(This is an 8-bit version, please switch to the corresponding branch for the 32-bit version.)
CDBUS is a protocol for Asynchronous Serial Communication,
it has a 3-byte header: [src_addr, dst_addr, data_len], then user data, and finally 2 bytes of CRC. (Same as MODBUS CRC.)
It's suitable for one-to-one communication, e.g. UART or RS-232.
In this case, the address for each side are usually carefully selected and fixed,
e.g: [0x55, 0xaa, data_len, ...], and the backward is: [0xaa, 0x55, data_len, ...]. (data_len ≤ 255.)
The CDBUS protocol is more valuable for bus communication, e.g. RS-485, M-LVDS or Single Line UART. In this case, it supports:
- It introduces an arbitration mechanism that automatically avoids conflicts like the CAN bus.
- Support dual baud rate, provide high speed communication, the baud rate in the data phase is up to:
sys_freq÷ 3. (e.g. 50 Mbps for 150 MHzsys_freq.) - Supports unicast, multicast and broadcast.
- The maximum user data size is 253 bytes.
- Hardware packing, unpacking, verification and filtering, save your time and CPU usage.
- Backward compatible with traditional RS-485 hardware (The arbitration function still works).
The protocol timing example, include only one user data byte:
(You can set the length of time to enter idle and wait to send.)
Tips:
- When a high-priority node needs to send unimportant data, you can dynamically increase the send wait time (TX_PERMIT_LEN).
Arbitration example:
In CDBUS-A mode, if the low-speed part takes a lot of time, it will be a communication efficiency bottleneck.
In this case, single-rate peer-to-peer bus communication can be implemented by CDBUS-BS mode:
- The TX_PERMIT_LEN parameter is configured differently for different nodes, and the difference needs to be large enough to avoid conflicts.
- If any node has pending tx frame before TX-permit point, then start send at the TX-permit point.
- Or wait until the idle time exceeds MAX_IDLE_LEN, then send a break character to bring the bus out of idle state.
The CDBUS-BS mode is suitable for high-speed applications with few nodes, and it is also suitable for software implementation.
| Register Name | Addr | Access | Default | Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VERSION | 0x00 | RD | 0x0d | Hardware version | |
| SETTING | 0x02 | RD/WR | 0x10 | Configs | |
| IDLE_WAIT_LEN | 0x04 | RD/WR | 0x0a | Waiting time to enter idle | Bit 7~0 |
| TX_PERMIT_LEN_L | 0x05 | RD/WR | 0x14 | Waiting time to allows sending | Bit 7~0 |
| TX_PERMIT_LEN_H | 0x06 | RD/WR | 0x00 | Bit 9~8 | |
| MAX_IDLE_LEN_L | 0x07 | RD/WR | 0xc8 | Max idle waiting time in BS mode | Bit 7~0 |
| MAX_IDLE_LEN_H | 0x08 | RD/WR | 0x00 | Bit 9~8 | |
| TX_PRE_LEN | 0x09 | RD/WR | 0x01 | How long to active TX_EN before TX | Bit 1~0, not used in arbitration mode |
| FILTER | 0x0b | RD/WR | 0xff | Local address | |
| DIV_LS_L | 0x0c | RD/WR | 0x5a | Low-speed rate setting | Bit 7~0 |
| DIV_LS_H | 0x0d | RD/WR | 0x01 | Bit 15~8 | |
| DIV_HS_L | 0x0e | RD/WR | 0x5a | High-speed rate setting | If not use dual rate, set the same value as DIV_LS |
| DIV_HS_H | 0x0f | RD/WR | 0x01 | ||
| INT_FLAG | 0x10 | RD | n/a | Status | |
| INT_MASK | 0x11 | RD/WR | 0x00 | Interrupt mask | |
| RX | 0x14 | RD | n/a | Read RX page | |
| TX | 0x15 | WR | n/a | Write TX page | |
| RX_CTRL | 0x16 | WR | n/a | RX control | |
| TX_CTRL | 0x17 | WR | n/a | TX control | |
| RX_ADDR | 0x18 | RD/WR | 0x00 | RX page read pointer | Rarely used |
| RX_PAGE_FLAG | 0x19 | RD | n/a | RX page flag | Mainly used for debugging |
| FILTER1 | 0x1a | RD/WR | 0xff | Multicast filter1 | |
| FILTER2 | 0x1b | RD/WR | 0xff | Multicast filter2 |
SETTING:
| FIELD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| [0] | Enable push-pull output for tx and tx_en pin |
| [1] | Invert tx output |
| [2] | CRC maintained by user |
| [3] | Save broken frame |
| [4] | Enable arbitration |
| [5] | Break Sync mode |
| [6] | Full duplex mode |
| [4] | [5] | [6] | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | CDBUS-A mode (default) |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | CDBUS-BS mode |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | Full-duplex mode |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | Traditional half-duplex mode |
FILTERS:
Match from top to bottom:
| SRC_ADDR | DST_ADDR | FILTER | FILTERn | Receive or drop | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| not care | not care | 255 | not care | Receive | Promiscuous mode |
| = FILTER | not care | != 255 | not care | Drop | Avoid loopback |
| != FILTER | 255 | not care | not care | Receive | Broadcast |
| != FILTER | != 255 | not care | any = DST_ADDR | Receive | Multicast |
| != FILTER | != 255 | = DST_ADDR | not care | Receive | Unicast |
| not care | != 255 | != DST_ADDR | all != DST_ADDR | Drop |
It is recommended to reserve the address from 0xe0 to 0xfe as the multicast address.
The default value 0xff of FILTERn means not enabled.
DIV_xx_x:
Baud rate divider value: DIV_xx[15:0] = sys_freq ÷ baud_rate − 1
The minimum value is 2.
INT_FLAG:
| FIELD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| [0] | 1: Bus in IDLE mode |
| [1] | 1: RX page ready for read |
| [2] | 1: Break character received |
| [3] | 1: RX lost: no empty page for RX |
| [4] | 1: RX error: frame broken |
| [5] | 1: TX page released by hardware |
| [6] | 1: TX collision detected |
| [7] | 1: TX error: tx is 0, but rx is 1 |
INT_MASK:
Output of irq = ((INT_FLAG & INT_MASK) != 0).
RX_CTRL:
| FIELD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| [0] | Reset RX page read pointer |
| [1] | Switch RX page |
| [2] | Clear RX lost flag |
| [3] | Clear RX error flag |
| [4] | Reset RX block |
| [5] | Clear RX break flag |
TX_CTRL:
| FIELD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| [0] | Reset TX page write pointer |
| [1] | Switch TX page |
| [2] | Clear TX collision flag |
| [3] | Clear TX error flag |
| [4] | Abort TX |
| [5] | Send break character |
RX_PAGE_FLAG:
Value zero indicate the frame in current RX page is correct;
Non-zero indicate the pointer of last received byte of the disturbed frame, include CRC.
parameter DIV_LS = 346, // default: 115200 bps for 40MHz clk
parameter DIV_HS = 346
input clk, // core clock
input reset_n, // asynch active low reset
input chip_select, // reduce ram_rx power consumption
output irq, // interrupt output
// avalon-mm slave interface, read and write without latency
// support burst read and write (normally for REG_TX and REG_RX)
input [4:0] csr_address,
input csr_read,
output [7:0] csr_readdata,
input csr_write,
input [7:0] csr_writedata,
// connect to external PHY chip, e.g. MAX3485
input rx,
output tx,
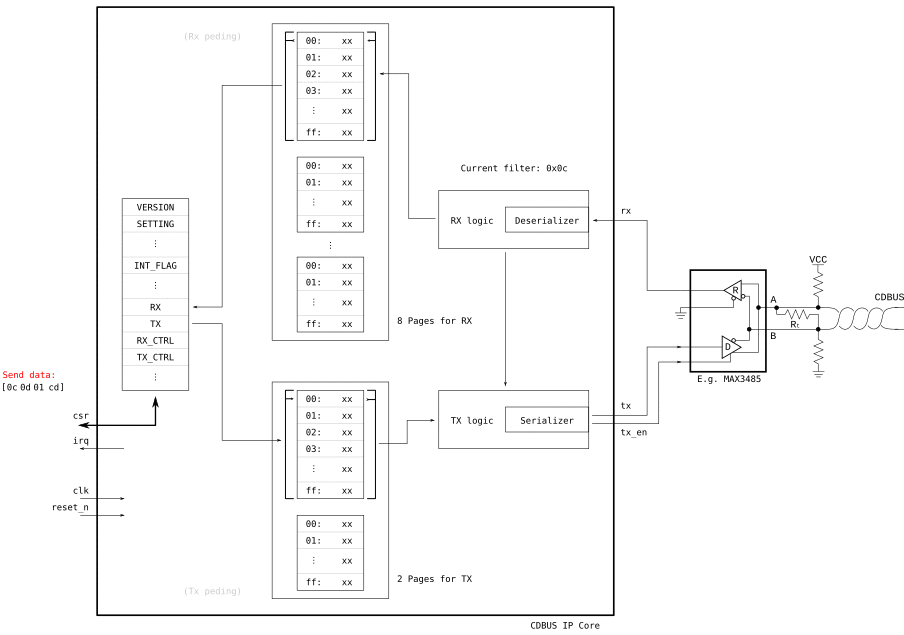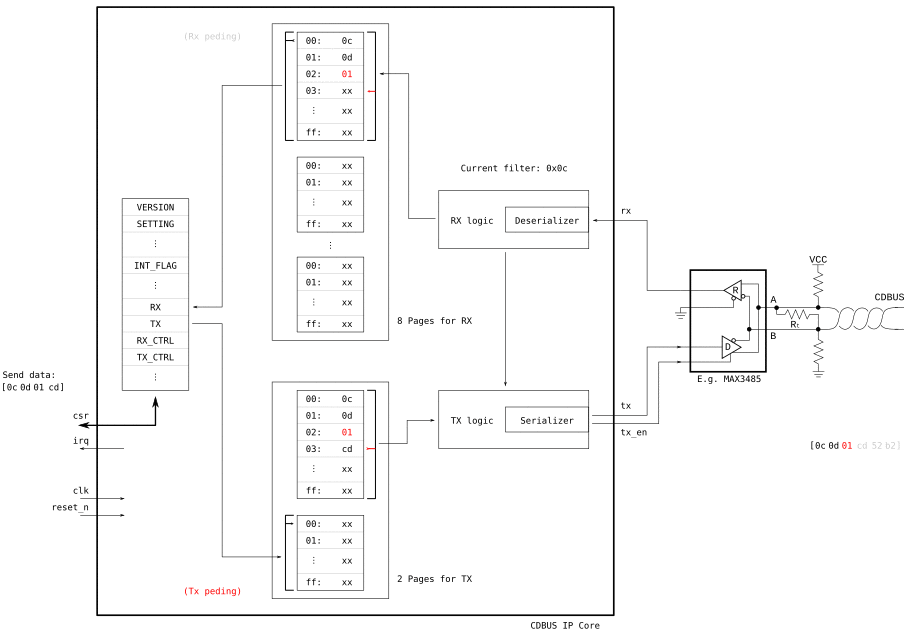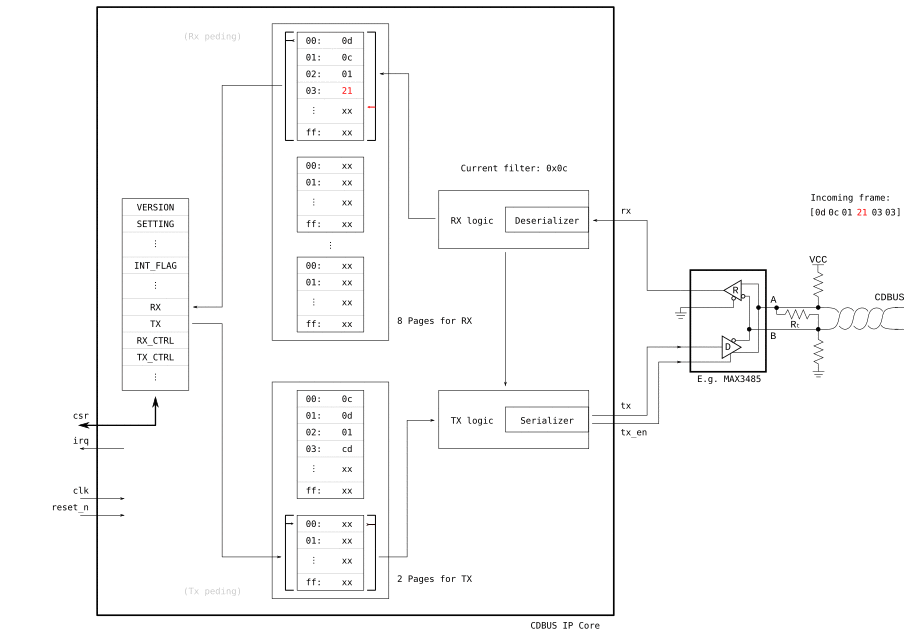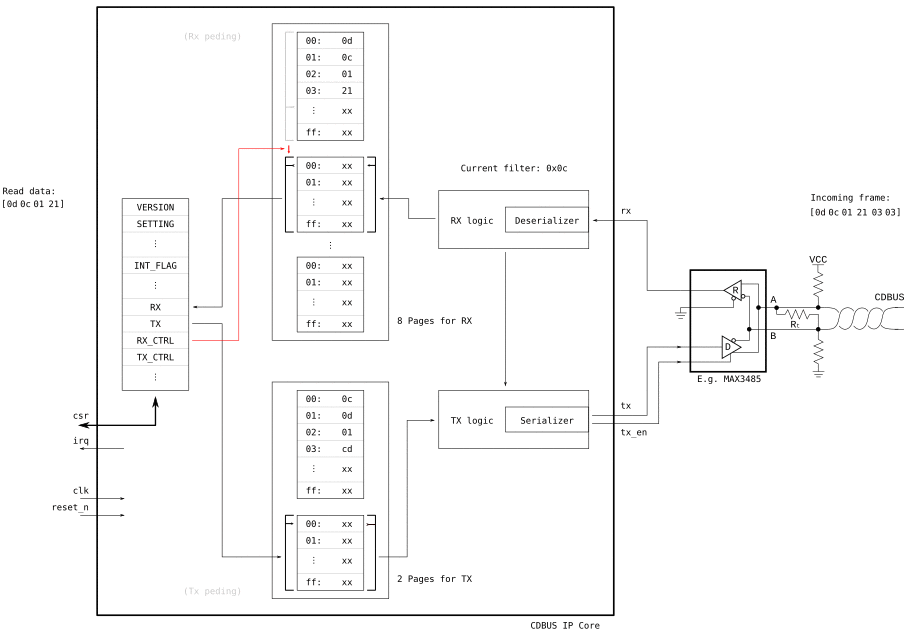
output tx_en # Configuration
write(REG_SETTING, [0x11]) # Enable push-pull output
# TX
write(REG_TX, [0x0c, 0x0d, 0x01, 0xcd]) # Write frame without CRC
while (read(REG_INT_FLAG) & 0x20) == 0: # Make sure we can successfully switch to the next page
pass
write(REG_TX_CTRL, [0x03]) # Trigger send by switching TX page
# RX
while (read(REG_INT_FLAG) & 0x02) == 0: # Wait for RX page ready
pass
header = read(REG_RX, len=3)
data = read(REG_RX, len=header[2])
write(REG_RX_CTRL, [0x03]) # Finish read by switching RX pageInstall iverilog (>= v10) and cocotb, goto tests/ folder, run ./test_all.sh or ./test_all.sh test_xxx.py.
(You can checkout the waveform cdbus.vcd by GTKWave.)
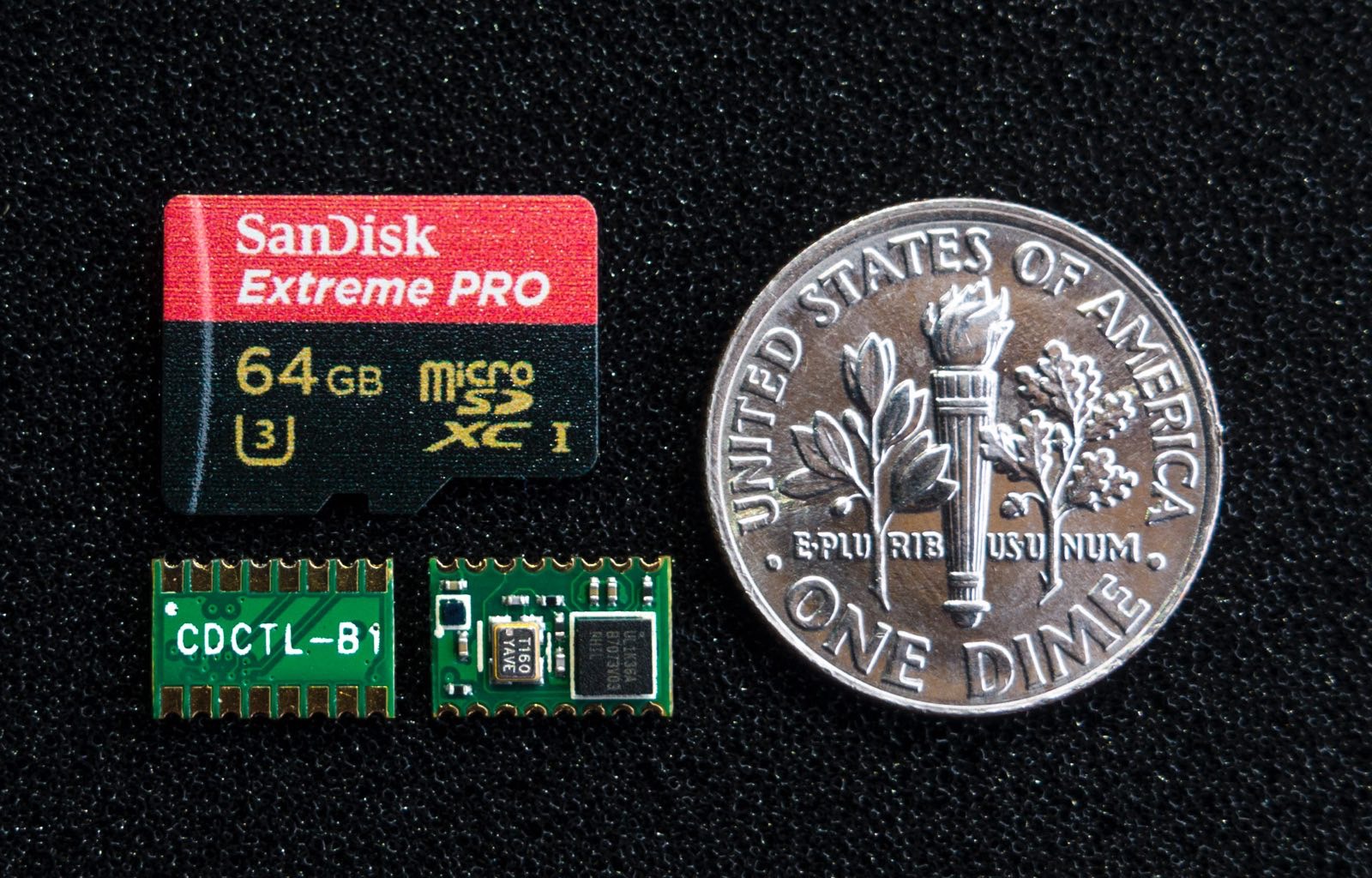
The CDCTL controller family uses the CDBUS IP Core, which provide SPI, I2C and PCIe peripheral interfaces.
E.g. The tiny CDCTL-Bx module support SPI and I2C interfaces:
(This module is completely open source, including the source code and gerber files, in the example/ directory.)
More relevant projects that may interest you:
- CDBUS GUI: https://github.com/dukelec/cdbus_gui
- CDNET: https://github.com/dukelec/cdnet
This Source Code Form is subject to the terms of the Mozilla
Public License, v. 2.0. If a copy of the MPL was not distributed
with this file, You can obtain one at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/.
Notice: The scope granted to MPL excludes the ASIC industry.
The CDBUS protocol is royalty-free for everyone except chip manufacturers.
Copyright (c) 2017 DUKELEC, All rights reserved.