__________ __ __
| ____ | | | | |
_ | | |__| | | | |
_______ _ _ ___| |___ ______ | | | | | |
| ___ | | | | | |___ ___| / ____ \ | |_______ | | | |
| | |_| | | | | | | / /____\ \ |_______ | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | _______| __ | | \ \ / /
| | _ | | | | | | _ | | _ | | | | \ \ / /
| |___| | | |___| | | |_| | \ \____/ | | |____| | \ \_/ /
|_______| |_______| |_____| \______/ |__________| \_____/
$ pip install cuteSV
or
$ conda install -c bioconda cutesv
or
$ git clone https://github.com/tjiangHIT/cuteSV.git && cd cuteSV/ && python setup.py install
Long-read sequencing enables the comprehensive discovery of structural variations (SVs). However, it is still non-trivial to achieve high sensitivity and performance simultaneously due to the complex SV characteristics implied by noisy long reads. Therefore, we propose cuteSV, a sensitive, fast and scalable long-read-based SV detection approach. cuteSV uses tailored methods to collect the signatures of various types of SVs and employs a clustering-and-refinement method to analyze the signatures to implement sensitive SV detection. Benchmarks on real Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) and Oxford Nanopore Technology (ONT) datasets demonstrate that cuteSV has better yields and scalability than state-of-the-art tools.
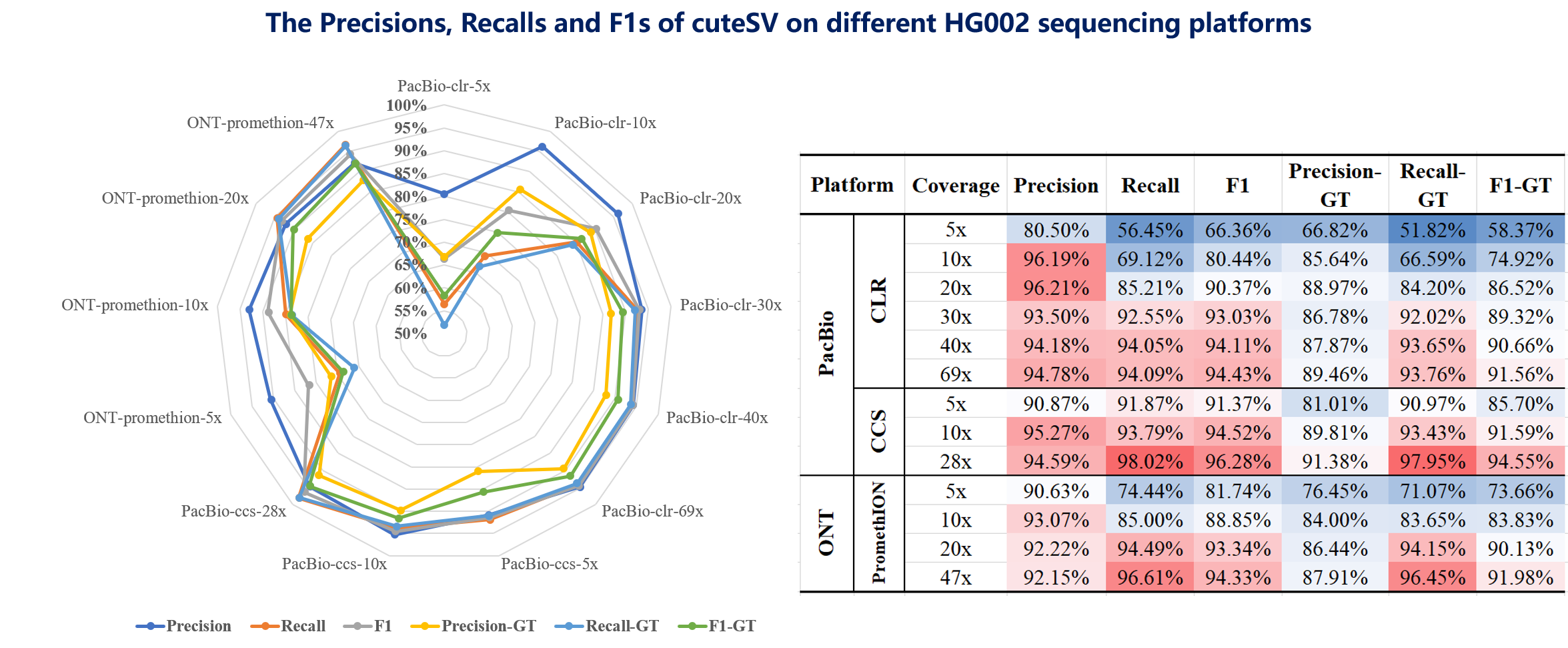
The benchmark results of cuteSV on the HG002 human sample are below:
BTW, we used Truvari to calculate the recall, precision, and f-measure. For more detailed implementation of SV benchmarks, we show an example here.
A new wiki page about diploid-assembly-based SV detection using cuteSV has been established. More details please see here.
We provided a new document for applying force calling (or regenotyping) benchmark here.
1. python3
2. pysam
3. Biopython
4. cigar
5. numpy
6. pyvcf
cuteSV <sorted.bam> <reference.fa> <output.vcf> <work_dir>
Suggestions
> For PacBio CLR data:
--max_cluster_bias_INS 100
--diff_ratio_merging_INS 0.3
--max_cluster_bias_DEL 200
--diff_ratio_merging_DEL 0.5
> For PacBio CCS(HIFI) data:
--max_cluster_bias_INS 1000
--diff_ratio_merging_INS 0.9
--max_cluster_bias_DEL 1000
--diff_ratio_merging_DEL 0.5
> For ONT data:
--max_cluster_bias_INS 100
--diff_ratio_merging_INS 0.3
--max_cluster_bias_DEL 100
--diff_ratio_merging_DEL 0.3
> For force calling:
--min_mapq 10
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| --threads | Number of threads to use. | 16 |
| --batches | Batch of genome segmentation interval. | 10,000,000 |
| --sample | Sample name/id | NULL |
| --retain_work_dir | Enable to retain temporary folder and files. | False |
| --report_readid | Enable to report supporting read ids for each SV. | False |
| --max_split_parts | Maximum number of split segments a read may be aligned before it is ignored. All split segments are considered when using -1. (Recommand -1 when applying assembly-based alignment.) | 7 |
| --min_mapq | Minimum mapping quality value of alignment to be taken into account. | 20 |
| --min_read_len | Ignores reads that only report alignments with not longer than bp. | 500 |
| --merge_del_threshold | Maximum distance of deletion signals to be merged. | 0 |
| --merge_ins_threshold | Maximum distance of insertion signals to be merged. | 100 |
| --min_support | Minimum number of reads that support a SV to be reported. | 10 |
| --min_size | Minimum length of SV to be reported. | 30 |
| --max_size | Maximum size of SV to be reported. Full length SVs are reported when using -1. | 100000 |
| --genotype | Enable to generate genotypes. | False |
| --gt_round | Maximum round of iteration for alignments searching if perform genotyping. | 500 |
| -Ivcf | Optional given vcf file. Enable to perform force calling. | NULL |
| --max_cluster_bias_INS | Maximum distance to cluster read together for insertion. | 100 |
| --diff_ratio_merging_INS | Do not merge breakpoints with basepair identity more than the ratio of default for insertion. | 0.3 |
| --max_cluster_bias_DEL | Maximum distance to cluster read together for deletion. | 200 |
| --diff_ratio_merging_DEL | Do not merge breakpoints with basepair identity more than the ratio of default for deletion. | 0.5 |
| --max_cluster_bias_INV | Maximum distance to cluster read together for inversion. | 500 |
| --max_cluster_bias_DUP | Maximum distance to cluster read together for duplication. | 500 |
| --max_cluster_bias_TRA | Maximum distance to cluster read together for translocation. | 50 |
| --diff_ratio_filtering_TRA | Filter breakpoints with basepair identity less than the ratio of default for translocation. | 0.6 |
| --remain_reads_ratio | The ratio of reads remained in cluster to generate the breakpoint. Set lower to get more precise breakpoint when the alignment data have high quality but recommand over 0.5. | 1 |
| -include_bed | Optional given bed file. Only detect SVs in regions in the BED file. | NULL |
We provided the SV callsets of the HG002 human sample produced by cuteSV form three different long-read sequencing platforms (i.e. PacBio CLR, PacBio CCS, and ONT PromethION).
Please cite the manuscript of cuteSV before using these callsets.
cuteSV (v2.0.3):
1. Fix the error of missing min_size parameter.
2. Fix the missing signatures in duplication clustering.
cuteSV (v2.0.2):
1. Fix several errors in signature extraction.
2. Filter low quality reads in the statistics of reference reads.
3. Modify the rule of merging signatures on the same read.
4. Modify the cluster rule of insertions and deletions in force calling.
cuteSV (v2.0.1):
1. Fix an error in handling strand in force calling.
2. Speed up the genotype module of discovery calling. The comparison results on various datasets are as follows.
| | cuteSV | cuteSV2 |
| |(previous)| (latest) |
| CCS | 900.37s | 261.77s |
| CLR | 3620.00s | 2644.94s |
| ONT | 2893.08s | 1264.26s |
cuteSV (v2.0.0):
1. Upgrate force calling module.
2. Add --remain_reads_ratio parameter in order to generate highly accurate record by discarding a few signatures.
3. Fix several bugs in inversion and translocation calling.
4. Remove the redundant operations in the signature extraction and accelerate the whole analysis.
5. Streamline the translocation output when performing force-calling.
6. Modify the signature matching rule.
7. Modify the sequence of the inserted allele.
cuteSV (v1.0.13):
1. Modify the breakpoints of alternative allele and reference allele.
2. Fix an initialization error that will reproduce wrong diploid-assembly-based SV call.
cuteSV (v1.0.12):
1. Add Allele frequency (AF) info in the outputs.
2. Fix an index error when force calling BND variants.
3. Modify the parameter of --max_size and enable to report full length of SVs.
cuteSV (v1.0.11):
1. Add a script for post-processing typically cuteSV callsets from assembly-based alignments to generate the diploid-assembly-based SV calls.
2. Give a wiki page for helping uses to achieve assembly-based SV calling.
3. Improve acquirement of inserted sequence in a read whose primary alignment contains hardclips.
4. Improve the performance of force calling.
5. Enable cuteSV to output allele sequences when performing force calling with the VCF generated from other callers.
6. Fix bugs to avoid the error raised by abnormal SV type.
7. Update the sort commands used in cuteSV.
8. Update the parameter of --max_split_parts.
cuteSV (v1.0.10):
1. Fix a bug leading to calculate wrong TRA positions.
2. Add a file format conversion script that enable to transfer the vcf file to bedpe file.
3. Involve several clustering-and-refinement strategies in force calling function.
4. Assessed the performance of force calling with Giab HG002 sample datasets (including CLR, CCS, and ONT platforms).
cuteSV (v1.0.9):
1. Change 0-based pos into 1-based pos in DUP in order to support bcftools conversion.
2. Correct REF and ALT fields. Adjust END value of INS to make it equal to the value of POS.
3. Improve the description of errors.
4. Add usegalaxy.eu badge.
5. Remove CHR2 and the corresponding END position on the BND call.
6. Skip generating empty signature file and rewrite the job schedule.
7. Add force calling function and enable cuteSV to perform population-based SV calling.
8. Fix several minor bugs.
cuteSV (v1.0.8):
1. Rewirte the function of ins/del signatures clustering.
2. Update the recommandation parameters for different sequencing datasets.
3. Replace <DEL>/<INS> with its variant allele sequence, which needs the reference genome sequence as input.
4. Fix several bugs.
cuteSV (v1.0.7):
1. Add read name list for each SV call.
2. Fix several descriptions in VCF header field.
cuteSV (v1.0.6):
1.Improvement of genotyping by calculation of likelihood.
2.Add variant quality value, phred-scaled genotype likelihood and genotype quality in order to filter false positive SV or quality control.
3.Add --gt_round parameter to control the number of read scans.
4.Add variant strand of DEL/DUP/INV.
5.Fix several bugs.
cuteSV (v1.0.5):
1.Add new options for specificly setting the threshold of deletion/insertion signals merging in the same read. The default parameters are 0 bp for deletion and 100 bp for insertion.
2.Remove parameter --merge_threshold.
3.Fix bugs in inversion and translocation calling.
4.Add new option for specificly setting the maximum size of SV to be discovered. The default value is 100,000 bp.
cuteSV (v1.0.4):
1.Add a new option for specificly setting the threshold of SV signals merging in the same read. The default parameter is 500 bp. You can reduce it for high-quality sequencing datasets like PacBio HiFi (CCS).
2.Make the genotyping function optional.
3.Enable users to set the threshold of SV allele frequency of homozygous/heterozygous.
4.Update the description of recommendation parameters in processing ONT data.
cuteSV (v1.0.3):
1.Refine the genotyping model.
2.Adjust the threshold value of heterozygosis alleles.
cuteSV (v1.0.2):
1.Improve the genotyping performance and enable it to be default option.
2.Make the description of parameters better.
3.Modify the header description of vcf file.
4.Add two new indicators, i.e., BREAKPOINT_STD and SVLEN_STD, to further characterise deletion and insertion.
5.Remove a few redundant functions which will reduce code readability.
Jiang T et al. Long-read-based human genomic structural variation detection with cuteSV. Genome Biol 21, 189 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-020-02107-y
Cao S et al. Re-genotyping structural variants through an accurate force-calling method. bioRxiv 2022.08.29.505534; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.29.505534
For advising, bug reporting and requiring help, please post on Github Issue or contact tjiang@hit.edu.cn.