly and one from go2rtc.
Also you can specify your streams in go2rtc config file and use RTSP links to this addon. With additional features: multi-source codecs negotiation or FFmpeg transcoding for unsupported codecs. Or use them as source for Frigate. And your cameras will have one connection from go2rtc. And go2rtc will have multiple connection - some from Hass via RTSP protocol, some from your browser via WebRTC/MSE/HLS protocols.
Use any config what you like.
Q. What about lovelace card with support 2-way audio?
At this moment I am focused on improving stability and adding new features to go2rtc. Maybe someone could write such a card themselves. It's not difficult, I have some sketches.