We are happy to announce that Xplace 2.0 is now released. Compared to Xplace 1.0, this version supports the following new features:
- Support deterministic mode with only 5~25% extra GP runtime overhead.
- Implement an extremely fast GPU-accelerated detailed-routability-driven placement algorithm Xplace-Route.
- Integrate with a GPU-accelerated detailed placer and a GPU-accelerated global router GGR.
- Support a superfast GPU-accelerated place and global route flow! Input your LEF/DEF, the flow will output the placement DEF and the global routing guide! xplace_route_flow.png
- Provide benchmark download and preprocess scripts, and three routability evaluation scripts.
- Code refactoring.
Please check our TCAD paper for more details about Xplace-Route!
Xplace is a fast and extensible GPU-accelerated global placement framework developed by the research team supervised by Prof. Evangeline F. Y. Young at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK). It achieves around 3x speedup per GP iteration compared to DREAMPlace and shows high extensibility.
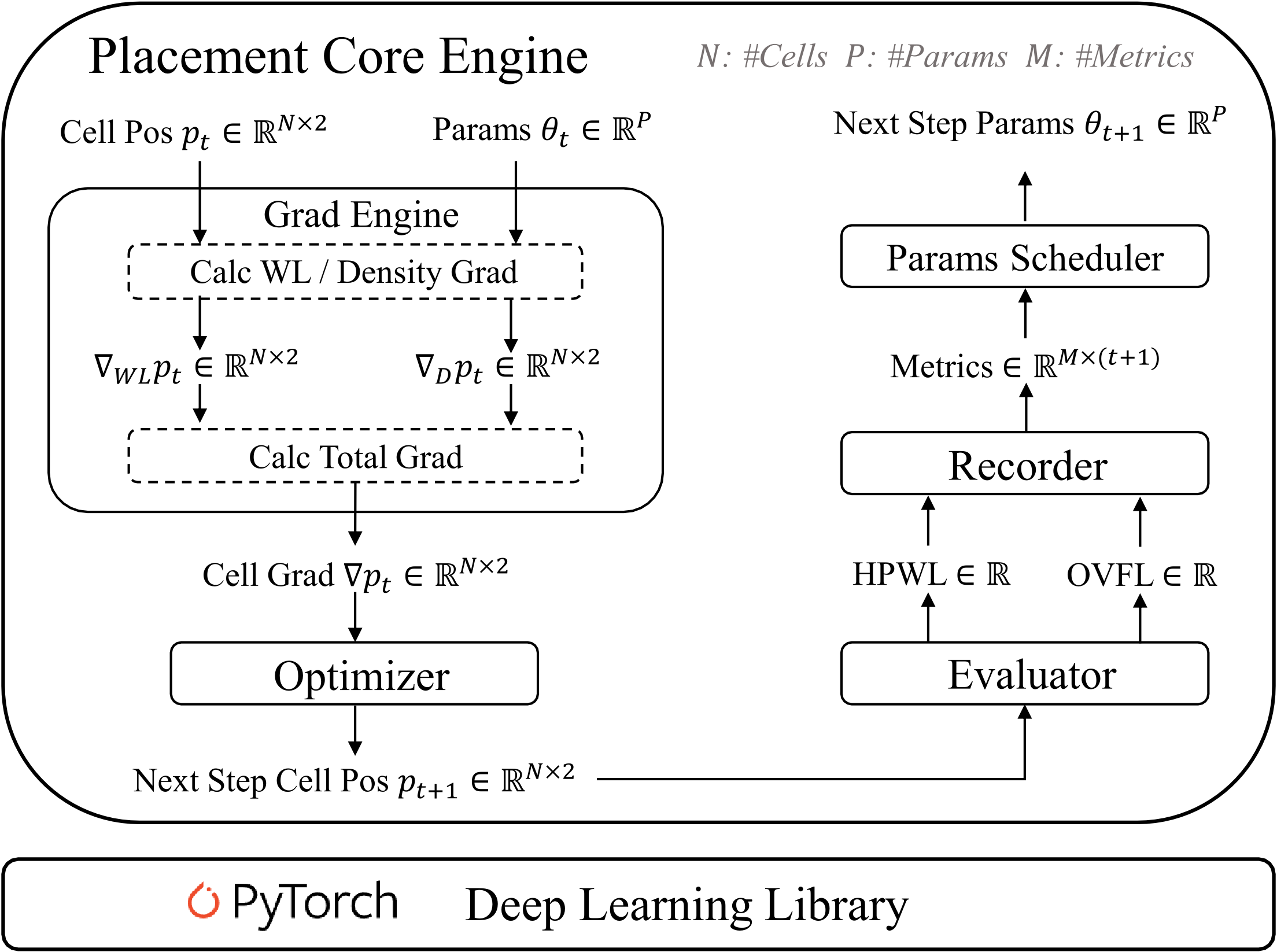
As shown in the following figure, Xplace framework is built on top of PyTorch and consists of several independent modules. One can easily extend Xplace by applying scheduling techniques, gradient functions, new placement metrics, and so on.
More details are in the following paper:
Lixin Liu, Bangqi Fu, Shiju Lin, Jinwei Liu, Evangeline F.Y. Young, Martin D.F. Wong. "Xplace: An Extremely Fast and Extensible Placement Framework". In IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (TCAD), doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2023.3346291.
Lixin Liu, Bangqi Fu, Martin D. F. Wong, and Evangeline F. Y. Young. "Xplace: an extremely fast and extensible global placement framework". In Proceedings of the 59th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC '22). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 1309–1314.
(For the Xplace-NN, please refer to branch neural)
Step 1: Clone the Xplace repository. We'll call the directory that you cloned Xplace as $XPLACE_HOME.
git clone --recursive https://github.com/cuhk-eda/XplaceStep 2: Build the shared libraries used in Xplace.
cd $XPLACE_HOME
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=$(which python) ..
make -j40 && make install- CMake >= 3.18
- GCC >= 7.5.0
- Boost >= 1.56.0
- CUDA >= 11.3
- Python >= 3.8
- PyTorch >= 1.12.0
- Cairo
- Innovus® (version 20.14, optional, for detailed routing and design rule checking)
The following script will automatically download ispd2005, ispd2015, iccad2019, ispd2018, and ispd2019 benchmarks in ./data/raw. It also preprocesses ispd2015 benchmark to fix some errors. Note that Innovus® can run detailed routing on this fixed ispd2015.
cd $XPLACE_HOME/data
./download_data.sh- To run GP + DP flow for ISPD2005 dataset:
# only run adaptec1
python main.py --dataset ispd2005 --design_name adaptec1
# run all the designs in ispd2005
python main.py --dataset ispd2005 --run_all True- To run GP + DP flow for ISPD2015 dataset:
# only run mgc_fft_1
python main.py --dataset ispd2015_fix --design_name mgc_fft_1
# run all the designs in ispd2015
python main.py --dataset ispd2015_fix --run_all True- To run Routability GP + DP flow for ISPD2015/2018/2019 dataset:
# run all the designs with routability optimization
python main.py --dataset ispd2015_fix --run_all True --use_cell_inflate True
python main.py --dataset ispd2018 --run_all True --use_cell_inflate True
python main.py --dataset ispd2019_no_fence --run_all True --use_cell_inflate True- To run Mixed-Size flow for MMS dataset:
python main.py --dataset mms --run_all True --mixed_size TrueNOTE: We default enable the deterministic mode. If you don't need determinism and want to run placement in an extremely fast mode, please try to set --deterministic False in the Python arguments.
- Each run will generate several output files in
./result/exp_id. These files can provide valuable information for parameter tuning.
In ./result/exp_id
- eval # parameter curves and the visualization of placement solutions
- log # log and statistics
- output # placement solutions
- Custom Path Mode: You can use the argument
--custom_pathto run your custom LEF/DEF or bookshelf benchmark.
Suppose there is a LEF/DEF benchmark named toy in data/raw, you can use the following command line to run the GP + DP flow:
python main.py --custom_path lef:data/raw/toy_input.lef,def:data/raw/toy_input.def,design_name:toy,benchmark:test --load_from_raw True --detail_placement True- Custom JSON Mode: You can also use the argument
--custom_jsonto run multiple LEFs + DEF + Verilog:
python main.py --custom_json examples/examples.json --load_from_raw True --target_density 0.9
Please provide your LEFs/DEF in the input json file. An example of ASAP7 input is given in ./examples/examples.json. Note that the verilog format is only partially supported.
Please refer to main.py.
Set --final_route_eval True in Python arguments to invoke the internal global router GGR to run GPU-accelerated PnR flow. The flow will output the placement DEF and the global routing guide in ./result/exp_id/output. Besides, GR metrics are reported in the log and recorded in ./result/exp_id/log/route.csv.
- To run Place and Global Route flow for ISPD2015 dataset:
python main.py --dataset ispd2015_fix --run_all True --load_from_raw True --detail_placement True --use_cell_inflate True --final_route_eval TrueMore details about using GGR in Xplace can be found in cpp_to_py/gpugr/README.md.
We provide three ways to evaluate the routability of a placement solution:
-
Set
--final_route_eval Trueto invoke GGR to evaluate the placement solution. -
Use CU-GR to evaluate the placement solution by global routing. Please refer to tool/cugr_ispd2015_fix/README.md for instructions.
-
(Optional). If Innovus® has been properly installed in your OS, you may try to use Innovus® to detailedly route the placement solution. Please refer to tool/innovus_ispd2015_fix/README.md for instructions.
The following script will dump the parsed design into a single torch pt file so Xplace can load the design from the pt file instead of parsing the input file from scratch.
cd $XPLACE_HOME/data
python convert_design_to_torch_data.py --dataset ispd2005
python convert_design_to_torch_data.py --dataset ispd2015_fix
python convert_design_to_torch_data.py --dataset iccad2019Preprocessed data is saved in ./data/cad.
To develop a new global placement technique in Xplace, we highly suggest using the pt mode to save the parser time. (set --load_from_raw False)
python main.py --dataset ispd2005 --run_all True --load_from_raw FalseNOTE:
- Please remember to use the raw mode (set
--load_from_raw True) when measuring the total running time. - We currently do not support
ptmode in the routability-driven global placement. - If you want to run
ptmode for the custom dataset, you need to add the custom dataset path inutils/get_design_params.py.
If you find Xplace useful in your research, please consider to cite:
@article{xplace_tcad,
author={Liu, Lixin and Fu, Bangqi and Lin, Shiju and Liu, Jinwei and Young, Evangeline F.Y. and Wong, Martin D.F.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems},
title={Xplace: An Extremely Fast and Extensible Placement Framework},
year={2023},
}
@inproceedings{liu2022xplace,
author={Liu, Lixin and Fu, Bangqi and Wong, Martin D. F. and Young, Evangeline F. Y.},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 59th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference},
title={Xplace: An Extremely Fast and Extensible Global Placement Framework},
year={2022},
}Thanks the authors of ePlace, RePlAce, and DREAMPlace for their great work.
@article{lu2015eplace,
author={Lu, Jingwei and Chen, Pengwen and Chang, Chin-Chih and Sha, Lu and Huang, Dennis Jen-Hsin and Teng, Chin-Chi and Cheng, Chung-Kuan},
journal={ACM Trans. Des. Autom. Electron. Syst.},
title={ePlace: Electrostatics-Based Placement Using Fast Fourier Transform and Nesterov's Method},
year={2015},
}
@article{cheng2019replace,
author={Cheng, Chung-Kuan and Kahng, Andrew B. and Kang, Ilgweon and Wang, Lutong},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems},
title={RePlAce: Advancing Solution Quality and Routability Validation in Global Placement},
year={2019},
}
@article{lin2021dreamplace,
author={Lin, Yibo and Jiang, Zixuan and Gu, Jiaqi and Li, Wuxi and Dhar, Shounak and Ren, Haoxing and Khailany, Brucek and Pan, David Z.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems},
title={DREAMPlace: Deep Learning Toolkit-Enabled GPU Acceleration for Modern VLSI Placement},
year={2021},
}- Lixin Liu (lxliu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk)
- Bangqi Fu (bqfu21@cse.cuhk.edu.hk)
- Shiju Lin (sjlin@cse.cuhk.edu.hk)
- Jinwei Liu (jwliu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk)
Xplace is an open source project licensed under a BSD 3-Clause License that can be found in the LICENSE file.