The Goldibox is an insulated box that maintains temperature using a thermoelectric device and a controller. Originally conceived to incubate biological organisms that thrive best within a particular maximum/minimum temperature range, it can both heat and cool to avoid extremes, but still allow variability within a habitable "Goldilocks zone": not too hot, not too cold, but just right.
The Goldibox's smart controller exposes a remote, network-connected graphical interface for setting temperatures, checking current state, and viewing history through time series graphs. Anyone may modify the open-source control to add new features.
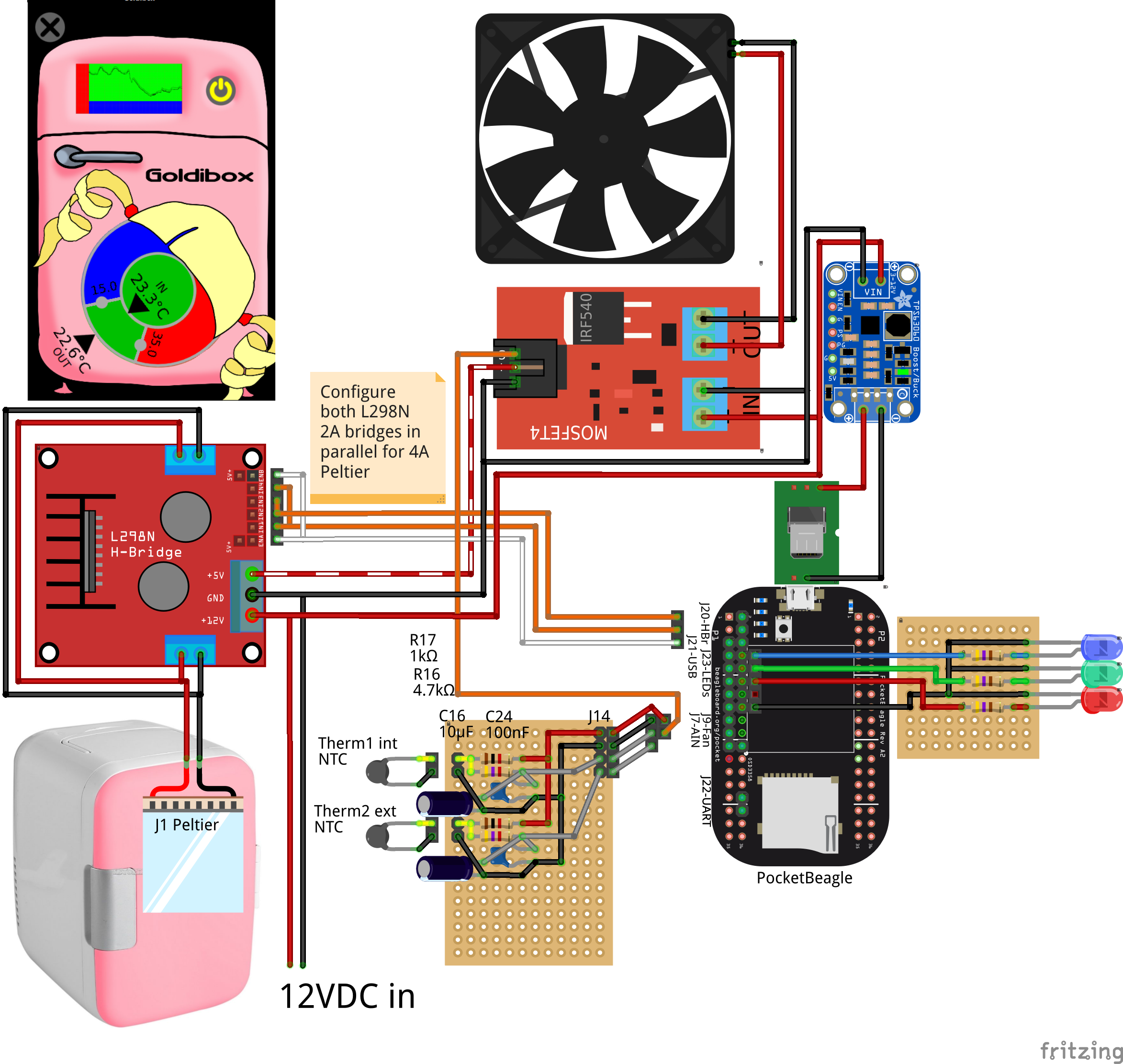
The Goldibox is built from a portable fridge with a Peltier junction that can be switched either to cool or to heat by reversing the input voltage.
The Goldibox controller, a tiny PocketBeagle computer
that runs Debian, fits in the cramped space next to the Peltier
junction fan and heat sink. It senses internal and external
temperatures through a pair of thermistors attachd to its analog
inputs, and it switches the Peltier junction and fan through an
H-bridge and a MOSFET, respectively, connected through GPIO digital
output pins. See BOM.md for a list of hardware components, and
fritzing/goldibox.fzz for connecting them.
The Machinekit software runs the configuration in this
repository: some python user-space components in the bin/
directory, and HAL configuration in the hal/ directory. The
goldibox-control component decides whether to switch the Peltier
junction to cool, heat, or off, depending on the measured temperature
compared to the user's Goldilocks temperature settings. The
goldibox-logger component logs to a RRD database, from which time
series charts are generated.
The goldibox-control component exposes a remote UI, used by the
MachinekitClient software, which can be downloaded for Android from
the Google Play store, and for Linux, Mac OS X and Windows directly
from the QtQuickVCP project. The configuration in the qml
directory defines the simple user interface with thermostat controls
for the "too hot" and "too cold" zones, readouts for internal and
external temperature, a power control to enable and disable the
Goldibox, and a time series chart showing temperatures over the last
day.
Follow the instructions at machinekit.io to download and install a mini-SD card image with Machinekit.
Log into the BeagleBone, clone this repository, and cd into the
repository directory.
On the PocketBeagle, start the Goldibox control from the command line (load the overlay file for non-system installs):
# Install minimal apache and other config
sudo make install MININSTALL=1
# Start control
bin/goldibox -o
The Goldibox should now be ready for control. Start the MachinekitClient and open the Goldibox app.
Alternatively, run a Goldibox simulated control and GUI in a Docker container from the command line:
# Start the container
docker/qqvcp.sh
# Install minimal apache and other config
sudo make install MININSTALL=1
# Start control
bin/goldibox &
# Start GUI
MachinekitClient &
The Goldibox may be installed to the system so that it is run at every boot:
sudo make install
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable goldibox
sudo systemctl start goldibox
The apache2 package must be installed and the web server running for
the time-series chart to work.
See the jumble of notes in NOTES.md