by Paraskevas Chatzithanos, Grigoris Nikolaou, Rustam Stolkin, Manolis Chiou
This paper under review for publication in SMC 21.
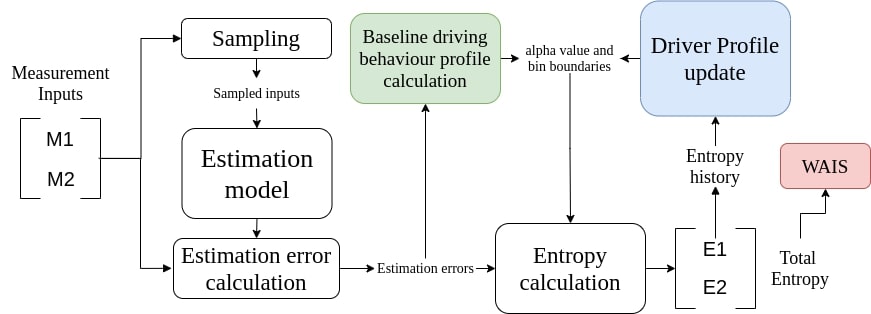
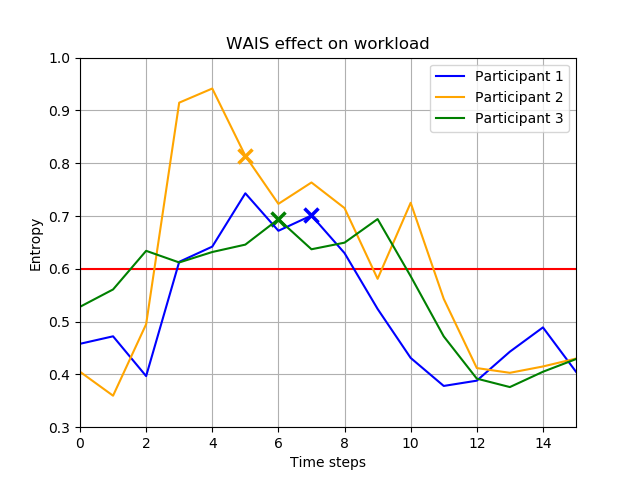
This work presents a real-time cognitive workload estimation, from multiple parameters of an operator’s driving behaviour,via the use of behavioural entropy. With the introduction of a Driver Profile Update (DPU) algorithm the cognitive workload estimation adapts to the evolving driving profile of individual operators. Finaly, the effects of a Warning And Indication System (WAIS) are presented. WAIS uses cognitive workload estimations to issue warnings to the operator.
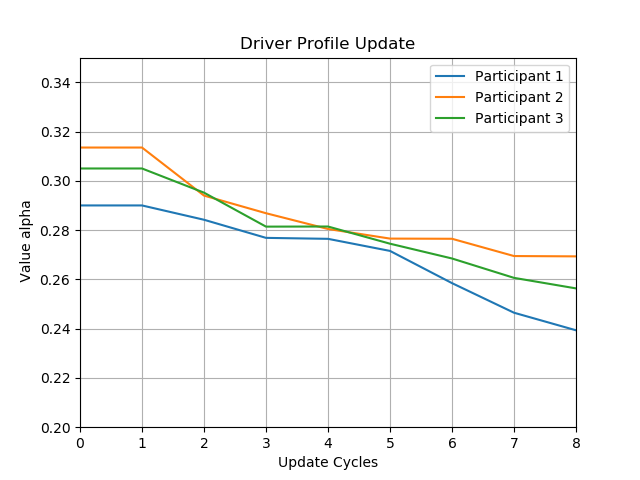
This paper addresses the problem of the human operator cognitive workload estimation while controlling a robot. Being capable of assessing, in real-time, the elevated operator workload could help prevent calamitous events from occurring. This estimation could enable an AI to make informed decisions to assist or advise the operator, in an advanced human-robot interaction framework. We propose a method, named Fessonia, for real-time cognitive workload estimation, from multiple parameters of an operator's driving behaviour, via the use of behavioural entropy. Fessonia is comprised of: a method to calculate the entropy (i.e. unpredictability) of the operator driving behaviour profile; the Driver Profile Update (DPU) algorithm which adapts the entropy calculations to the evolving driving profile of individual operators; and a Warning And Indication System (WAIS) that uses workload estimations to issue advices to the operator. Fessonia is evaluated in a robot teleoperation scenario that incorporated cognitively demanding secondary tasks to induce varying degrees of workload. The results demonstrate the ability of Fessonia to estimate different levels of imposed workload. Additionally, it is demonstrated that our approach is able to detect and adapt to the evolving driving profile of the different operators. Lastly, based on data obtained, a decrease in entropy is observed when a warning indication is issued, suggesting a more attentive approach focused on the primary navigation task.
The simulation environment used in this work was developed with ROS. The code us split into three parts, the entropy calculation, the DPU and WAIS. The behaviour_detection_package is comprised of estimation_error_node.py and entropy_node.py. The former python file is handling the estimation model and the estimation errors, while the latter handles the entropy calculation, the DPU and the WAIS.
All source code used to generate the results and figures in the paper are in
the /behaviour_detection_package/scripts folder. The experiment results might slightly vary from the ones presented in the paper, due to the nature of the experiments. Human participants might present different levels of workload during operation and during secondary tasks.
You can download a copy of all the files in this repository by cloning the git repository:
git clone https://github.com/uob-erl/hrt_entropy.git
The repository should be cloned inside the src folder of a catkin workspace and then build the workspace with catkin make.
You'll need an Ubuntu machine and a working ROS environment to run the code. In order to install all the dependencies of the packages, go to the top directory of your catkin workspace where the source code of the ROS packages you'd like to use are. Then run:
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
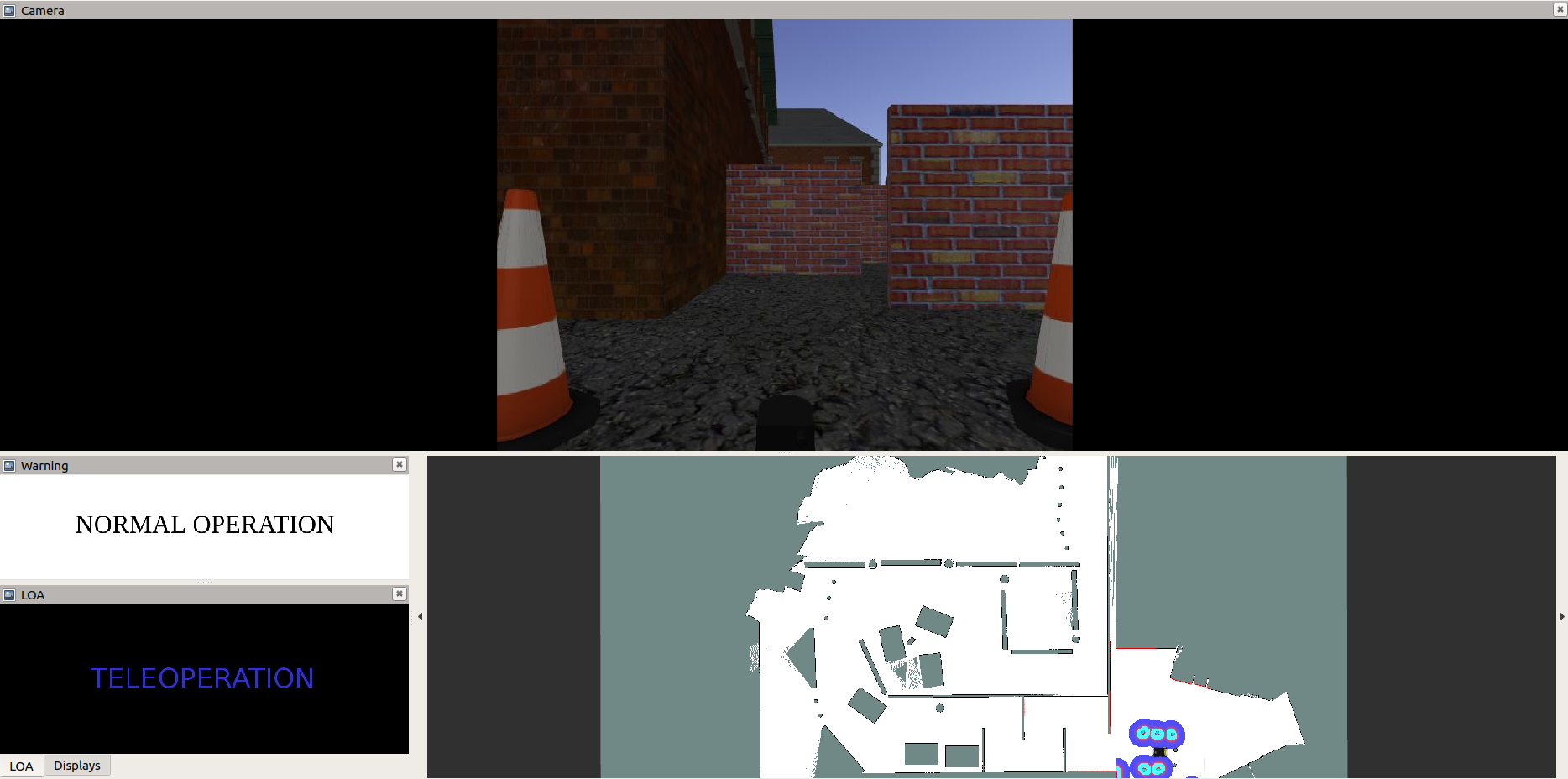
In order to run the simulation environment (with the GUI of the operator) and the entropy scripts execute:
roslaunch experiments_launch entropy_world.launch
This experiment uses a joystick to navigate the robot. The default input device name used in the entropy_world.launch file is js1 and a playstation 4 joystick was used for the experiments. If using a ps4 joystick install ds4drv sudo pip install ds4drv. For a bluetooth connected joystick execute sudo ds4drv or sudo ds4drv --hidraw for a usb connected joystick.
If using another joystick controller then execute ls -l /dev/input/ and cat /proc/bus/input/devices to find your joystick controller.
| Participants and secondary task trial portions | Baseline trial portion | Low workload trial portion | Medium workload trial portion | High workload trial portion | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Participant 1 | 0.1375 | 0.1298 | 0.1946 | 0.1204 | 0.3493 | 0.1184 | 0.4441 | 0.1051 |
| Participant 2 | 0.1641 | 0.1319 | 0.2238 | 0.1279 | 0.3501 | 0.1201 | 0.4918 | 0.1174 |
| Participant 3 | 0.1407 | 0.1346 | 0.1993 | 0.1308 | 0.3418 | 0.1247 | 0.4248 | 0.1091 |
| Total | 0.1474 | 0.1321 | 0.2059 | 0.1264 | 0.3471 | 0.1211 | 0.4546 | 0.1105 |
All source code is made available under a MIT license.