A python package for automated processing of point clouds to simplify elevation creation, co-registration and differencing to facilitate the production of snow depth and vegetation products.
- Free software: MIT license
- Documentation: https://Surfix.github.io/snow-pc
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) and Structure from Motion (SfM) photogrammetry currently provide the most advanced and accurate approaches for monitoring topographic variation and snow distribution across a range of platforms, scales, and repeat intervals. These techniques generate high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) by producing georeferenced point clouds from overlapping imagery in the case of photogrammetry or from high frequency laser pulses in the case of LiDAR. However, post-processing of point clouds for generation of snow depth rasters remains complex compared to many other earth science applications such as topographic mapping, vegetation monitoring, geomorphology and landform analysis. Existing point cloud processing software suite such as Point Data Abstraction Library (PDAL) and LAStools provide general purpose tools for pre-processing, filtering and analyzing large point cloud data. Yet, there is a lack of tool that leveraged these capacities for optimized automated workflows specifically tailored for snow and ice applications. Consequently, complex manual interventions are often required for tasks like merging point cloud files from different flight lines or acquisitions, point clouds filtering, construction of (DTMs), aligning the DTMs and generation of products. This hinders efficient production of snow depth and limits full utilization of rich information in point clouds datasets.
snow_pc addresses this challenge by leveraging pdal and Stereo Pipeline (ASP) to automate point clouds management in a standardized workflow for generating elevation models, snow depths and vegetation products. This allows diverse users of developers, data processors and snow scientists to automate core point clouds processing tasks like merging, coordinate transformations, classification, co-registration and rasterization to simplify effort and facilitate multi-temporal analysis.
To install snow_pc, run this command:
pip install snow-pcYou can also install from sources with this command:
pip install git+https://github.com/Surfix/snow-pcsnow_pc.py module features the pc2uncorrectedDEM function which takes a user directory contain point cloud files, performs the necessary preparation (remove white space, covers las to laz and mosaic) and generate DTM and DSM files (laz and tif). DEM is required to perform dem_filtering so pc2uncorrectedDEM takes the path to a dem as an optional argument. If this argument is not defined, the DEM within the bounds of the point cloud file will be automatically download from Py3DEP.
from snow_pc import pc2uncorrectedDEM
dtm_laz, dtm_tif, dsm_laz, dsm_tif = pc2uncorrectedDEM(in_dir)There is also the pc2correctedDEM function which in additional to generating the DTM and DSM rasters, co-register these rasters to a reference object. {coming soon}
from snow_pc import pc2correctedDEM
pc2correctedDEM(in_dir, align_shp, asp_dir)
For snow application, a more comprehensive function is the pc2snow which further generates snow depth and canopy height from the co-registered snow-on DEMs. {coming soon}
from snow_pc import pc2snow
pc2snow(in_dir, align_shp, asp_dir)The main module builds on other modules in snow_pc including the common, prepare, modeling, align and product module.
To learn more about snow_pc, check out the snow_pc api reference on the documentation website- https://Surfix.github.io/snow-pc
Contain tools for common tasks
download_dem(las_fp): Download DEM within the bounds of the las file.def make_dirs(laz_fp): Create result directory for the tasks.
This module includes tools for performing preprocessing tasks like removing whitespace from files, converting LAS to LAZ format, and merging files within a directory.
-
replace_white_spaces(in_dir): remove white spaces in the point cloud files. -
las2laz(in_dir): Takes a user directory full of las files and convert the files to LAZ files. LAZ is a compressed version of LAS so it provides optimal data transfer and computation efficiency. -
merge_laz_files(in_dir): merge all LAZ files in the project directory into one LAZ file. This step is crucial to mosaic point cloud data from different flight lines to ensure seamless coverage over the area of interest, simplify data management tasks and facilitate processing in subsequent commands that take a single point cloud file. -
prepare_pc(in_dir): Steps through all preparing tools in one call
from snow_pc.prepare import prepare_pc
prepare_pc('project_dir')This module provides terrain_models and surface_models function for generating dtm and dsm models.
terrain_models(laz_fp): Use filters.dem, filters.mongo, filters.elm, filters.outlier, filters.smrf, and filters.range to filter the point cloud for terrain modelssurface_models(laz_fp): Use filters.dem, filters.mongo and filters.range to filter the point cloud for surface points
from snow_pc.modeling import terrain_models, surface_models
dtm_laz, dtm_tif = terrain_models('laz_fp')
dsm_laz, dsm_tif = surface_models('laz_fp')For users that want to explore the result of each filtering steps in the main and modeling module, filtering module will come handy.
return_filtering(laz_fp): removes points with invalid returns where the return number or number of returns is zero. This is only required for LiDAR point clouds.dem_filtering(laz_fp): extracts only points within a defined elevation range relative to the reference DEM. This filter is important to remove atmospheric or MTA noise from the data thereby eliminating outlier points too far above or below the ground surface.elm_filtering(laz_fp): finds isolated low points that are likely errors or noise far below the actual ground level.outlier_filtering(laz_fp): removes extreme outlier points in the point cloud that deviate significantly from surrounding points.ground_segmentation(laz_fp): Classify the terrain points using the Simple Morphological Filter (SMRF) algorithmsurface_segmentation(laz_fp): Isolate the surface points from the point clouds
from snow_pc.filtering import return_filtering, elm_filtering, outlier_filtering, dem_filtering, ground_segmentation
return_filtering('unfiltered_merge.laz')
dem_filtering('returns_filtered.laz', 'dem.tif', dem_low= 10, dem_high=50)
elm_filtering('dem_filtered.laz')
outlier_filtering('elm_filtered.laz', multiplier=2.5)
ground_segmentation('outlier_filtered.laz')clip_pc(in_laz, buff_shp): Clip the point cloud to a shapefile.align(in_laz, dem): Align the point clouds to a reference [To do]
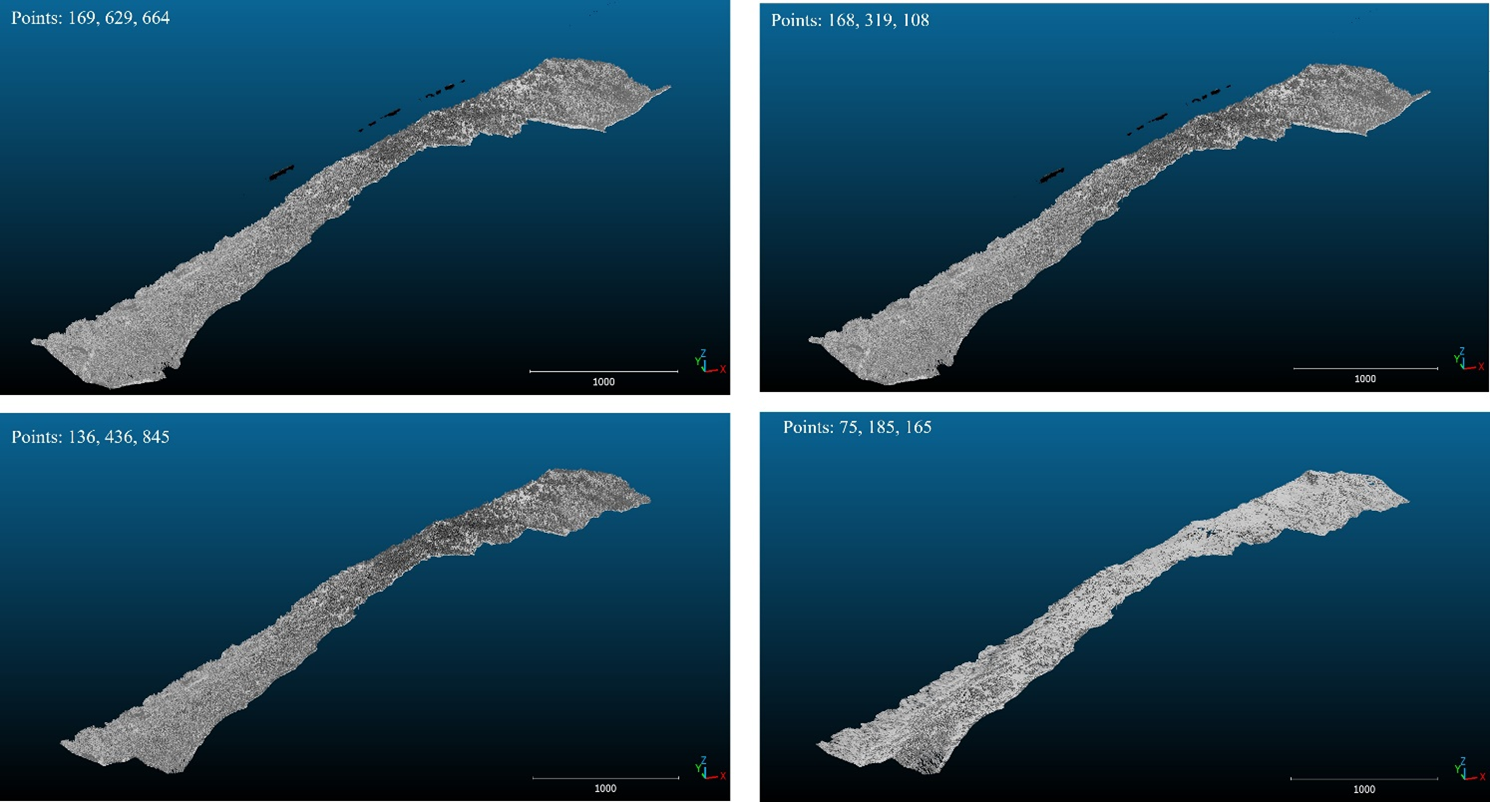 Intermittent results of DTM pipeline workflow for a track. The original point cloud is shown in top left. Point clouds after removal of invalid return is shown in top right. Bottom left is applying dem filter while the bottom right is the ground segmented points. Dem filter effectively removes noise in the point cloud such that no point is left for elm and outlier filter.
Intermittent results of DTM pipeline workflow for a track. The original point cloud is shown in top left. Point clouds after removal of invalid return is shown in top right. Bottom left is applying dem filter while the bottom right is the ground segmented points. Dem filter effectively removes noise in the point cloud such that no point is left for elm and outlier filter.
snow_pc builds on many GIS tools particularly leafmap, gdal, pdal and ASP so these packages are automatically available after installing snow_pc and can be used as necessary. For example, the resulting point clouds at any stage can be view using the view_lidar() of leafmap.
import leafmap
leafmap.view_lidar('unfiltered_merge.laz', cmap="terrain")- Add ground segmentation function to the filtering module
- Refactor the modeling module
- Complete surface segmentation function to the filtering module
- pc2correctedDEM and pc2snow
- [] Add a function for combining LiDAR and photogrammetry point clouds