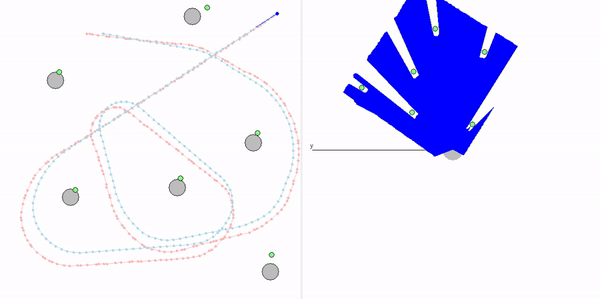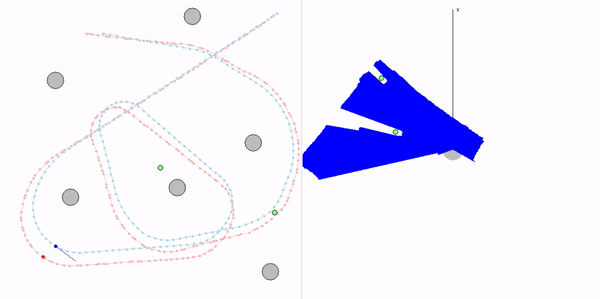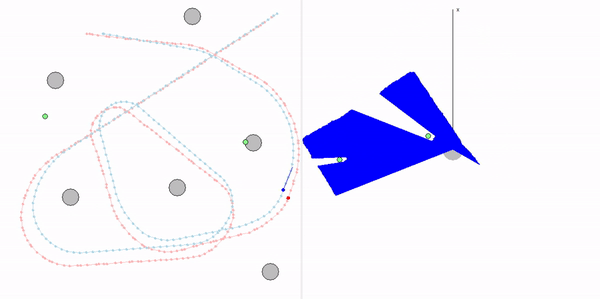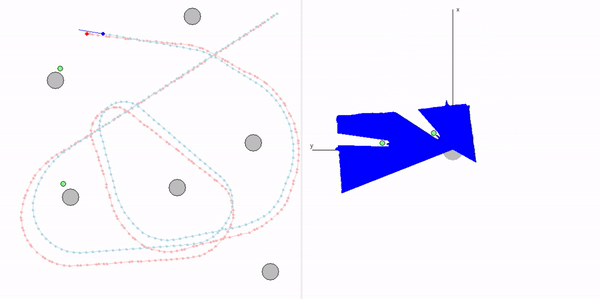
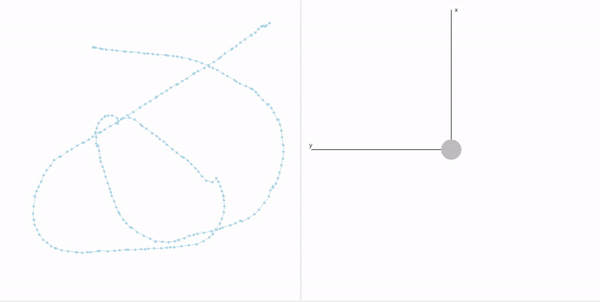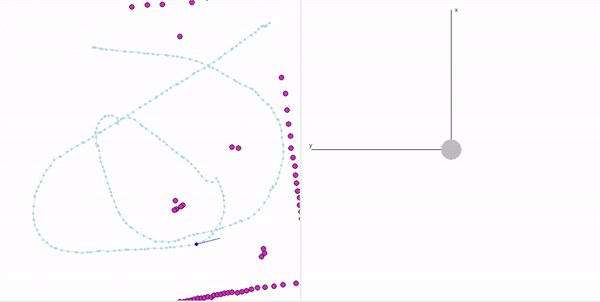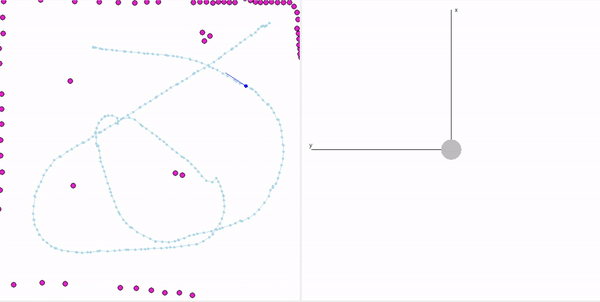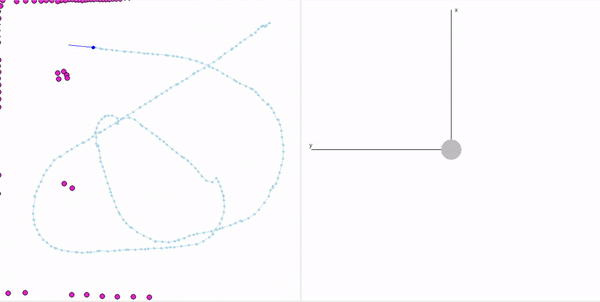
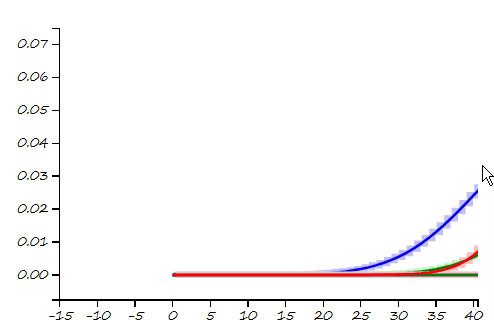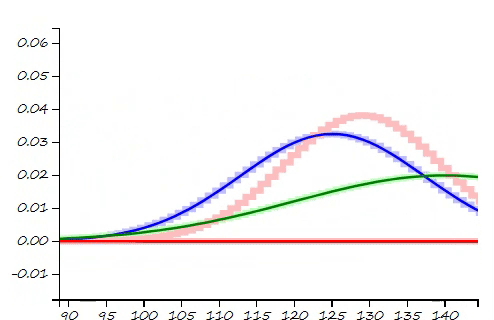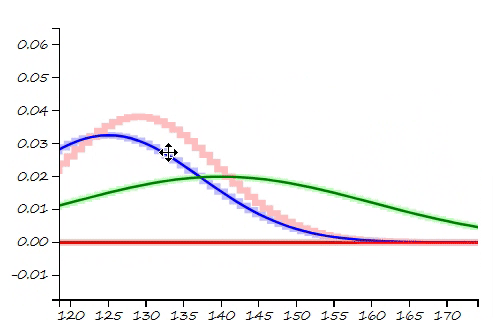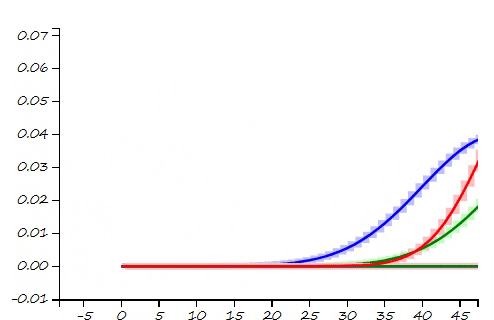
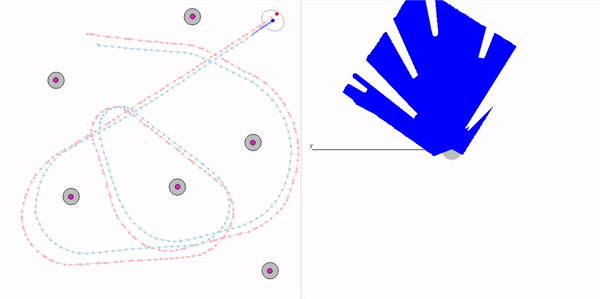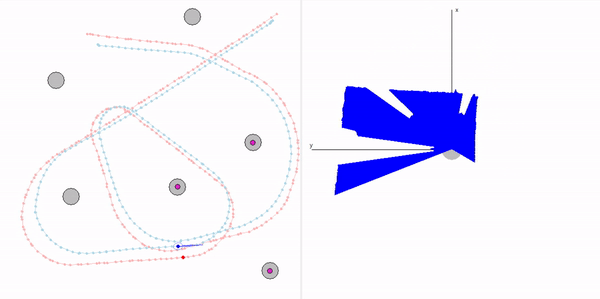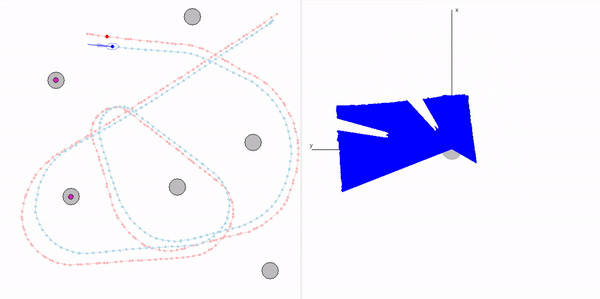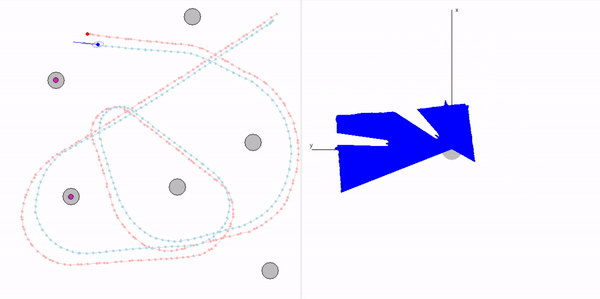
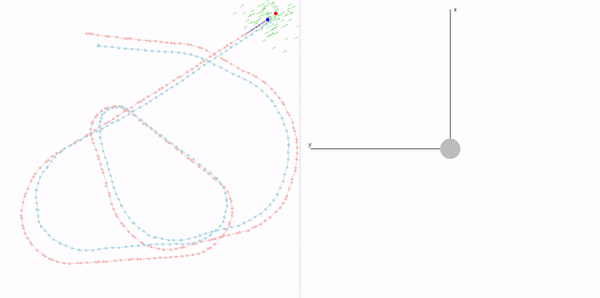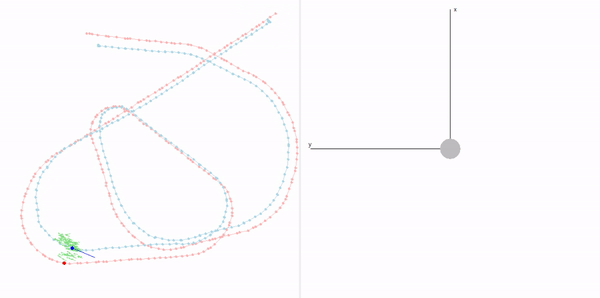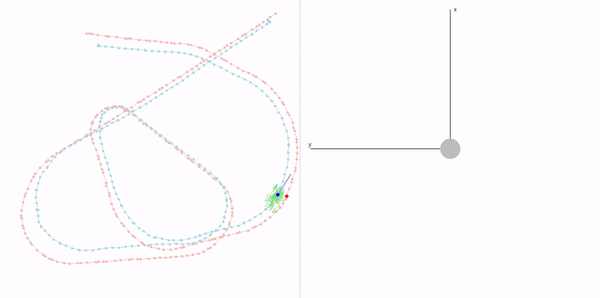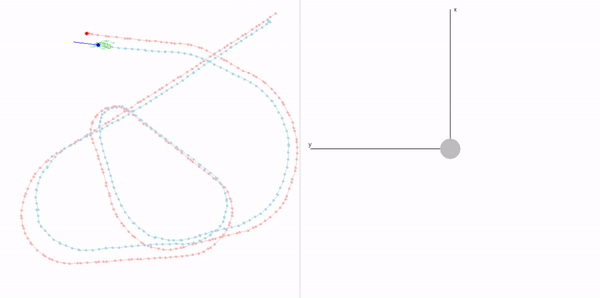
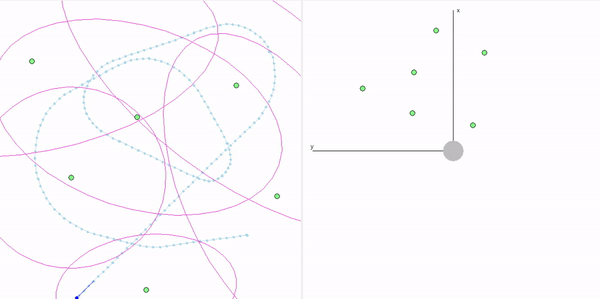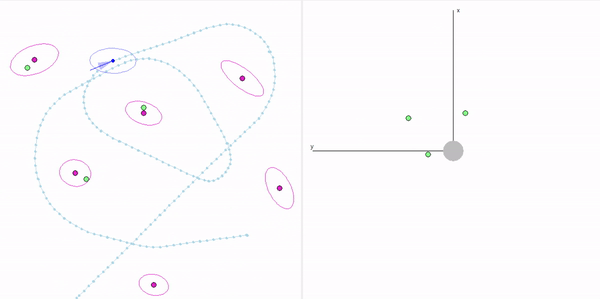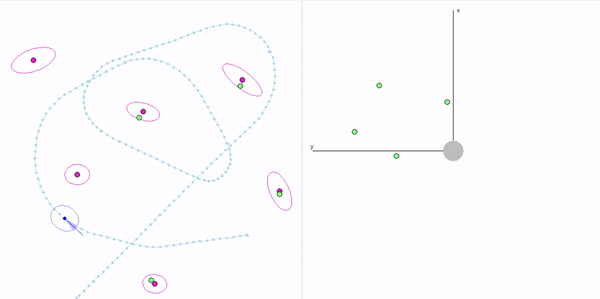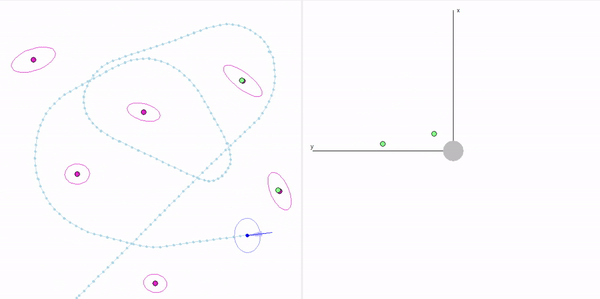
This project is a part of SLAM and Path Planning course given by the professor Claus Brenner from the University of Leibniz. The course is based on the data (LiDAR and Encoder) collected from a lego based robot with caterpillar tracks navigated through a controlled environment.
- Summary: Developed a motion model of the robot, transformed the motor ticks of the robot into a real world trajectory and corrected the calibration error with the sensor model, developed using the LiDAR data by detecting the location of the landmarks in scanner's coordinate system.
- Keywords: Motion model, motor control, LiDAR and encoder data.
- Summary Feature Based Localization: Assigned the detected landmarks to the respective landmarks in the map, developed the mathematics for similarity transformation and applied as a direct solution, and corrected the pose of the robot based on the transform. Featureless localization: Assigned the scan points to the walls of the arena and applied Iterative Closest Point to find the optimal transformation.
- Keywords: Similarity transformation, ICP
- Summary: Developed a histogram filter and a 1-D Kalman filter which are recursive Bayes filters, to estimate the true position of the Robot, which is uncertain about its movement and has measurement noise.
- Keywords: Histogram filter, 1-D Kalman filter.
- Summary: Augmented the Kalman filter developed in Unit 3 to n dimensions and implemented Exteded Kalman filter to localize our robot which has non linear states and control commands.
- Keywords: Sensor fusion, Extended Kalman filter.
- Summary: Implemented a Monte Carlo Localization algorithm knows as Particle Filter, which could handle any kind of model (not just Gaussian) by discretizing the problem into individual particles to generate different system states. The states which are supported by the sensor data are assigned high weights. Rhe particles with low weights are ignored and new random sampling is done to keep the number of particles constant.
- Keywords: Sensor fusion, Particle filter localization
- Summary: What if the robot is not given the map of the environment? This is the common problem in the field of autonomous navigation. We have to estimate both the position and heading of the robot and the position of the landmarks. These 2 processes cannot be separated from each other and must be done simultaneously. In this part of the project, I implement an Extended Kalman Filter Simultaeous Localization and Mapping algorithm, as a solution to this problem.
- Keywords: Sensor fusion, EKF SLAM