This project proposes a framework for outdoor visual place recognition.
It can recognize visually similar places in GPS-denied environments. Thus, can serve as a candidate search technique in the context of full 6 DoF robot pose estimation.
Visual place recognition, also known as "weak localization", is performed here by matching sequences of images. The assumption is then that the input is a sequence of images or image features respectively. The program outputs the ids of image pairs that represent the same place.
Prerequisites:
sudo apt-get install -y libopencv-dev libyaml-cpp-dev libprotobuf-dev libprotoc-dev protobuf-compiler
Tested on Ubuntu 20.04.
To build the code:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j4
To be able to use the python part, for example for visualization, I recommend setting up a virtual environment of your choice and installing the provided requirements through:
pip install -r requirements.txt
The code is under continuous development but at any point in time you should be able to run the matching procedure through:
cd src/python
python run_matching.py \
--query_features <path_to_features> \
--reference_features <path_to_features> \
--dataset_name <dataset_name> \
--output_dir <path_to_folder>The framework assumes that there is a query image sequence, for every image of which the user wants to find the corresponding image in the reference image sequence. The script takes the query and reference features that are stored in protobuf messages of type ".Feature.pb" defined in this project. The assumption is that for every image there is a corresponding feature vector that is stored in a separate file. The code, for now, works with image features that can be represented as a single vector and for which the cosine similarity metric makes sense, for example, features from NetVLAD. For details on the features please refer to localization_protos.proto.
The run_matching.py script stores all the results in the user-provided output_dir. The user also needs to specify the name of the dataset, for example, "my_awesome_dataset".
For more details about the parameters, please use python run_matching.py --help.
For more details about the underlying method and the interpretation of the results, please have a look at paper.
Here is a sketch of what roughly is happening for those who don't like to read much 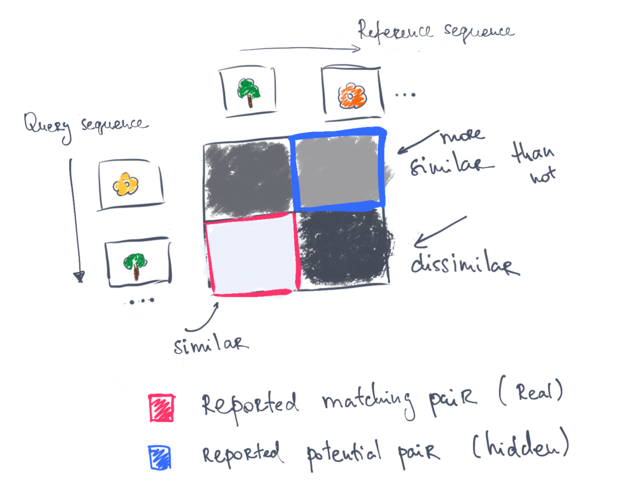
Perfect. Here is a python script that will convert your NxD matrix of features to the needed protobufs.
python convert_numpy_features_to_protos.py \
--filename <your_features>.txt \
--feature_type NetVLAD \
--output_folder <folder_name> \
--output_file_prefix <fancy_feature_name>This repository is a continuation of my previous works vpr_relocalization and online_place_recognition.
The plan is to gradually modernize and improve the code by preserving the essential capabilities of the system.
Essential capabilities:
- Given two sequences of image features compute the matching image pairs.
- Scripts to visualize the results.