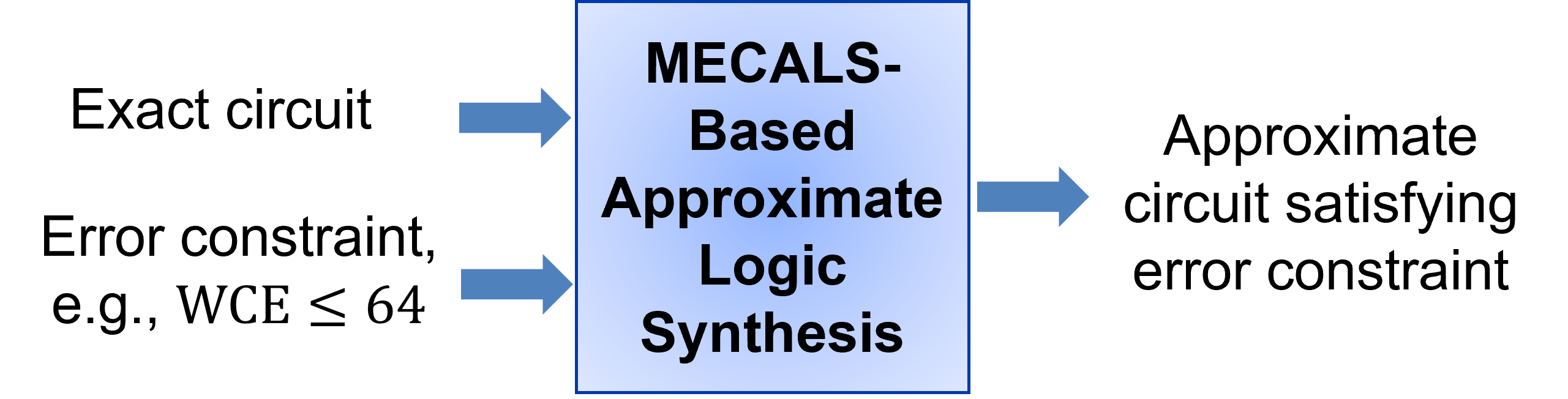
MECALS: maximum error checking technique for approximate logic synthesis.
This tool synthesizes approximate circuits under the maximum error constraint, such as worst-case error (WCE) and maximum square error (MaxSE) constraint. Its diagram is as follows.
-
Reference environment, Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with the following tools and libraries:
-
gcc 10.3.0 & g++ 10.3.0
You can install these tools with the following command:
sudo apt install gcc-10 sudo apt install g++-10
You also need to check whether the default versions of gcc and g++ are 10.3.0:
gcc --version g++ --version
If the default versions of gcc and g++ are not 10.3.0, please change them to 10.3.0.
-
cmake 3.16.3
You can install the tool using the following command:
sudo apt install cmake
-
You can install the tool using the following command:
sudo apt install yosys
-
You need to manually compile abc and add the path where the executable program abc locates to the environment variable.
-
libboost 1.75.0
You can download libboost 1.75.0, manually compile it, and then install it.
-
libreadline 8.0-4
You can install the library using the following command
sudo apt install libreadline-dev
-
-
Alternatively, we package a docker image containing the above dependencies:
This project relies on two submodules:
There are two ways of downloading this project:
- Clone the project, and then update the submodules:
git clone https://github.com/SJTU-ECTL/MECALS.git
git submodule init
git submodule update- Alternatively, clone the project as well as the submodules:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/SJTU-ECTL/MECALS.git- To build, go to the root directory of the project, and then execute:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
cd ..An executable program called als.out will be generated at the project root directory.
- To clean up, go to the root directory of the project, and then execute:
rm -r build- Example command:
./als.out -i input/benchmark/aig/mac.aig -m input/miter/width_8_wce_31.aig -l ./input/standard-cell/nangate_45nm_typ.lib -o tmp/ -p 1.0 --fSASIMI 1In this example,
-
The tool inputs the accurate circuit "input/benchmark/aig/mac.aig"
-
The error constraint is specified by the error miter "input/miter/width_8_wce_31.aig". A general error miter is shown below.
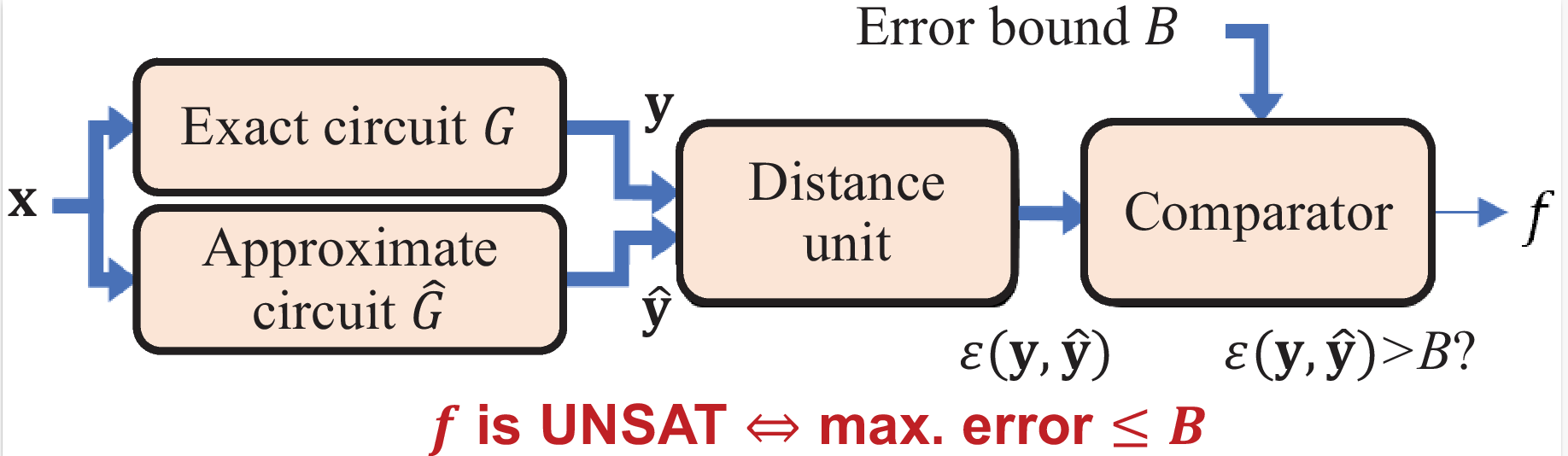
In the file "input/miter/width_8_wce_31.aig", both the outputs of exact and approximate circuits,
$\mathbf y$ and$\mathbf {\hat y}$ , have a bit width of 8. The WCE bound$B=31$ , which means WCE should not exceed 31. -
It uses the standard cell library "./input/standard-cell/nangate_45nm_typ.lib" for technology mapping.
-
The approximate circuits will be outputted to the folder ./tmp
Use the following command to get help:
./als.out -hThe following information will be returned:
usage: ./als.out --accCirc=string --mitCirc=string [options] ...
options:
-i, --accCirc path to accurate circuit (string)
-m, --mitCirc path to miter circuit (string)
-a, --appCirc path to approximate circuit; if this option is not empty, then error checking is performed (string [=])
-l, --standCell path to standard cell library (string [=input/standard-cell/nangate_45nm_typ.lib])
-o, --outpPath path to approximate circuits (string [=tmp/])
-s, --seed seed (unsigned int [=0])
-f, --nFrame #simulation patterns (int [=8192])
--fSASIMI flag of using SASIMI (int [=1])
-p, --exactPBDPerc proportion of exact PBD (double [=1])
-h, --help print this message| Long parameter | Short parameter | Default value | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| --accCirc | -i | None | Path to accurate circuit, e.g., input/benchmark/aig/mac.aig |
| --mitCirc | -m | None | Path to error miter circuit, e.g., input/miter/width_8_wce_31.aig. You can find more error miters in the folder input/miter/. To specify an arbitrary miter, you can refer to the functions GenWCEMit and GenMaxSEMit in the Python code script/run.py |
| --appCirc | -a | "" | Path to approximate circuit. When "--appCirc" specifies a non-empty string, then the program will iteratively simplify the accurate circuit provided by "--accCirc". Otherwise, if "--appCirc" specifies an empty string "", then the program will check the maximum error of the approximate circuit provided by "--appCirc", compared to the accurate circuit provided by "--accCirc". |
| --standCell | -l | input/standard-cell/mcnc.genlib | Path to standard cell library, e.g., ./input/standard-cell/nangate_45nm_typ.lib |
| --outpPath | -o | tmp | Specify the directory where the approximate circuits are outputed. |
| --seed | -s | 0 | The seed used for generating random input patterns for logic simulation. When seed "0" is used, then the program randomly picks a seed. Otherwise, the program uses the specified seed. |
| --nFrame | -f | 8192 | The number of random input patterns in logic simulation. In our work, simulation is used for quickly filtering some invalid local approximate changes (LACs). |
| --fSASIMI | 1 | Whether to use SASIMI LAC or not. If "--fSASIMI" is set to 1, then both SASIMI and CONST LACs will be applied. Otherwise, if "--fSASIMI" is set to 0, then only the CONST LAC will be applied. Please refer to our paper to see the definitions of LACs. | |
| --exactPBDPerc | -p | 1 | The proportion of nodes using exact partial Boolean difference. This value is a float-point number, ranging from 0.0 to 1.0. Its detailed definition is introduced in our paper. |
| --help | -h | None | Print help. |