These scripts are used for the calculation of the rates of adaptation from raw Illumina reads. The rates of adaptation are estimated by means of:
-
$\alpha$ (alpha): Proportion of non-synonymous mutations fixed by positive selection -
$\omega$ A (omegaA): Rate of adaptive non-synonymous substitutions -
$\omega$ NA (omegaNA): Rate of non-adaptive non-synonymous substitutions
Furthermore the scripts were used for the estimation of recombination rate per species & across the genome, neutral genetic diveristy (proxy for Ne), core & accessory protein-coding gene repertoire, protein functional prediction (effectors, secreted and non-secreted proteins), phylogenetic inferences and statistical modeling.
These scripts were used in the project: "Large-scale analyses reveal the contribution of adaptive evolution in pathogenic and non-pathogenic fungal species", available at https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.08.28.555124v1
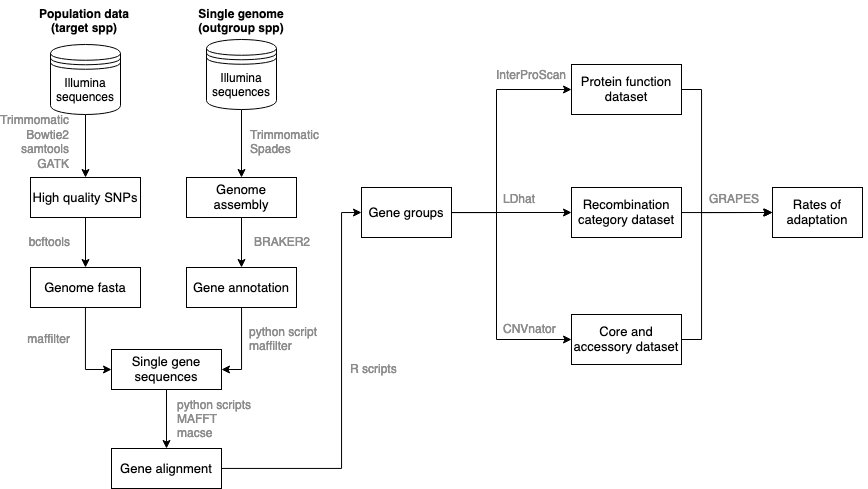
Fig1. Methodology schematic showing the various steps and tools used
These scripts use a series of tools that you might need depending on the step you want to run. Some important tools are:
Trimmomatic is used to trim adaptors and low quality reads from all illumina data. Instructions can be found in https://speciationgenomics.github.io/Trimmomatic/
bowtie2 is used to map trimmed reads on the referece genome of each target species. Instructions can be found in https://github.com/BenLangmead/bowtie2
GATK is used to perform haplotype calling, SNP calling and assign quality filteres to SNPs before hardfiltering. Instructions can be found in https://github.com/broadinstitute/gatk
bcftools is used to extract one fasta sequence per isolate after considering SNP mutations in the dataset. Instructions can be found in https://samtools.github.io/bcftools/bcftools.html
mafft is used to add the outgroup sequence to the aligned fasta file and perform a new alignment. Instructions can be found in https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/
MACSE is used to polish the alignment output of maft. Installation instructions can be found in https://github.com/ranwez/MACSE_V2_PIPELINES
Maffilter is used for the extraction of CDS/exon regions from consensus fasta files. For details see https://jydu.github.io/maffilter/
BppPopstat is used for the calculation of kappa (the transition over transversion ratio) and quantification of polymorphism and divergence mutations across gene alignments. Installation instruction can be found in https://github.com/BioPP/bppsuite or here.
CNVnator is used to identify deleted regions across the genome. Installation instructions can be found in https://github.com/abyzovlab/CNVnator
LDhat is used to calculate the population recombination rate (
ANGSD is used to estimate Watterson
GRAPES is used to estimate the rates of adaptive evolution. Installation instructions can be found in https://github.com/BioPP/grapes
SPAdes is used to perform de novo assembly on the raw reads from the outgroup species. Installation instructions can be found in https://github.com/ablab/spades
BRAKER2 is used to predict genes on the outgroup assembled genomes. Installation instructions can be found in https://github.com/Gaius-Augustus/BRAKER
OrthoFinder is used to identify single copy orthologs between the protein list of target and outgroup species. Installation instructions can be found in https://github.com/davidemms/OrthoFinder
SLiM: Simulation of several population structure scenarios. Installation instructions can be found in https://github.com/MesserLab/SLiM
Data preparation: Raw illumina reads are trimmed, filtered for quality and mapped onto a reference genome. After hardfiltering and sanity checks, a consensus genome is extracted from each sample in the VCF, and Maffilter is used to extract the coding region of reach consensus genome. A custom python script is then used to merge all conding regions per gene. Scripts in 1_DataPreparation. For the outgroup species, raw genome reads were downloaded from NCBI and de novo assembly and gene predictions were performed. Scripts in 9_Outgroup_assembly_gene_prediction
Gene alignment: Orthologous genes will be identified among the reference isolates. For the population data, individual genes files will extracted into fasta files containing isolate's sequence and the outgroup sequence will be added. Mafft and MACSE will be used for the alignment and polishment, and custom python scripts will be used for quality control. Scripts in 2_GeneAlignment.
Protein functional analysis: Using interpro scan and effectorP to classify proteins into non-secreted, secreted but not effector and predicted effectors. Scripts in 3_Protein_FunctionalAnalysis.
bppPopStat: Calculation of kappa, polymorphism and substitutions counts are performed using this tool on each gene individually. A first run is performed for the estimation of the median kappa across all genes. Here, the distribution of kappa must be unimodal (see Fig2). Next, kappa is fixed to the previously determined median and the counts of mutations are performed. Scripts in 4_bppPopStat.
Fig2. Example of kappa estimations in the fungus Zymoseptoria tritici
GRAPES: Calculation of the rates of adaptive evolution based on the unfolded SFS of a group of protein coding genes. Note that calculations are not based on single genes. First, an initial run is performed for the identification of the best model for the distribution of fitness effects (DFE) using -model all. All subsequent runs are performed with the best model per species. In adition, the flag -no_div_param was used in all runs. All scripts for the generation of in-put files, bootstraps, permutation and for parsing the output files are provided in 5_GRAPES.
Recombination rate: Calculation of the population recombination rate paramenter (n>100 samples were splitted into multiple runs with random selection of samples per run. Next, with information of
Identification of accessory genes: First CNVnator was used to identify deleted regions across the genome of each sample. Runs were performed on each BAM file. Next, the coordinates of deletions and protein-coding genes were overlaped and gene coordinates completly within deletions were considered missing from a sample, and thus acessory. Scripts in 7_Identify_Accessory_genes.
Generalized least squares modeling: To access the significance of correlations and account for phylogenetic signals a generalized least squares modeling procedure was implemented. The following effects were tested against the rates at adaptation, at both genome-wide and species-wide levels: (i) gene categories (non-secreted, secreted but not effectors and effectors), (ii) recombination (
Simulations: To infer on the robustness of our inferences to population structure, we performed several simulations prior to estimations of the rates of adaptation. Detailed information and scripts are available in 10_Simulations
One important point when scalating to multiple species is related to how annotation files (GFF) are coded and how to extract correct information from it.