R package that provides a set of tools to manipulate, visualize and compute metrics from quantitative structural model of trees (i.e the so-called ‘QSM’) . It can be used in various context of forest ecology (i.e biomass estimation) and tree architecture (i.e architectural metrics). The package is based on a new S4 class called ‘aRchi’.
All the function allowing visualization, metrics computation or QSM modification needs an object of class aRchi as input. A class archi can be build using the build_aRchi() function.
This Class contains five slots:
- The QSM of a tree. See next section for more details.
- The point cloud that was used to generate the QSM. It can be imported as XYZ data.frame/data.table or a LAS.
- The paths. It can be constructed using the Make_path() function and is needed for several metric computation and QSM modifications.
- The nodes. It can be constructed using the Make_Node() function and is required only for some metrics (see function WBEparameters() or LeonardoRatio() for example)
- The operations. It records all the operations that have been made on the aRchi object (QSM modifications, paths and node construction…)
The read_QSM() function provides methods to import QSMs generated by some of the most commonly used QSM models (treeQSM (last version and even .mat file), SimpleTree, SimpleForest and pypeTree). The imported QSMs are automatically converted into a common QSM format defined in the aRchi class.
Since the version 2.1.0 of the package, aRchi also provides the possibility to generate QSMs. To do so, three functions are provided :
- skeletonize_pc() allow to build a skeleton.
- smooth_skeleton().
- add_radius() computes the radius of each cylinder based on point distance to the skeleton.
The aRchi's QSM method was designed to build very detailed QSMs from
high quality TLS scans. However, it also allow to quickly reconstruct
the coarse architecture of large point clouds of lower quality. A basic
explaination of QSMs building in aRchi is shown in the figure bellow.

aRchi also allow to add the non reconstructed axes to a QSM using the add_non_reconstructed() function.
aRchi provides the ability to compute many topological informations from a QSM :
- build_aRchi() and skeletonize() include the computation of a basic tree topology at different levels of the tree architecture (cylinders, nodes, axes and branching orders).
- segment_annual_shoots() segments annual shoots in QSM of trees that exhibit acrotonic growth pattern.
- add_physiological_ages() class annual shoots into N physiological ages based on their length.
- compute_AO() automatically identify the dominant axis of a tree
based on the informations available in the QSM.
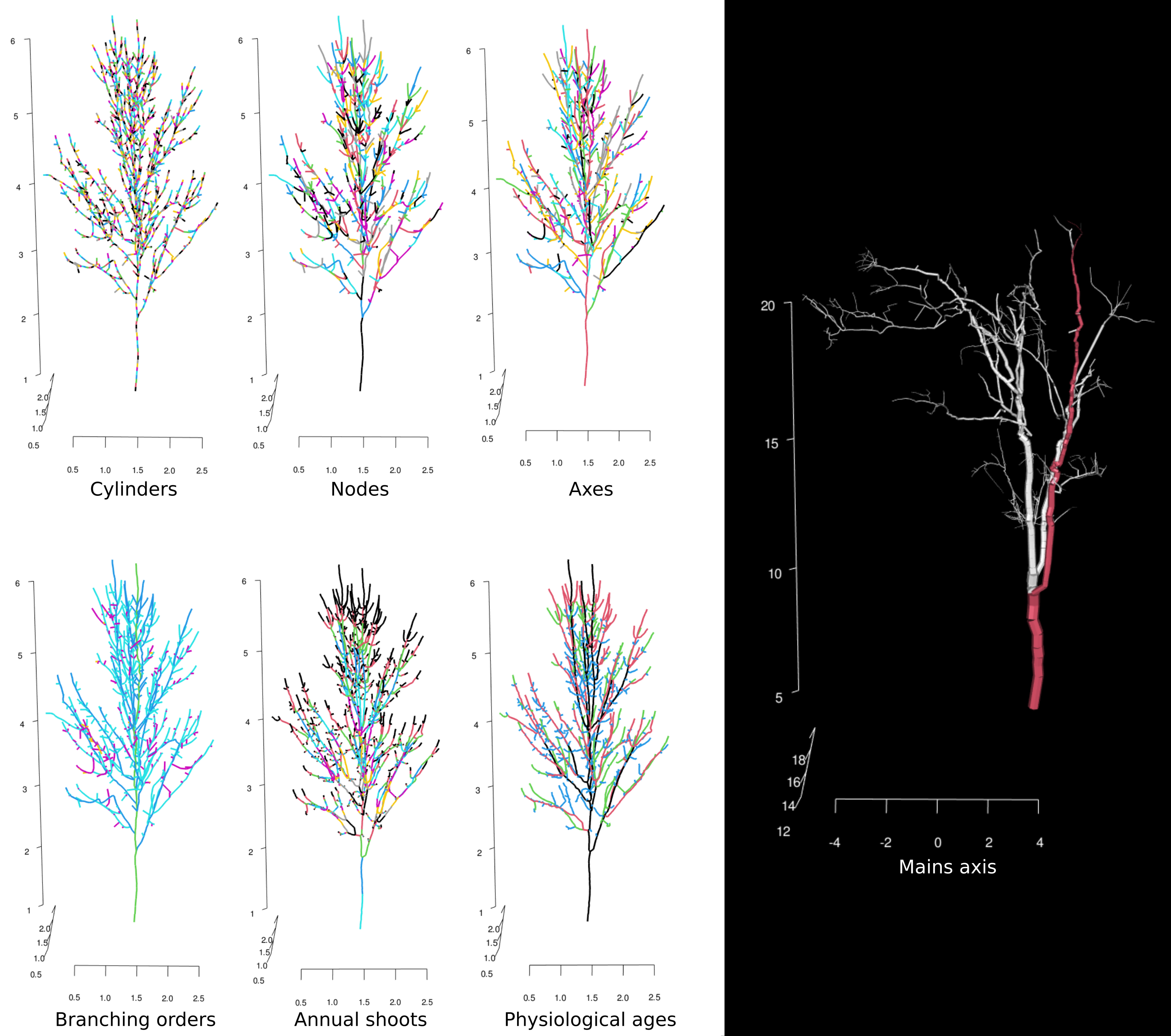
It is possible to visualize the QSM with or without the point cloud and showing only the skeleton or the whole QSM (i.e with cylinder volume) in a 3D interactive window using the function plot(). Different level of organization such as branch order, segment or cylinder can be colorized.
3d plot with Branch order colorized or the QSM with point cloud:
Some function allows modifying the QSM (e.g cleanQSM(), TruncateQSM(), simplify_skeleton()) and propose a visualization of the results.
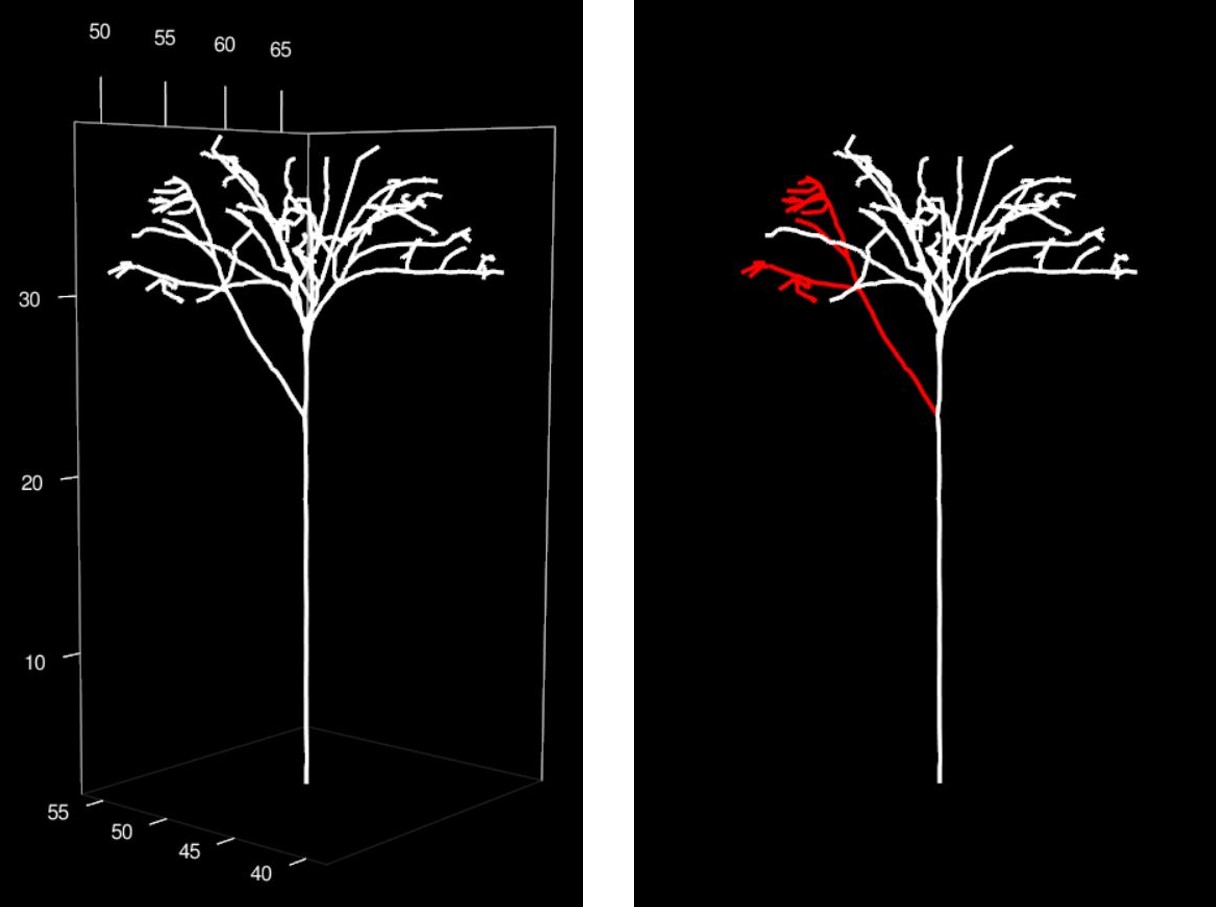
The kept part in red and the removed part in white obtained with TruncateQSM():
It is also possible to select a part of the QSM in a 3D interactive window by following the instruction of the function selectinQSM_3d(). It allows selecting different level of organization (cylinder, branch, segment, node….) and return a table of the selected part of the QSM with all the informations available. For example, If the biomass and mechanical constrains have been computed using Compute_mf() function, the returned table will contains the biomass and moment of force of all the cylinders/segments/node… selected.
Select a part of the QSM by following selectinQSM_3d() function instruction:
All the characteristics of the selected part are returns:
For more information on some metrics such as WBE parameters (WBEparameters()), Dominance apical index (DAI()), fork rate (ForkRate()) or branch angle (BranchAngle()) see article.
The latest released version from CRAN:
install.packages("aRchi")The latest version from Github (in development):
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github('umr-amap/aRchi')To use it :
library("aRchi")