The target is to implement a 2 dimensional particle filter in C++.
Dynamic visualization of the results of the particle filter (localization) with the simulator here
A robot has been transported to a new location. The data input informations are :
- a map of this location,
- a (noisy) GPS estimate of its initial location,
- a lots of (noisy) sensor and control data.
The particle filter will be given a map and some initial localization information (analogous to what a GPS would provide). At each time step the filter will also get observation and control data.
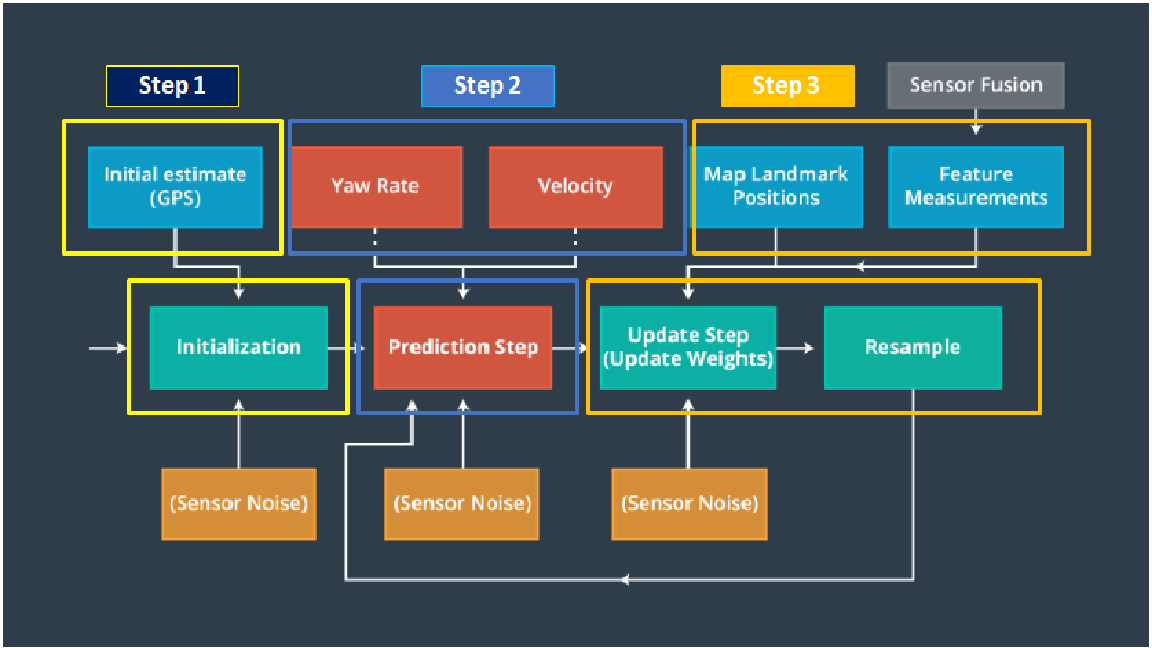
This picture presents the concept of a particle filter :
- Set the number of particles
- Initialization of all particles to first position (based on estimates x,y,theta, and their uncertainties from GPS)
- Initialization of all weights to 1
- Addition of random gaussian noise to each particle
- Use of the CTRV (Constant Turn Rate and Velocity Magnitude Model) for the prediction
- Noise addition fo all the particles in X,Y and Theta
Data association between :
- the observation measurement from the Lidar
- the predicted measurement between every specific particle and all the landmarks observed from the sensor
- Transformation of each observations from vehicle local coordinates to map coordinates
- Measurement prediction for all landmarks within sensor range for each particle
- Association of the predicted landmark for every transformed observation (Call the intermediate Step)
- Update the weights of each particle with the multivariate gaussian probability density
- Normalize the weights of all particles since resampling using probilistic approach
- Resampling with the resampling probability with the weight importance (use of the wheel strategy: every particle with his respective weight has a part of the wheel)
This project involves the Term 2 Simulator which can be downloaded here
This repository includes two files that can be used to set up and install uWebSocketIO for either Linux or Mac systems. For windows you can use either Docker, VMware, or even Windows 10 Bash on Ubuntu to install uWebSocketIO.
Once the install for uWebSocketIO is complete, the main program can be built and ran by doing the following from the project top directory.
- mkdir build
- cd build
- cmake ..
- make
- ./particle_filter
Alternatively some scripts have been included to streamline this process, these can be leveraged by executing the following in the top directory of the project:
- ./clean.sh
- ./build.sh
- ./run.sh
Tips for setting up your environment can be found here
The program main.cpp has already been filled out. Here is the main protocol that main.cpp uses for uWebSocketIO in communicating with the simulator.
// sense noisy position data from the simulator
["sense_x"]
["sense_y"]
["sense_theta"]
// get the previous velocity and yaw rate to predict the particle's transitioned state
["previous_velocity"]
["previous_yawrate"]
// receive noisy observation data from the simulator, in a respective list of x/y values
["sense_observations_x"]
["sense_observations_y"]
// best particle values used for calculating the error evaluation
["best_particle_x"]
["best_particle_y"]
["best_particle_theta"]
//Optional message data used for debugging particle's sensing and associations // for respective (x,y) sensed positions ID label
["best_particle_associations"]
// for respective (x,y) sensed positions
["best_particle_sense_x"] <= list of sensed x positions
["best_particle_sense_y"] <= list of sensed y positions
The directory structure of this repository is as follows:
root
| build.sh
| clean.sh
| CMakeLists.txt
| README.md
| run.sh
|
|___data
| |
| | map_data.txt
|
|
|___src
| helper_functions.h
| main.cpp
| map.h
| particle_filter.cpp
| particle_filter.h
The file contains the scaffolding of a ParticleFilter class and some associated methods.
The file src/main.cpp contains the code that will actually be running your particle filter and calling the associated methods.
The inputs to the particle filter are present in the data directory.
map_data.txt includes the position of landmarks (in meters) on an arbitrary Cartesian coordinate system.
Each row has three columns:
- x position
- y position
- landmark id
2 importants points for the evaluation :
-
Accuracy : the particle filter should localize vehicle position and yaw to within the values specified in the parameters
max_translation_errorandmax_yaw_errorinsrc/main.cpp. -
Performance : execution time of the particle filter max : 100 seconds.