Innopolis VTOL dynamics simulator is a set of ROS packages suggested full simulation for UAV based on PX4.
Typical PX4 simulations ways are SITL and HITL:
- SITL (software in the loop) allows you to run simulation and flight stack fully on your computer, it doesn't cover hardware related modules,
- HITL (hardware in the loop) allows to run flight stack on real device, but it still doesn't cover actuator and sensor related modules because autopilot works in special mode and uses special MAVLink HITL messages instead of real actuators and sensor drivers.
The key feature of this simulation is to run it in such way that the hardware knows nothing about simulation. This could be possible using uavcan. For users, expecialy those using the uavcan network for uav, it can be very usefull, because it covers more PX4 modules than standard SITL and HITL.
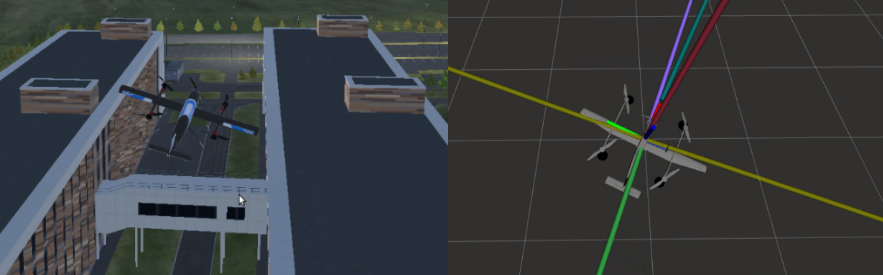
So, Inno VTOL dynamics simulation allows to run simulation in both SITL and uavcan HITL mode. It also allows to run InnopolisSimulator (left part of the first figure) and visualize forces and moments in RVIZ (right part of the first figure).
Innopolis VTOL dynamics simulator is designed to support several dynamics and both MAVLink SITL and UAVCAN HITL modes. As an example, beside inno_vtol dynamics flightgoggles_multicopter dynamics was integrated into simulator as well. You also may use different airframes based on your version of PX4-Autopilot.
At that moment following combination of dynamics and airframes are supported:
| № | dynamics | HITL airframe | SITL airframe (vehicle) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | inno_vtol | inno_standard_vtol (13070) | innopolis_vtol (1050) |
| 2 | flightgoggles_multicopter | iris (10016) | iris (10016) |
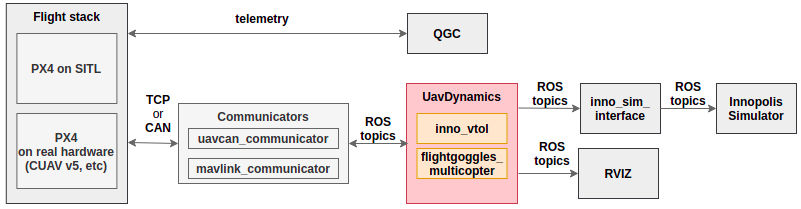
The simulator is divided into following main components:
UAV dynamicsis the main node that handles actuator commands from communicator, performs dynamics simulation and publishes vehicle and sensors states.Communicatoris the set of nodes which communicate withPX4 flight stackin HITL (via UAVCAN) and SITL (via MAVLink) modes.inno_sim_interfaceis a bridge for interaction withInno Simulatorthrough ROS.
The design of the simulator is shown below.
To communicate with the flight stack via communicator UAV dynamics node subscribes on following topics:
| № | UAVCAN->ROS topics | msg |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | /uav/actuators | sensor_msgs/Joy |
| 2 | /uav/actuators | std_msgs::Bool |
and publishes to following topics:
| № | ROS->UAVCAN topics | msg |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | /uav/static_temperature | uavcan_msgs/StaticTemperature |
| 2 | /uav/static_pressure | uavcan_msgs/StaticPressure |
| 3 | /uav/raw_air_data | uavcan_msgs/RawAirData |
| 4 | /uav/gps_position | uavcan_msgs/Fix |
| 5 | /uav/imu | sensor_msgs/Imu |
| 6 | /uav/mag | sensor_msgs/MagneticField |
| 7 | /uav/esc_status | uavcan_msgs/EscStatus |
| 8 | /uav/ice_status | uavcan_msgs/IceReciprocatingStatus |
| 9 | /uav/fuel_tank_status | uavcan_msgs/IceFuelTankStatus |
| 10 | /uav/battery_status | sensor_msgs/BatteryState |
Here topics 1-6 are necessary for any simulation. Last 4 topics are auxilliary and you may enable/disable them in sim_params.yaml config file. You may implement your own sensors in sensors.cpp file.
To work in pair with InnoSimulator as physics engine via inno_sim_interface it publishes and subscribes on following topics.
| № | topic | msg |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | /uav/actuators | sensor_msgs/Joy |
| 2 | /uav/gps_position | uavcan_msgs/Fix |
| 3 | /uav/attitude | geometry_msgs/QuaternionStamped |
First thing you need to do is to decide in which mode you are going to use the simulator.
Typically, you can run the simulator in:
- either HITL mode (using real hardware and UAVCAN sniffer) or SITL (by running px4 flight stack on the computer),
- and either with docker (the easiest way to start playing with the simulator), or by building and installing the simulator manually (might be preffered if you are going to contribute something).
Then follow the instruction below. The steps you need to take will depend on the selected mode.
This repository is the only necessary component to start work with the simulator.
Step 1. Firstly, you need to clone the repository with submodules.
git clone https://github.com/InnopolisAero/innopolis_vtol_dynamics.git --recursiveEvery time when you pull this repository, don't forget to update submodules:
git submodules update --init --recursiveStep 2. Then, you should either build/pull the docker image, or install and build everything manually.
-
With Docker. All work with docker is recommended to do via
./scripts/docker.shscript. For example, you can build it by typing./scripts/docker.sh buildor you can pull the image by typing./scripts/docker.sh pull. This script is simply configurate the correct image name and run all necessary auxilliary scripts. -
Without Docker. If you are going to build this repository and install all dependencies manually, please follow the instruction from Dockerfile or from build workflow.
Anyway, to start the simulator at least initially, you need to install PX4 Autopilot Firmware.
Docker image of this repository doesn't include PX4 Autopilot to make the work more flexible and image ligher.
- In HITL mode the PX4 Autopilot is necessary for uploading the firmware to the hardware.
- In SITL mode the PX4 Autopilot is required any time when you run the simulator.
Most probably, you need exactly the following version of PX4 Autopilot. It has 2 differences compared to the master branch:
- Firstly, it has the ability to disable board sensors. This feature is higly necessary for working in HITL mode.
- Secondly, it has
inno_vtolcustom airframe.
So, the only way when you can use the master or any other branch based on the original software, is SITL simulator with flight_goggles (MR) dynamics. It is based on default iris airframe.
Step 1. Installation
For installation use the official PX4 instruction, but the custom firmware version InnopolisAero/PX4-Autopilot (or the original one, if you are going to use the simuator in SITL for iris airframe only as mentioned above).
Step 2. Build
To build either in SITL or in TRUE HITL mode run:
cd PX4-Autopilot
git checkout px4_v1.12.1_inno_vtol_dynamics
git submodule update --init --recursive && make clean && make distclean
Then for SITL mode:
DONT_RUN=1 make px4_sitl gazebo_standard_vtolor
DONT_RUN=1 make px4_sitl gazebo_irisAnd for HITL mode for Cuav V5+ type line below. If you use another hardware, read the PX4 doc for details.
make px4_fmu-v5_default upload
If you want to use SITL, don't forget to add these lines to your .bashrc file, don't forget to change ~/PX4-Autopilot to your actual Firmware path
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash # (optional)
source ~/PX4-Autopilot/Tools/setup_gazebo.bash ~/PX4-Autopilot ~/PX4-Autopilot/build/px4_sitl_default
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:~/PX4-Autopilot
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=$ROS_PACKAGE_PATH:~/PX4-Autopilot/Tools/sitl_gazebo
InnoSimulator is a photorealistic simulator.
At that moment we use it for visualization purpose only.
To use it you need to download it from inno-robolab/InnoSimulator repository.
This step is higtly different for HITL and SITL modes.
1. SITL mode requires running PX4 flight stack on your PC.
Depending on which airframe you are going to use, you need to run px4.launch file with argument correponded to your airframe.
If you are going to use the simulator for inno_vtol dynamics, you may run:
roslaunch px4 px4.launch vehicle:=innopolis_vtol
If you are going to use the simulator for flight_goggles dynamics, you may run:
roslaunch px4 px4.launch vehicle:=iris
For extended documentation about PX4 SITL flight stack, please check the official PX4 instruction.
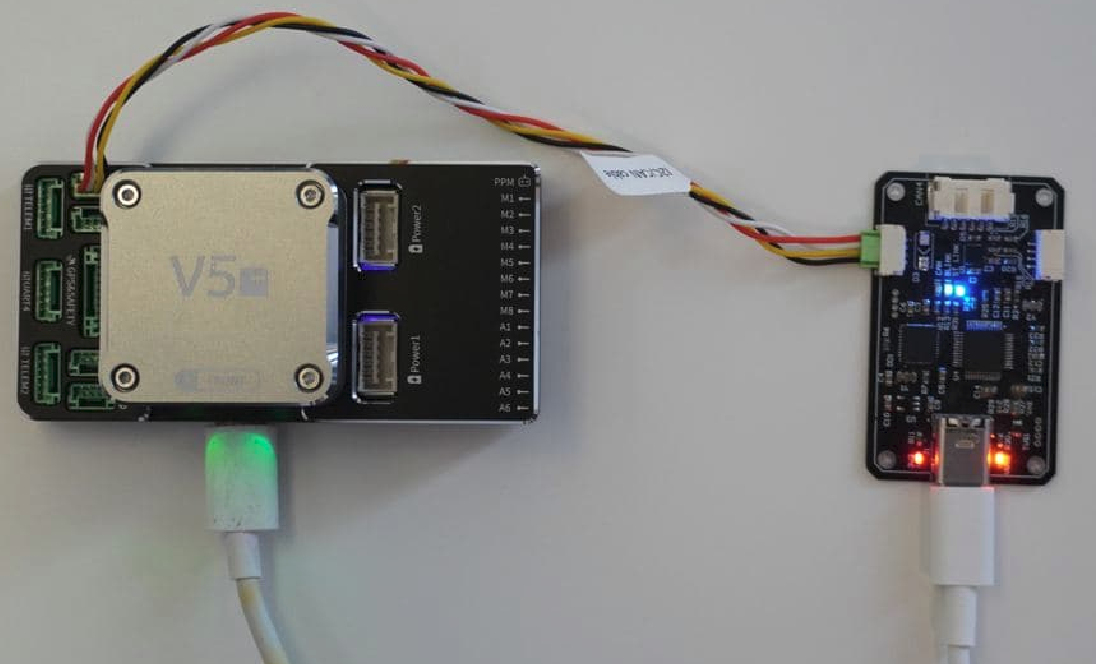
2. HITL mode requires physical connection of your autopilot and PC via CAN/UART sniffer.
The example of connection shown on the picture below.
Typically we use cuav v5+ and inno-programmer-sniffer, but it might be anything else.
It is recommended to play with the simulator with one of 2 scripts depending on your mode:
- use scripts/docker.sh if you build the docker image
- use scripts/run_sim.sh if you build and install all necessary dependencies manually.
The usage of these scripts are the same. Moremore, docker.sh actually internally call the run_sim.sh script. To get extended info about these scripts try them with help command, for example: ./scripts/docker.sh help.
Both HITL and SITL modes requires only to run a single command in the termianl. Below your can see an example how to run HITL mode for inno_vtol dynamics and SITL simulator for flight goggles dynamics.
./scripts/docker.sh hitl_inno_vtol
./scripts/run_sim.sh sitl_flight_goggles
If you are using SITL mode, don't forget to run PX4 SITL flight stack according to 3.1. Autopilot setup.
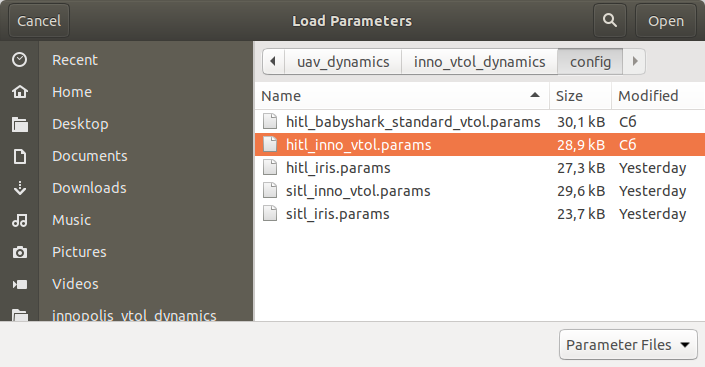
This step is the same for all modes. Each vehicle especially need to update his default parameters. Especially for HITL it is necessary to disable board sensors and disable few pre-flight checks.
- Run QGC and load correposponded params into your vehicle,
- Restart your vehicle and QGC,
- Note: if your QGC is turned off right after the loading of parameters, you need to run QGC again and perform device rebooting manually,
- Note: sometimes from the first attempt params are not loaded correctly, so it's better to load them twice. Usually it happens in HITL mode.
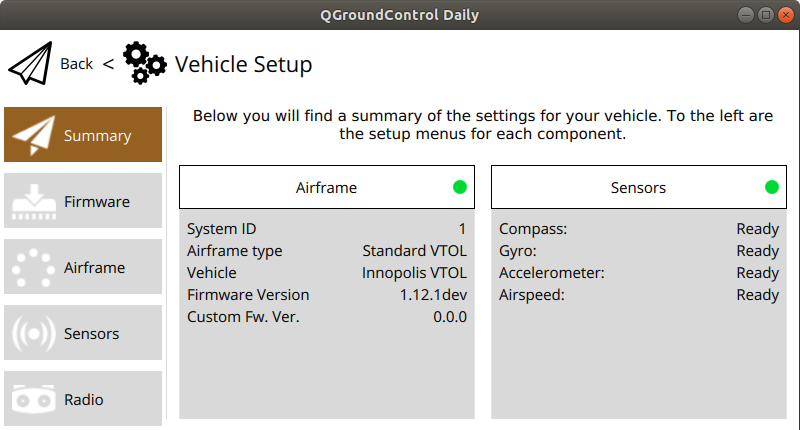
After restarting check correspondences of your airframe and that vehicle is Ready To Fly
If you set parameter run_inno_sim_bridge:=true or leave it by default, you will only need to type something like that:
~/software/InnoSimulator-Linux64-2021.1.3/InnoSimulator.x86_64Then choose a drone and press Launch button.
Check the video below.
- flightgoggles_uav_dynamics (multicopter) - read their paper
- PX4 mavlink communicator
- sitl_gazebo
- innopolis_vtol_indi - dynamics written in Octave
- InnoSimulator - photorealistic simulator
- inno_sim_interface - bridge between dynamics and photorealistic simulator
We use GoogleTest. To install this you should follow official instruction or this sequence:
git clone https://github.com/google/googletest.git -b release-1.10.0
cd googletest # Main directory of the cloned repository.
mkdir build # Create a directory to hold the build output.
cd build
cmake .. -DBUILD_GMOCK=OFF # Generate build scripts for GoogleTest without GoogleMock.
make
sudo make install # Install in /usr/local/ by default
To run test, type (and read here and here if you don't configured and launched accordingly gtest from ros yet):
roscd innopolis_vtol_dynamics
./catkin_test