Text-Driven Video Acceleration: A Weakly-Supervised Reinforcement Learning Method
[Project Page] [Paper] [Video]
This repository contains the original implementation of the paper Text-Driven Video Acceleration: A Weakly-Supervised Reinforcement Learning Method, published at the TPAMI 2022.
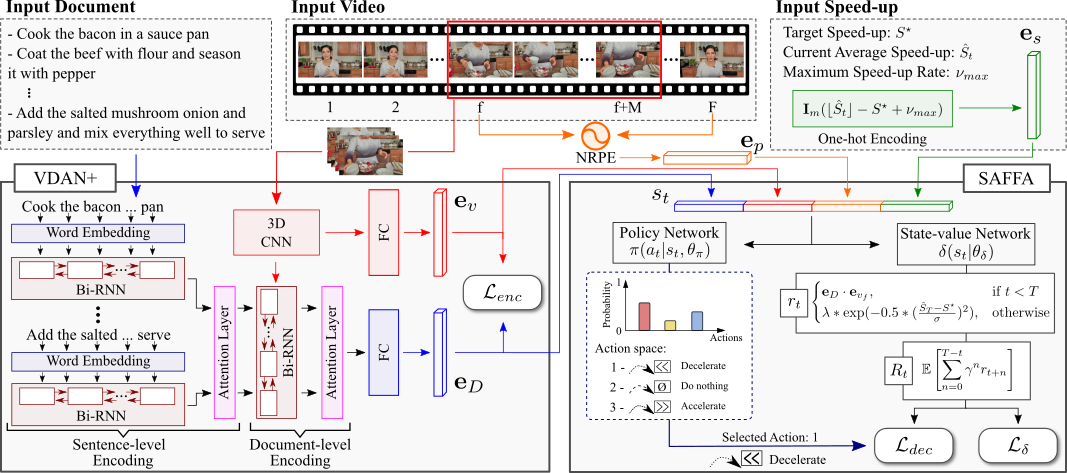
We present a novel weakly-supervised methodology based on a reinforcement learning formulation to accelerate instructional videos using text. A novel joint reward function guides our agent to select which frames to remove and reduce the input video to a target length without creating gaps in the final video. We also propose the Extended Visually-guided Document Attention Network (VDAN+), which can generate a highly discriminative embedding space to represent both textual and visual data.
If you find this code useful for your research, please cite the paper:
@ARTICLE{Ramos_2023_TPAMI,
author={Ramos, Washington and Silva, Michel and Araujo, Edson and Moura, Victor and Oliveira, Keller and Marcolino, Leandro Soriano and Nascimento, Erickson R.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
title={Text-Driven Video Acceleration: A Weakly-Supervised Reinforcement Learning Method},
year={2023},
volume={45},
number={2},
pages={2492-2504},
doi={10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3157198}}
Following, we describe different ways to use our code.
We provide PyTorch Hub integration.
Loading a pretrained model and fast-forwarding your own video is pretty simple!
import torch
model = torch.hub.load('verlab/TextDrivenVideoAcceleration_TPAMI_2022:main', 'TextDrivenAcceleration', pretrained=True)
model.cuda()
model.eval()
document = ['sentence_1', 'sentence_2', ..., 'sentence_N'] # Document of N sentences that will guide the agent semantically
sf = model.fast_forward_video(video_filename='video_filename.mp4',
document=document,
desired_speedup=12,
output_video_filename='output_filename.avi') # Returns the selected frames
print('Selected Frames: ', sf)We provide convinient demos in CoLab.
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
| Process a video using our agent | |
| Train VDAN+ using VaTeX | |
| Train the agent using YouCook2 | |
| Extract VDAN+ feats from a video |
If you want to download the code and run it by yourself in your environment, or reproduce our experiments, please follow the next steps:
-
git clone https://github.com/verlab/TextDrivenVideoAcceleration_TPAMI_2022.git cd TextDrivenVideoAcceleration_TPAMI_2022 pip install -r requirements.txt -
Download & Organize the VaTeX Dataset (Annotations and Videos) + Download the Pretrained GloVe Embeddings
## Download VaTeX JSON data wget -O semantic_encoding/resources/vatex_training_v1.0.json https://eric-xw.github.io/vatex-website/data/vatex_training_v1.0.json wget -O semantic_encoding/resources/vatex_validation_v1.0.json https://eric-xw.github.io/vatex-website/data/vatex_validation_v1.0.json ## Download the Pretrained GloVe Embeddings wget -O semantic_encoding/resources/glove.6B.zip http://nlp.stanford.edu/data/glove.6B.zip unzip -j semantic_encoding/resources/glove.6B.zip glove.6B.300d.txt -d semantic_encoding/resources/ rm semantic_encoding/resources/glove.6B.zip ## Download VaTeX Videos (We used the kinetics-datasets-downloader tool to download the available videos from YouTube) # NOTE: VaTeX is composed of the VALIDATION split of the Kinetics-600 dataset; therefore, you must modify the script to download the validation videos only. # We adpated the function download_test_set in the kinetics-datasets-downloader/downloader/download.py file to do so. # 1. Clone repository and copy the modified files git clone https://github.com/dancelogue/kinetics-datasets-downloader/ semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/kinetics-datasets-downloader/ cp semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/download.py semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/kinetics-datasets-downloader/downloader/download.py cp semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/config.py semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/kinetics-datasets-downloader/downloader/lib/config.py # 2. Get the kinetics dataset annotations wget -O semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/kinetics600.tar.gz https://storage.googleapis.com/deepmind-media/Datasets/kinetics600.tar.gz tar -xf semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/kinetics600.tar.gz -C semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/ rm semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/kinetics600.tar.gz # 3. Download the videos (This can take a while (~28k videos to download)... If you want, you can stop it at any time and train with the downloaded videos) python3 semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/kinetics-datasets-downloader/downloader/download.py --val # Troubleshooting: If the download stops for a long time, experiment increasing the queue size in the parallel downloader (semantic_encoding/resources/VaTeX_downloader_files/kinetics-datasets-downloader/downloader/lib/parallel_download.py)
If you want just to train VDAN+, you're now set!
-
Download & Organize the YouCook2 Dataset (Annotations and Videos)
# Download and extract the annotations wget -O rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/youcookii_annotations_trainval.tar.gz http://youcook2.eecs.umich.edu/static/YouCookII/youcookii_annotations_trainval.tar.gz tar -xf rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/youcookii_annotations_trainval.tar.gz -C rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/ rm rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/youcookii_annotations_trainval.tar.gz # Download the scripts used to collect the videos wget -O rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/scripts.tar.gz http://youcook2.eecs.umich.edu/static/YouCookII/scripts.tar.gz tar -xf rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/scripts.tar.gz -C rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/ rm rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/scripts.tar.gz wget -O rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/splits.tar.gz http://youcook2.eecs.umich.edu/static/YouCookII/splits.tar.gz tar -xf rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/splits.tar.gz -C rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/ rm rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/splits.tar.gz # Install youtube-dl and download the available videos pip install youtube_dl # PS.: The YouTube-DL have been slow lately. If your download speed is under 100KiB/s, consider changing it to the YT-DLP fork (https://github.com/yt-dlp/yt-dlp) cd rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/scripts python download_youcookii_videos.py
After running the setup above, you're ready to train the networks.
To train VDAN+, you first need to set up the model and train parameters (current parameters are the same as described in the paper) in the semantic_encoding/config.py file, then run the training script semantic_encoding/train.py.
The training script will save the model in the semantic_encoding/models folder.
-
model_params = { 'num_input_frames': 32, 'word_embed_size': 300, 'sent_embed_size': 512, # h_ij 'doc_embed_size': 512, # h_i 'hidden_feat_size': 512, 'feat_embed_size': 128, # d = 128. We also tested with 512 and 1024, but no substantial changes 'sent_rnn_layers': 1, # Not used in our paper, but feel free to change 'word_rnn_layers': 1, # Not used in our paper, but feel free to change 'word_att_size': 1024, # c_p 'sent_att_size': 1024, # c_d 'use_sentence_level_attention': True, # Not used in our paper, but feel free to change 'use_word_level_attention': True, # Not used in our paper, but feel free to change 'use_visual_shortcut': True, # Uses the R(2+1)D output as the first hidden state (h_0) of the document embedder Bi-GRU. 'learn_first_hidden_vector': False # Learns the first hidden state (h_0) of the document embedder Bi-GRU. } ETA_MARGIN = 0. # η from Equation 1 - (Section 3.1.3 Training) train_params = { # VaTeX 'captions_train_fname': 'resources/vatex_training_v1.0.json', # Run semantic_encoding/resources/download_resources.sh first to obtain this file 'captions_val_fname': 'resources/vatex_validation_v1.0.json', # Run semantic_encoding/resources/download_resources.sh first to obtain this file 'train_data_path': 'datasets/VaTeX/raw_videos/', # Download all Kinetics-600 (10-seconds) validation videos using the semantic_encoding/resources/download_vatex_videos.sh script 'val_data_path': 'datasets/VaTeX/raw_videos/', # Download all Kinetics-600 (10-seconds) validation videos using the semantic_encoding/resources/download_vatex_videos.sh script 'embeddings_filename': 'resources/glove.6B.300d.txt', # Run semantic_encoding/resources/download_resources.sh first to obtain this file 'max_sents': 20, # maximum number of sentences per document 'max_words': 20, # maximum number of words per sentence # Training parameters 'train_batch_size': 64, # We used a batch size of 64 (requires a 24Gb GPU card) 'val_batch_size': 64, # We used a batch size of 64 (requires a 24Gb GPU card) 'num_epochs': 100, # We ran in 100 epochs 'learning_rate': 1e-5, 'model_checkpoint_filename': None, # Add an already trained model to continue training (Leave it as None to train from scratch)... # Video transformation parameters 'resize_size': (128, 171), # h, w 'random_crop_size': (112, 112), # h, w 'do_random_horizontal_flip': True, # Horizontally flip the whole video randomly in block # Training process 'optimizer': 'Adam', 'eta_margin': ETA_MARGIN, 'criterion': nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(ETA_MARGIN), # Machine and user data 'username': getpass.getuser(), 'hostname': socket.gethostname(), # Logging parameters 'checkpoint_folder': 'models/', 'log_folder': 'logs/', # Debugging helpers (speeding things up for debugging) 'use_random_word_embeddings': False, # Choose if you want to use random embeddings 'train_data_proportion': 1., # Choose how much data you want to use for training 'val_data_proportion': 1., # Choose how much data you want to use for validation } models_paths = { 'VDAN': '<PATH/TO/THE/VDAN/MODEL>', # OPTIONAL: Provide the path to the VDAN model (https://github.com/verlab/StraightToThePoint_CVPR_2020/releases/download/v1.0.0/vdan_pretrained_model.pth) from the CVPR paper: https://github.com/verlab/StraightToThePoint_CVPR_2020/ 'VDAN+': '<PATH/TO/THE/VDAN+/MODEL>' # You must fill this path after training the VDAN+ to train the SAFFA agent } deep_feats_base_folder = '<PATH/TO/THE/VDAN+EXTRACTED_FEATS/FOLDER>' # Provide the location you stored/want to store your VDAN+ extracted feature vectors
-
First, make sure you have
punktinstalled...import nltk nltk.download('punkt')
Finally, you're ready to go! 😃
cd semantic_encoding python train.py
-
To train the agent, you will need the features produced the VDAN+ model. You can have these features here and here. To get it via terminal, use:
# Download YouCook2's VDAN+ video feats wget -O rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/VDAN+/youcook2_vdan+_vid_feats.zip https://verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/TextDrivenVideoAcceleration/youcook2_vdan+_vid_feats.zip unzip -q rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/VDAN+/youcook2_vdan+_vid_feats.zip -d rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/VDAN+/vid_feats/ rm rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/VDAN+/youcook2_vdan+_vid_feats.zip # Download YouCook2's VDAN+ document feats wget -O rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/VDAN+/youcook2_vdan+_doc_feats.zip https://verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/TextDrivenVideoAcceleration/youcook2_vdan+_doc_feats.zip unzip -q rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/VDAN+/youcook2_vdan+_doc_feats.zip -d rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/VDAN+/doc_feats/ rm rl_fast_forward/resources/YouCook2/VDAN+/youcook2_vdan+_doc_feats.zip
-
If you want to extract them by yourself, you can have a VDAN+ pretrained model by following the instructions in the previous step or downloading a pretrained one we provide here. In terminal, use:
# Download the pretrained model wget -O semantic_encoding/models/vdan+_model_pretrained.pth https://github.com/verlab/TextDrivenVideoAcceleration_TPAMI_2022/releases/download/pre_release/vdan+_pretrained_model.pth -
Now, prepare the data for training...
cd rl_fast_forward python resources/create_youcook2_recipe_documents.py -
You are set! Now, you just need to run it...
python train.py -s ../semantic_encoding/models/vdan+_model_pretrained.pth -d YouCook2
-
After training, the model will be saved in the rl_fast_forward/models folder.
-
You can test the agent using a saved model for the YouCook2 dataset as follows:
python test.py -s ../semantic_encoding/models/vdan+_model_pretrained.pth -m models/saffa_vdan+_model.pth -d YouCook2 -x 12
-
This script will generate a results JSON file with the pattern
results/<datetime>_<hostname>_youcookii_selected_frames.json
We provide, in the rl_fast_forward/eval folder, a script to evaluate the selected frames generated by the trained agent.
-
To compute Precision, Recall, F1 Score, and Output Speed for your results using the JSON output (generated when training the agent), run the following script:
cd rl_fast_forward/eval python eval_results.py -gt youcookii_gts.json -sf /path/to/the/JSON/output/file.json -
You may need to download the ground-truth file first:
cd rl_fast_forward/eval # For the YouCook2 dataset wget https://verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/TextDrivenVideoAcceleration/youcookii_gts.json # For the COIN dataset wget https://verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/TextDrivenVideoAcceleration/coin_gts.json
-
It will display the values in your screen and generate a JSON and a CSV output file formatted as:
/path/to/the/JSON/output/file_results.EXT -
If you want to reproduce our results, we also provide the selected frames for the compared approaches here. It can be downloaded by running:
wget https://verlab.dcc.ufmg.br/TextDrivenVideoAcceleration/results.zip unzip -q results.zip rm results.zip
- Washington Ramos - PhD Candidate - UFMG - washington.ramos@dcc.ufmg.br
- Michel Silva - Assistant Professor at Universidade Federal de Viçosa (UFV) - michelms@dcc.ufmg.br
- Edson Araujo - MSc Student - UFMG - edsonroteia@dcc.ufmg.br
- Victor Moura - Undergraduate Student - UFMG - victorhugomoura@dcc.ufmg.br
- Keller Oliveira - Undergraduate Student - UFMG - kellermartins@dcc.ufmg.br
- Leandro Soriano Marcolino - Lecturer at Lancaster University - l.marcolino@lancaster.ac.uk
- Erickson R. do Nascimento - Principal Investigator - UFMG - erickson@dcc.ufmg.br
Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG)
Departamento de Ciência da Computação
Belo Horizonte - Minas Gerais - Brazil
 |
 |
|---|
VeRLab: Laboratory of Computer Vison and Robotics
https://www.verlab.dcc.ufmg.br
We thank the agencies CAPES, CNPq, FAPEMIG, and Petrobras for funding different parts of this work.