This project is a 3 DOF robot arm constructed from acrylic and powered by servos. The arm is designed to be small and portable, making it easy to take with you wherever you go. In this project both forward and inverse kinematics were constructed to model the robot motion towards the desired postions.
MeArm.mp4
To install and set up the MeArm, you will need the following:
- A computer with Python and the Peter Corke robotics toolbox library installed
- An Arduino board and three servos
- The MeArm pocket size manipulator hardware
To install the necessary software, follow these steps:
- Install Python on your computer (if it is not already installed). You can download Python from the official website: https://www.python.org/downloads/
- ROS Neotic.
- Install Arduino IDE.
- Install ROSserial package.
sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-rosserial-arduino
sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-rosseria- Run the roscore command:
roscore - In the arduino libraries folder run the ROS node:
rosrun rosserial arduino make libraries.py .
- Run the roscore command:
- Install: Peter Corke robotics toolbox library, Spatial Maths for Python, tkinter library for GUI. You can do this by running the following commands in your terminal:
pip install robotics-toolbox-pythonpip install spatialmath-pythonpip install tk.
- Clone the repository:
git clone git@github.com:youssiefanas/MeArm.git
-
Copy the meArm_py folder to your ROS workspace (ex: catkin_ws).
-
Then make go to your ws directory and run
catkin_makein you terminal. -
Connect the Arduino board to your computer using a USB cable.
-
Upload the Arduino sketch (included in this repository) to the board.
-
Run :
roscorerosrun meArm_py mearm_gui.pyrosrun rosserial_arduino serial_node.py /dev/ttyACM0
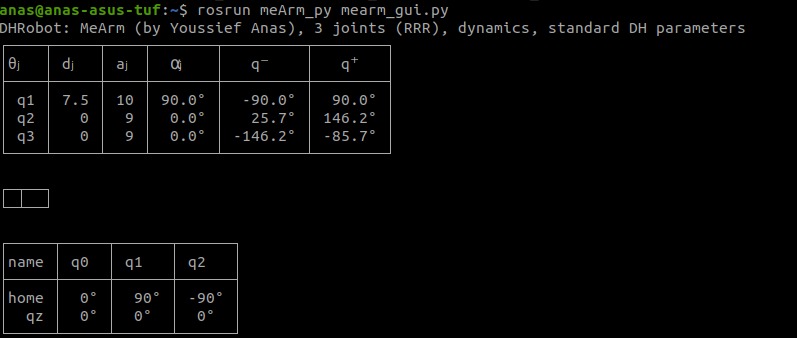
The Robot configuration was constructed using peter corke robotics toolbox.
The D-H parameters were solved according to the configuration.
The Robotics toolbox allow you to solve forward kinematics using fkine() and inverse kinematics using ikine_LM() function.
The workspace of the robot identified using the matlab with the same library.

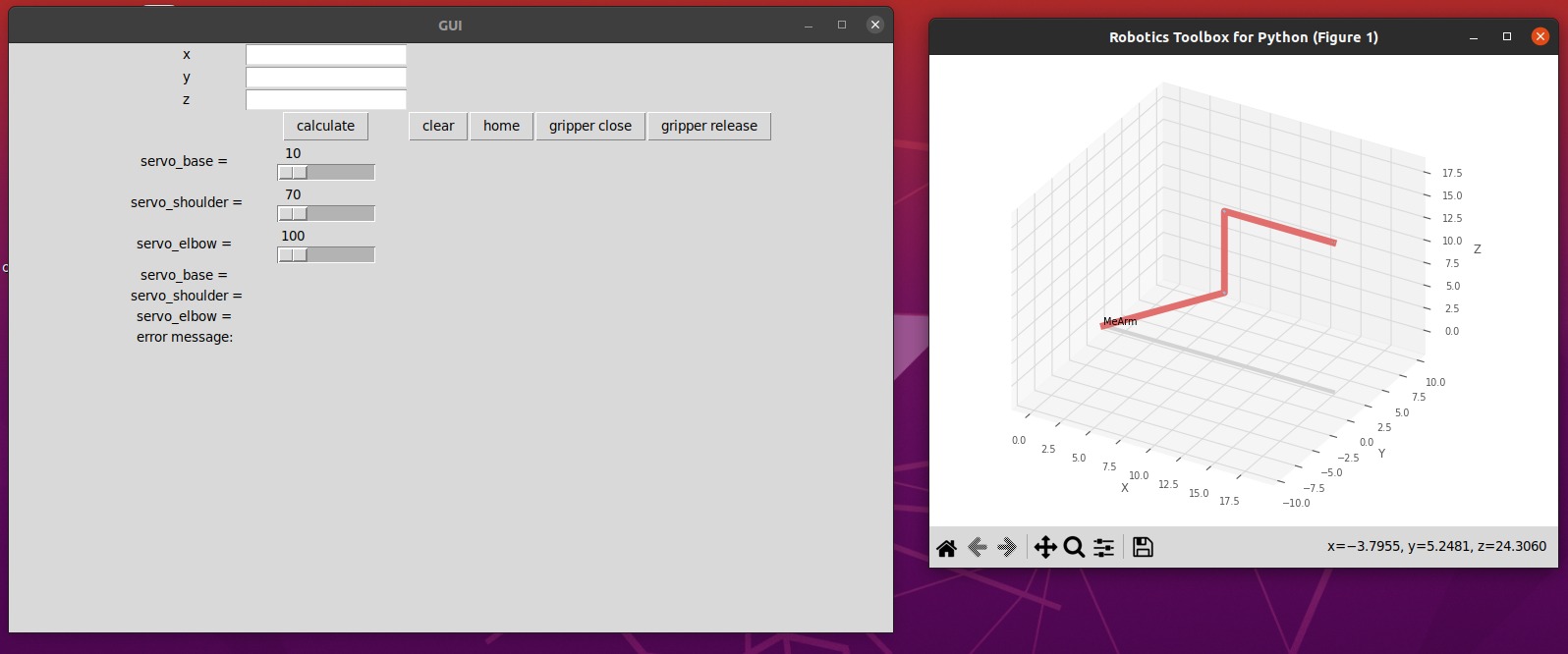
The GUI for this project allows you to control the MeArm and make it reach a certain position (x, y, z) coordinates or by moving each joint independently. It also includes buttons to move the MeArm to its home position and control the gripper.
To use the GUI, follow these steps:
- The GUI will appear when you run the ros node.
- Input x, y, z coordinates in the input boxes and press the "Calculate" button to move the MeArm to that position.
- Use the sliders to move each joint independently.
- Press the "Home" button to move the MeArm to its home position.
- Press the "Gripper release" and "Gripper Close" buttons to control the gripper.
In addition to the features described above, this project also includes the following:
- Solving the forward and inverse kinematics,
- Simulate the configuration according to the given position.
- The ability to send servo readings to the Arduino to control the physical MeArm.
- The output display of joint angles and servo readings in the GUI.
- The MeArm design is opensource, so anyone can access it easly.
There are many possibilities for future improvements to this project. Some ideas might include:
- Improving the accuracy of the inverse kinematics calculations.
- Adding more complex gripper designs.
- Adding a depth camera sensors to the end effector to spot the objects and its 3D position.
- Add motion on trajectory.
- Build more rigid body.
- Make better Servo calibration, as the position in real life is not matching the desired.
This project would not have been possible without the following resources:
- The Peter Corke robotics toolbox library: https://github.com/petercorke/robotics-toolbox
- Agustian, I., Daratha, N., Faurina, R., Suandi, A., & Sulistyaningsih, S. (2021). Robot manipulator control with inverse kinematics PD-pseudoinverse jacobian and forward Kinematics Denavit Hartenberg. Jurnal Elektronika Dan Telekomunikasi, 21(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.14203/jet.v21.8-18
- https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:360108/files