中文 | English
FPGA USB-device 控制器。可实现 CDC (USB串口), HID (USB键盘), Audio (USB音频输出) 设备。已在 Windows 和 Linux 上成功识别和工作。
_________________
| |
| usb_dp_pull |-------|
| | |
| | |-|
| | | | 1.5k resistor is to pull-up or pull-down USB D+
| | |_| ____________ __________
| | | | | |
| usb_dp |-------^-------------| USB_D+ | |
| | | | USB cable |
| usb_dn |---------------------| USB_D- |<------------>| Host PC
| | | | |
| GND |---------------------| GND | |
| | | | |
----------------- ------------ ----------
FPGA USB Connector 电脑
上图左侧, usb_dp_pull, usb_dp, usb_dn 是 FPGA 的 3 个普通引脚(电平必须为 3.3V)。其中:
usb_dn接USB_D-usb_dp接USB_D+usb_dp_pull要通过 1.5kΩ 的电阻接USB_D+
为了进行如上连接,最快捷的方式是用 USB Connector (USB 母座)进行飞线连接,建议用 USB TypeB(俗称方口)母座,因为引脚间距大,便于焊接(如图1)。你需要把方口母座下方的针脚焊接到杜邦线上(别忘了焊接那个1.5kΩ 的电阻);然后把杜邦线插在 FPGA 开发板上。
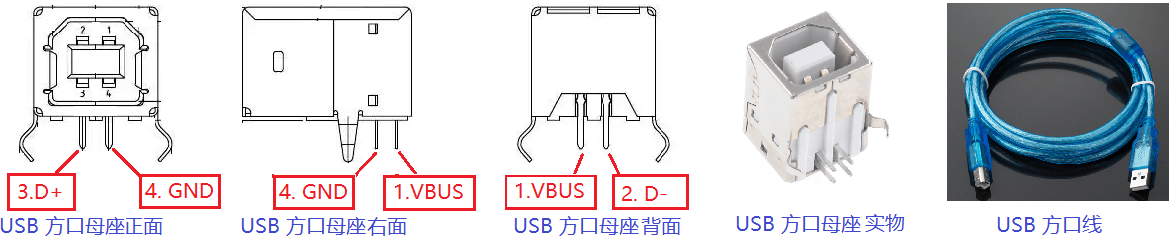 |
|---|
| 图1:USB 方口母座与线 |
注意:USB中有一根线是 VBUS ,是 Host 提供给 Device 的 5V 电源,在这里不需要连接。
制作专用于接口转换的PCB,具有最好的信号完整性表现。虽然 USB FS 仅有12Mbps速率,但是依然有必要保证USB_D-和USB_D+的等长、等间距布线,并且不要靠近时钟或其他高速信号,做包地处理是最理想的设计。
注意:虽然 USB FS 并不需要严格的阻抗设计,但是依然要使用合适的线宽、间距。
| 文件名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| RTL/usbfs_core/*.sv | 实现了一个 USB Device 控制器(Full Speed) |
| RTL/usb_cdc/usb_cdc_top.sv | 调用 USB-device 控制器,实现 CDC 设备,用于虚拟串口通信 |
| RTL/usb_cdc/fpga_top_usb_cdc.sv | FPGA顶层。展示如何用 usb_cdc_top.sv 实现一个回环的虚拟串口(通过minicom/超级终端/串口助手发送的字符会回传)。已在 Windows 和 Linux 上成功识别和工作(操作系统自带驱动程序,无需额外安装) |
| RTL/usb_hid/usb_hid_top.sv | 调用 USB-device 控制器,实现 HID 键盘,用于模拟键盘输入 |
| RTL/usb_hid/fpga_top_usb_hid.sv | FPGA顶层。展示如何用 usb_hid_top.sv 实现一个不断按下的键盘。已在 Windows 和 Linux 上成功识别和工作(操作系统自带驱动程序,无需额外安装) |
| RTL/usb_audio/usb_audio_top.sv | 调用 USB-device 控制器,实现 audio class,用于输出音频流 |
| RTL/usb_audio/fpga_top_usb_audio.sv | FPGA顶层。展示如何用 usb_audio_top.sv 实现一个双声道 16bit 48kHz采样率的USB声卡,采用usb audio class 1.0标准。已在 Windows 和 Linux 上成功识别和工作(操作系统自带驱动程序,无需额外安装) |
注意:以上代码都是 SystemVerilog 行为级实现,支持任意 FPGA 平台。但除了 fpga_top_usb_cdc.sv 、 fpga_top_usb_hid.sv 和 fpga_top_usb_audio.sv 里的 altpll 是仅限于 Altera Cyclone IV E 的原语,它用来生成 60MHz 时钟。如果你用的不是 Altera Cyclone IV E,请使用其它的 IP 核(例如 Xilinx 的 clock wizard)或原语来替换。
usb_cdc_top.sv 、 usb_hid_top.sv 和 usb_audio_top.sv 中,我提供了简洁的调用接口,如下:
input wire rstn, // active-low reset, reset when rstn=0 (USB will unplug when reset), normally set to 1
input wire clk, // 60MHz is required
// USB signals
output wire usb_dp_pull, // connect to USB D+ by an 1.5k resistor
inout usb_dp, // USB D+
inout usb_dn, // USB D-
// HID keyboard press signal
input wire [15:0] key_value, // Indicates which key to press, NOT ASCII code! see https://www.usb.org/sites/default/files/hut1_21_0.pdf section 10.
input wire key_request // when key_request=1 pulses, a key is pressed.
input wire rstn, // active-low reset, reset when rstn=0 (USB will unplug when reset), normally set to 1
input wire clk, // 60MHz is required
// USB signals
output wire usb_dp_pull, // connect to USB D+ by an 1.5k resistor
inout usb_dp, // USB D+
inout usb_dn, // USB D-
// CDC receive data (host-to-device)
output wire [ 7:0] recv_data, // received data byte
output wire recv_valid, // when recv_valid=1 pulses, a data byte is received on recv_data
// CDC send data (device-to-host)
input wire [ 7:0] send_data, // data byte to send
input wire send_valid, // when device want to send a data byte, set send_valid=1. the data byte will be sent successfully when (send_valid=1 && send_ready=1).
output wire send_ready // send_ready handshakes with send_valid. send_ready=1 indicates send-buffer is not full and will accept the byte on send_data. send_ready=0 indicates send-buffer is full and cannot accept a new byte.
input wire rstn, // active-low reset, reset when rstn=0 (USB will unplug when reset), normally set to 1
input wire clk, // 60MHz is required
// USB signals
output wire usb_dp_pull, // connect to USB D+ by an 1.5k resistor
inout usb_dp, // USB D+
inout usb_dn, // USB D-
// Audio 48kHz 16bit 2 channel
output reg [15:0] audio_lch, // connect to Audio DAC left channel
output reg [15:0] audio_rch // connect to Audio DAC right channel
RTL/usbfs_core/usbfs_core_top.sv 实现了 USB-Transfer 层往下的完整协议。留出了:
- descriptor ROM 读接口
- Endpoint 0x01 receive 接口
- Endpoint 0x81 send 接口
因此可以用来开发其它 USB-device。usb_cdc_top.sv 、 usb_hid_top.sv 和 usb_audio_top.sv 皆是调用 usbfs_core_top.sv 来实现的。
例如,你可以仿照 usb_hid_top.sv ,修改 descriptor(描述符),并实现自定义的 send & receive 行为来实现其它 USB-device 。我打算继续用它实现 USB Mass Storage Class (U盘) 和 USB Video Class (UVC 摄像头)。
- https://www.usbmadesimple.co.uk/ : USB Made Simple
- https://github.com/FengJungle/USB_Protocol_CH : USB 中文协议手册
- 其它 FPGA 实现:
- https://github.com/avakar/usbcorev : 一个 USB-device 控制器,仅支持到了 transaction 层。
- http://jorisvr.nl/article/usb-serial : 一个 USB-CDC,VHDL实现,需要额外的 UTMI PHY。
- https://github.com/pbing/USB : 一个 Low Speed 的 USB-HID 实现。
- https://github.com/ultraembedded/cores : 包含一些 USB-host 和 USB-device 实现,需要 UTMI PHY 或 ULPI PHY。
FPGA USB-device controller to realize CDC (virtual serial port), HID (keyboard input), and Audio (audio output) device. It has been successfully identified and working on Windows and Linux.
_________________
| |
| usb_dp_pull |-------|
| | |
| | |-|
| | | | 1.5k resistor is to pull-up or pull-down USB D+
| | |_| ____________ __________
| | | | | |
| usb_dp |-------^-------------| USB_D+ | |
| | | | USB cable |
| usb_dn |---------------------| USB_D- |<------------>| Host PC
| | | | |
| GND |---------------------| GND | |
| | | | |
----------------- ------------ ----------
FPGA USB Connector 电脑
You need to make the circuit connection as shown above, where usb_dp_pull, usb_dp, usb_dn are 3 common pins of FPGA (the level must be 3.3V):
usb_dnshould connect toUSB_D-usb_dpshould connect toUSB_D+usb_dp_pullshould connect toUSB_D+through a 1.5kΩ resistor.
Note: One of the USB pin is VBUS, which is the 5V power supply provided by the Host to the Device, and no connection is required on it.
In order to make the above connection, the fastest way is to use a USB Connector (USB female socket) and connect by flying leads. It is recommended to use USB TypeB female socket (commonly known as square socket), because the pin pitch is large, which is convenient for soldering (see Figure1). You need to solder the pins under the socket to the DuPont wire (don't forget to solder the 1.5kΩ resistor); then plug the DuPont wire into the FPGA board.
 |
|---|
| Figure1 : USB TypeB female socket and cable. |
Make a PCB dedicated to interface conversion with the best signal integrity performance. Although the speed of USB FS is only 12Mbps, it is still necessary to ensure that the wiring of USB_D- and USB_D+ is of equal length and spacing, and not close to the clock or other high-speed signals. Packet processing is the most ideal design.
| File Name | Introduction |
|---|---|
| RTL/usbfs_core/*.sv | The USB Device Controller core (Full Speed). |
| RTL/usb_cdc/usb_cdc_top.sv | Call the USB-device controller to implement a CDC device for virtual serial communication. |
| RTL/usb_cdc/fpga_top_usb_cdc.sv | FPGA's top-level. Show how to use usb_cdc_top.sv to implement a loopback virtual serial port (characters sent through minicom/hyperterminal will be returned). Successfully identifed and working on Windows and Linux (OS has its driver, no additional installation is required). |
| RTL/usb_hid/usb_hid_top.sv | Call the USB-device controller to implement an HID keyboard. |
| RTL/usb_hid/fpga_top_usb_hid.sv | FPGA's top-level. Shows how to use usb_hid_top.sv to implement a keyboard that keeps pressing. Successfully identifed and working on Windows and Linux (OS has its driver, no additional installation is required). |
| RTL/usb_audio/usb_audio_top.sv | Call the USB-device controller to implement an audio class for outputting audio streams. |
| RTL/usb_audio/fpga_top_usb_audio.sv | FPGA's top-level. Show how to use usb_audio_top.sv to implement a two-channel 16bit 48kHz sample rate USB sound card, using the usb audio class 1.0 standard. Successfully identifed and working on Windows and Linux (OS has its driver, no additional installation is required). |
Note: The above code are pure behavioral implementation in SystemVerilog, so they support any FPGA platform. But except that altpll in fpga_top_usb_cdc.sv , fpga_top_usb_hid.sv and fpga_top_usb_audio.sv is an Altera Cyclone IV E-only primitive that is used to generate the 60MHz clock. If you are not using Altera Cyclone IV E, use another IP core (such as Xilinx's clock wizard) or primitives instead.
In usb_cdc_top.sv, usb_hid_top.sv, usb_audio_top.sv, I provide concise calling interfaces, as follows:
input wire rstn, // active-low reset, reset when rstn=0 (USB will unplug when reset), normally set to 1
input wire clk, // 60MHz is required
// USB signals
output wire usb_dp_pull, // connect to USB D+ by an 1.5k resistor
inout usb_dp, // USB D+
inout usb_dn, // USB D-
// HID keyboard press signal
input wire [15:0] key_value, // Indicates which key to press, NOT ASCII code! see https://www.usb.org/sites/default/files/hut1_21_0.pdf section 10.
input wire key_request // when key_request=1 pulses, a key is pressed.
input wire rstn, // active-low reset, reset when rstn=0 (USB will unplug when reset), normally set to 1
input wire clk, // 60MHz is required
// USB signals
output wire usb_dp_pull, // connect to USB D+ by an 1.5k resistor
inout usb_dp, // USB D+
inout usb_dn, // USB D-
// CDC receive data (host-to-device)
output wire [ 7:0] recv_data, // received data byte
output wire recv_valid, // when recv_valid=1 pulses, a data byte is received on recv_data
// CDC send data (device-to-host)
input wire [ 7:0] send_data, // data byte to send
input wire send_valid, // when device want to send a data byte, set send_valid=1. the data byte will be sent successfully when (send_valid=1 && send_ready=1).
output wire send_ready // send_ready handshakes with send_valid. send_ready=1 indicates send-buffer is not full and will accept the byte on send_data. send_ready=0 indicates send-buffer is full and cannot accept a new byte.
input wire rstn, // active-low reset, reset when rstn=0 (USB will unplug when reset), normally set to 1
input wire clk, // 60MHz is required
// USB signals
output wire usb_dp_pull, // connect to USB D+ by an 1.5k resistor
inout usb_dp, // USB D+
inout usb_dn, // USB D-
// Audio 48kHz 16bit 2 channel
output reg [15:0] audio_lch, // connect to Audio DAC left channel
output reg [15:0] audio_rch // connect to Audio DAC right channel
RTL/usbfs_core/usbfs_core_top.sv implements the complete protocol down to the USB-transfer layer and give out:
- Descriptor ROM read interface,
- Endpoint 0x01 receive interface,
- Endpoint 0x81 send interface are reserved
, which can be used to develop other USB-devices. usb_cdc_top.sv, usb_hid_top.sv and usb_audio_top.sv are all implemented by calling usbfs_core_top.sv.
For example, you can imitate usb_hid_top.sv , modify descriptors, and implement custom send & receive behaviors to implement other USB-devices. I plan to continue using it to implement USB Mass Storage Class (U disk) and USB Video Class (UVC camera).
- https://www.usbmadesimple.co.uk/ : USB Made Simple.
- https://github.com/FengJungle/USB_Protocol_CH : USB Protocol Manual in Chinese.
- Other FPGA USB cores:
- https://github.com/avakar/usbcorev : A USB-device core, only support up to transaction layer.
- http://jorisvr.nl/article/usb-serial : A USB-CDC core in VHDL, requires additional UTMI PHY.
- https://github.com/pbing/USB : A Low-Speed USB-HID core.
- https://github.com/ultraembedded/cores : Contains some USB-host and USB-device implementations that require UTMI PHY or ULPI PHY.
-CAD09D.svg)

