ROS Packages for CHAMP Quadruped Controller.
CHAMP is an open source development framework for building new quadrupedal robots and developing new control algorithms. The control framework is based on "Hierarchical controller for highly dynamic locomotion utilizing pattern modulation and impedance control : implementation on the MIT Cheetah robot".
Core Features:
- Fully Autonomous (using ROS navigation Stack).
- Setup-assistant to configure newly built robots.
- Collection of pre-configured URDFs like Anymal, MIT Mini Cheetah, Boston Dynamic's LittleDog, and SpotMicroAi.
- Gazebo simulation environment.
- Demo robot built using accessible components so you can build it from home.
- Demo Applications like TOWR and chicken head stabilization.
- Lightweight C++ header-only library that can run on both SBC and micro-controllers.
Supported Hardware:
LIDAR:
- XV11 Lidar
- RPLidar
- YDLIDAR X4
- Hokuyo (SCIP 2.2 Compliant)
IMU:
- BNO080
SBC:
-
Nvidia Jetson Nano
This should also work on Single Board Computers that support Ubuntu 16/18 capable of running ROS Navigation Stack.
ACTUATORS:
- Digital Servos
- Dynamixel AX12
- Odrive Driven Brushless Motors - WIP
TESTED ON:
- Ubuntu 16.04 (ROS Kinetic)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (ROS Melodic)
1.1. Clone and install all dependencies:
sudo apt install -y python-rosdep
cd <your_ws>/src
git clone https://github.com/chvmp/champ
git clone https://github.com/chvmp/champ_teleop
cd ..
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
1.2. Build your workspace:
cd <your_ws>
catkin_make
source <your_ws/>/devel/setup.bash
You don't need a physical robot to run the following demos. If you're building a physical robot, you can find out more how to configure and run a new robot in step 3.
2.1.1. Run the base driver:
roslaunch champ_config bringup.launch rviz:=true
2.1.2. Run the teleop node:
roslaunch champ_teleop teleop.launch
If you want to use a joystick add joy:=true as an argument.
2.2.1. Run the Gazebo environment:
roslaunch champ_config gazebo.launch
2.2.2. Run gmapping package and move_base:
roslaunch champ_config slam.launch rviz:=true
To start mapping:
-
Click '2D Nav Goal'.
-
Click and drag at the position you want the robot to go.
-
Save the map by running:
roscd champ_config/maps rosrun map_server map_saver
2.3.1. Run the Gazebo environment:
roslaunch champ_config gazebo.launch
2.3.2. Run amcl and move_base:
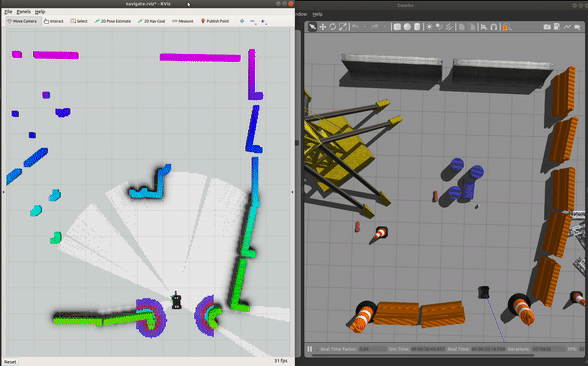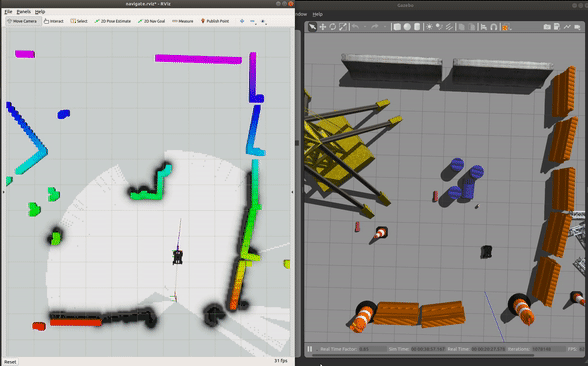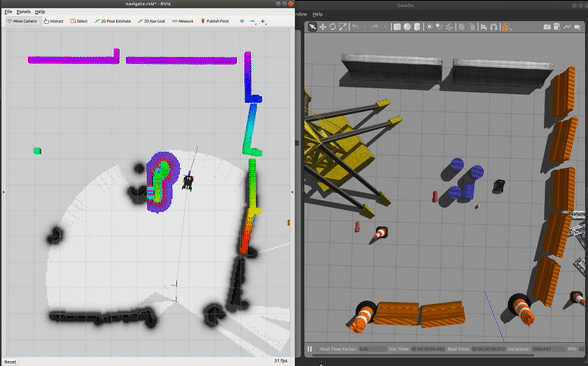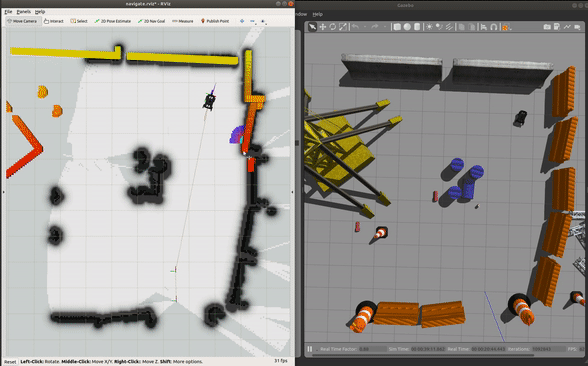
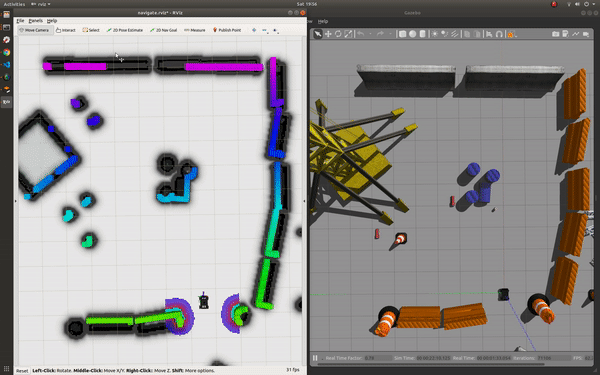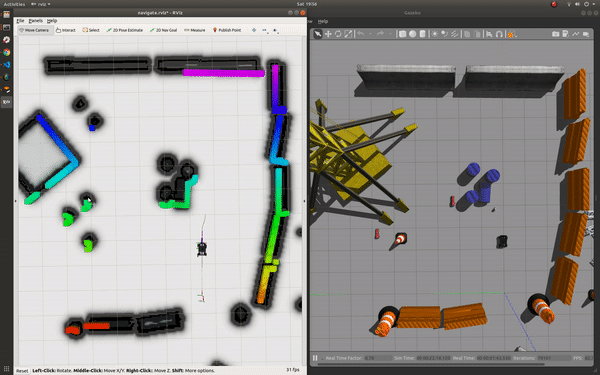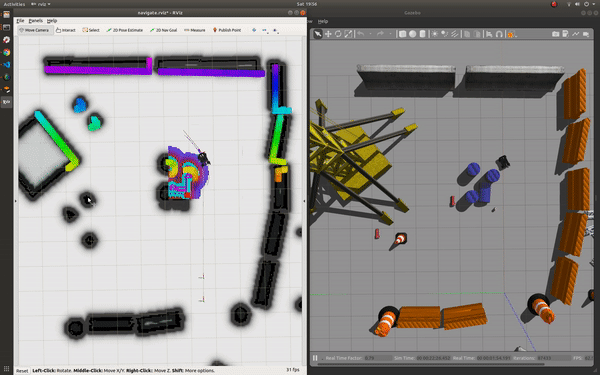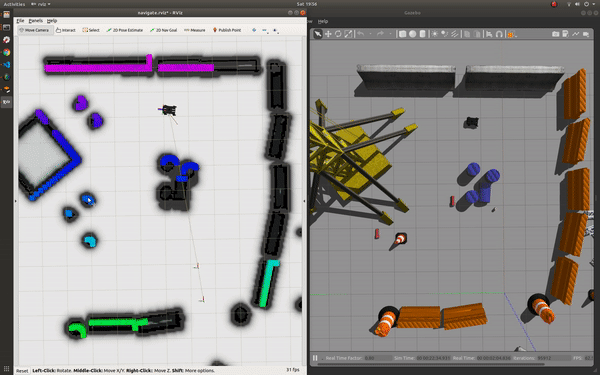
roslaunch champ_config navigate.launch rviz:=true
To navigate:
TODO:
- Hardware Documentation
- Microcontroller based configuration
-
First generate a configuration package using champ_setup_assistant. Follow the instructions in the README to configure your own robot. The generated package contains:
- URDF path to your robot.
- Joints and Links map to help the controller know the semantics of the robot.
- Gait parameters.
- Hardware Drivers.
- Navigation parameters (move_base, amcl and gmapping).
- Microcontroller header files for gait and lightweight robot description. This only applies to robot builds that use microcontroller to run the quadruped controller.
As a reference, you can check out the collection of robots that have been pre-configured here. In the list are some of the popular quadruped robots like Anymal, MIT Mini Cheetah, Boston Dynamic's LittleDog, and SpotMicroAI. Feel free to download the configuration packages in your catkin workspaces 'src' directory to try.
-
Next, build your workspace so your newly generated package can be found:
cd <your_ws> catkin_make
This will run the quadruped controller and all sensor/hardware drivers:
roslaunch <myrobot_config> bringup.launch
Available Parameters:
-
rviz - Launch together with RVIZ. Default: false
-
has_imu- Set this to true if the robot has no IMU. This is useful when you want to view your newly configured robot. Basically, this tells the robot to use the pose commands from champ_teleop as the current pose of the robot. Take note that this is only useful for debugging the robot. It is recommended to place an IMU on a physical robot. Default: true.
-
lite - Always set this to true if you're using a microcontroller to run the algorithms. Default false.
Example Usage:
View your newly configured robot:
roslaunch <myrobot_config> bringup.launch rviz:true
Run real robot with a microcontroller:
roslaunch <myrobot_config> bringup.launch lite:=true
The base driver described in 3.2 must be running to run gmapping and move_base.
Run gmapping package and move_base:
roslaunch <myrobot_config> slam.launch
To open RVIZ and view the map:
roscd champ_navigation/rviz
rviz -d navigate.rviz
To start mapping:
-
Click '2D Nav Goal'.
-
Click and drag at the position you want the robot to go.
-
Save the map by running:
roscd <myrobot_config>/maps rosrun map_server map_saver
The base driver described in 3.2 must be running to run amcl and move_base.
Run amcl and move_base:
roslaunch <myrobot_config> navigate.launch
To open RVIZ and view the map:
roscd champ_navigation/rviz
rviz -d navigate.rviz
To navigate:
Run Gazebo and the base driver in simulation mode:
roslaunch <myrobot_config> gazebo.launch
-
Take note that in order for this to work, the URDF has to be Gazebo compatible and has ros_control capability. The controllers have been set-up so all you need is to add the transmission of the actuators. You also need to get the physics parameters right like your mass, inertia, and foot friction.
Some useful resources on getting these parameters right:
-
Inertial Calculation - https://github.com/tu-darmstadt-ros-pkg/hector_models/blob/indigo-devel/hector_xacro_tools/urdf/inertia_tensors.urdf.xacro
-
List of Moment of Inertia - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_moments_of_inertia
-
Gazebo inertial parameters - http://gazebosim.org/tutorials?tut=inertia&cat=build_robot#Overview
-