Generate C-code for wrapping simple Keras models, by the simple expedient of putting the weights directly into the c files.
Of course, there are much better ways to do this with external packages (see: ONNX). But this is extremely easy to use for easy cases, and we should strive to "make the easy cases easy". Besides, it was fun to write.
Put keras_cmodel.py somewhere where you can import it, and mm_utils.c and mm_utils.h beside it.
Tested on Ubuntu 18.04 with Python 3.6.9, Tensorflow 2.3.0, and gcc 7.5.0.
With a trained model
import numpy as np, tensorflow as tf
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='tanh'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='tanh'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='linear'),
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-3), loss='mse')
x = np.random.uniform(size=(1000, 1), low=-1, high=1)
y = x ** 2
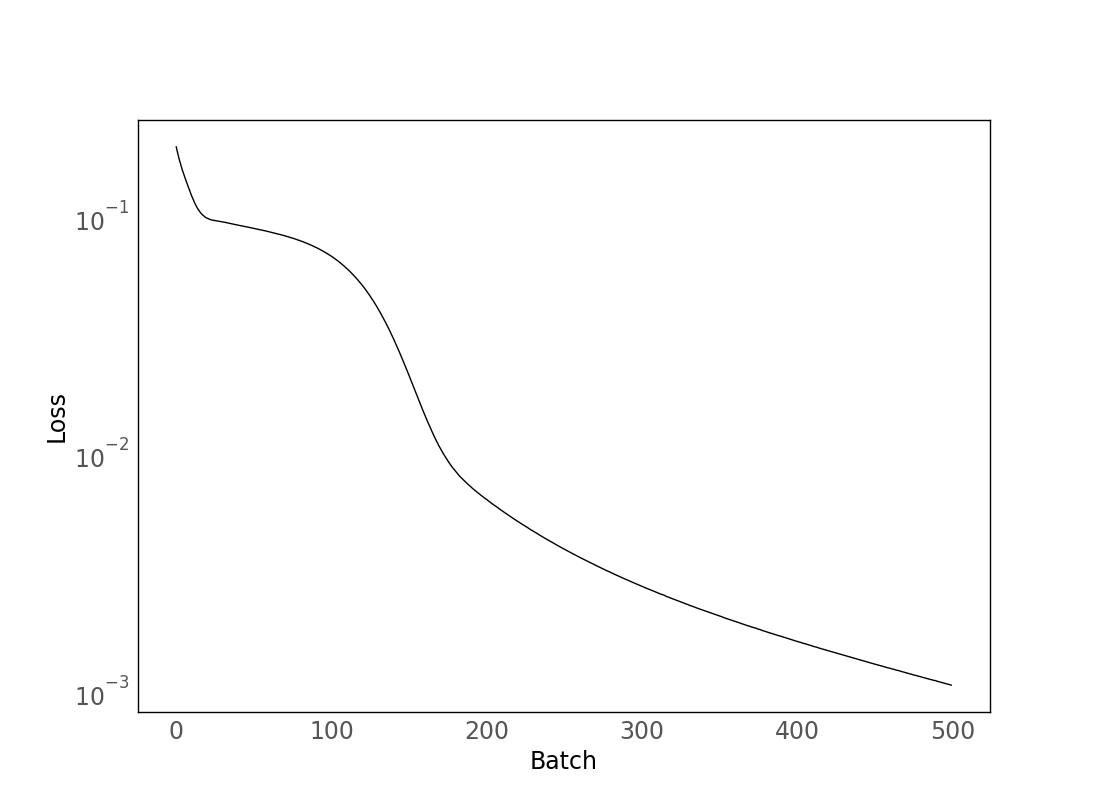
model.fit(x, y, epochs=500, batch_size=500)we create a C wrapper (for a fixed usage_batch_size) like this
from keras_cmodel import CModel
usage_batch_size = 5
cmodel = CModel(model, usage_batch_size)
cmodel.save(name='MLP')The save call here writes MLP.c and MLP.h. (Note that the size of MLP.c will grow with network size, but MLP.h will stay small. Here, our model has 1*10+10+10*10+10+10*1+1=141 parameters, and MLP.c has 378 lines.)
Then, you can have user code like e.g. MLP_test.c
#include "MLP.h"
int main() {
setup();
double inputs[] = {-1, -.5, 0, .5, 1};
double outputs[5];
MLP(inputs, outputs);
print_array("outputs", outputs, 5, 1);
}which you compile with gcc MLP_test.c MLP.c -lm -o MLP_test.
(Doing this for a larger np.linspace batch of inputs and plotting:)
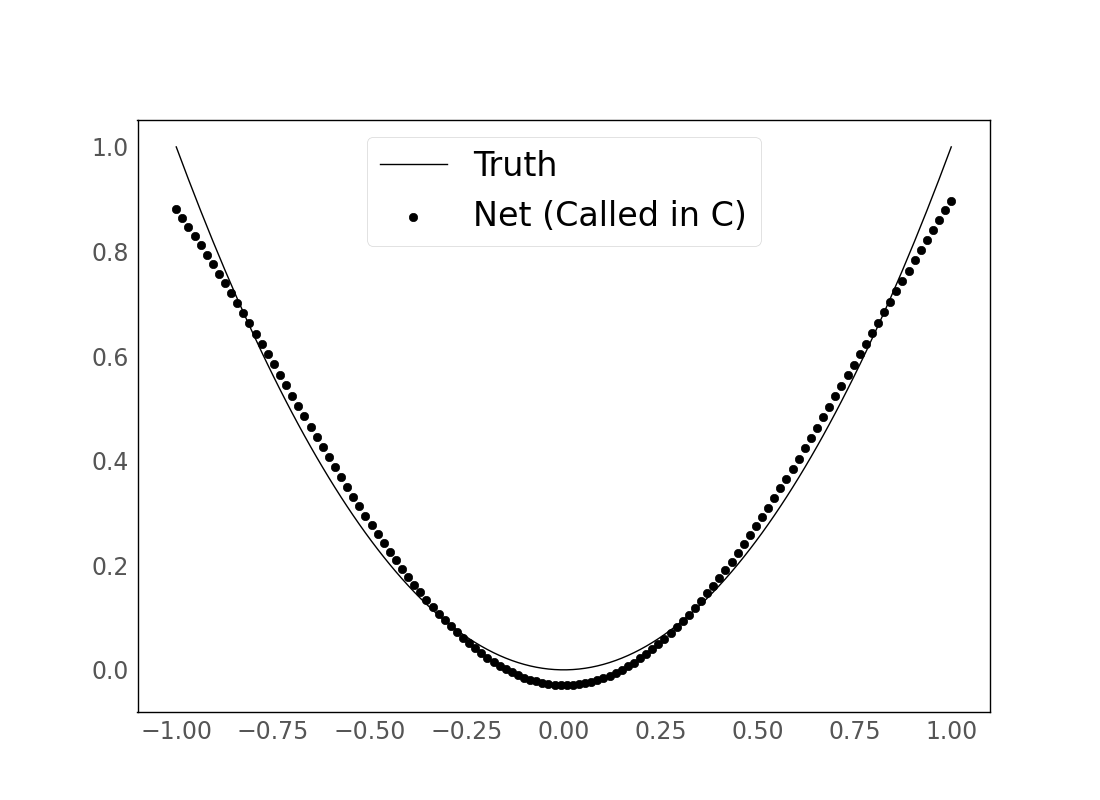
See demo.py for a fuller version of the demo described above.