roshell - An interactive shell for robotics applications
There are two options to build and run roshell.
If you do not have ROS installed, you cannot use the Robotic features that roshell offers.
git clone https://github.com/deepaktalwardt/roshell.git
cd roshell
makeThis will only work on Ubuntu 18.04 with ROS Melodic Morenia installed. If you wish you install ROS, please follow instructions here: http://wiki.ros.org/melodic/Installation
git clone https://github.com/deepaktalwardt/roshell.git
cd roshell
source build.shSourcing build.sh script file builds both ROS file (catkin_make) and roshell (make), launches separate terminals for roscore and rosbag, and starts roshell executable. From roshell command, you can run roslaunch to see the visualizer.
You should see a bunch of environment variables, and then a prompt in white/blue/yellow colors:
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak$ Currently, roshell supports many of the commands and features that bash supports. Some examples:
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell$ whoami
deepak
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell$ cd ros_ws
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell/ros_ws$
This is a list of features that we implemented along with a brief description on how to test them.
source command reads a text file with multiple lines of commands.
To test the command, source "test.sh" script file.
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell$ source test.sh
Pressing tab button auto-completes the input file name only when one match occurs.
When multiple matches occur, pressing tab second time, all matching files are listed.
For the first word in command line, it searches the matching files from $PATH.
For the other words in command line, it searches files the current directory only.
The user can interrupt program execution with Ctrl+C
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell$ sleep 10000
sleep will be sent a SIGINT, and will exit. However, roshell does not exit.
A variable can be assigned using '=' and retrieved with '$'
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell$ var=1
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell$ echo $var
1
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell$ history
History List:
whoami
var=1
echo $var
[roshell] deepak@deepak-pc:/home/deepak/roshell$ history clear
History Cleared
You can also use the up and down arrows to scroll through previously entered commands.
Before running these features, ensure that you have built roshell with ROS.
Then, you can run the ROS nodes provided inside the packages in the ros_ws/src directory.
To visualize a point cloud stored in the PCD file, you need to run the pcd_visualizer_node. First, download a test PCD file provided here and place it in ros_ws/src/roshell_graphics/test/ directory. Then, use rosrun
rosrun roshell_graphics pcd_visualizer_node
If you downloaded the PCD file somewhere else, you can change the path in ros_ws/src/roshell_graphics/src/pcd_visualizer_node.cpp and recompile and run.
To visualize point clouds streaming from a rosbag inside the terminal, you will need to launch the ROS Node pcl2_visualizer_node and play the rosbag provided here. Download it to a location and navigate there.
First, make sure that roscore is running, then play the rosbag
rosbag play test_bag_filtered.bag
In a different terminal, start the visualizer
roslaunch roshell_graphics pcl2_visualizer.launch colormap:=false
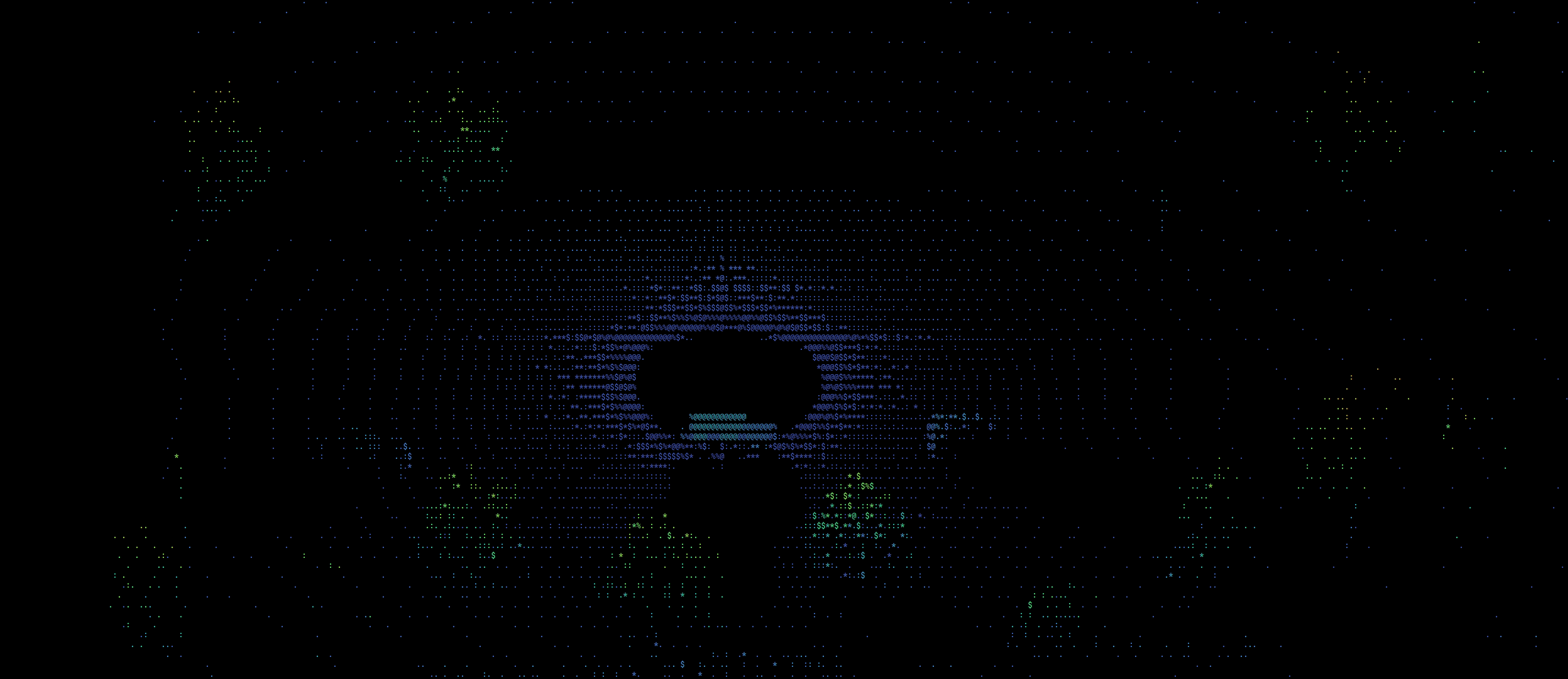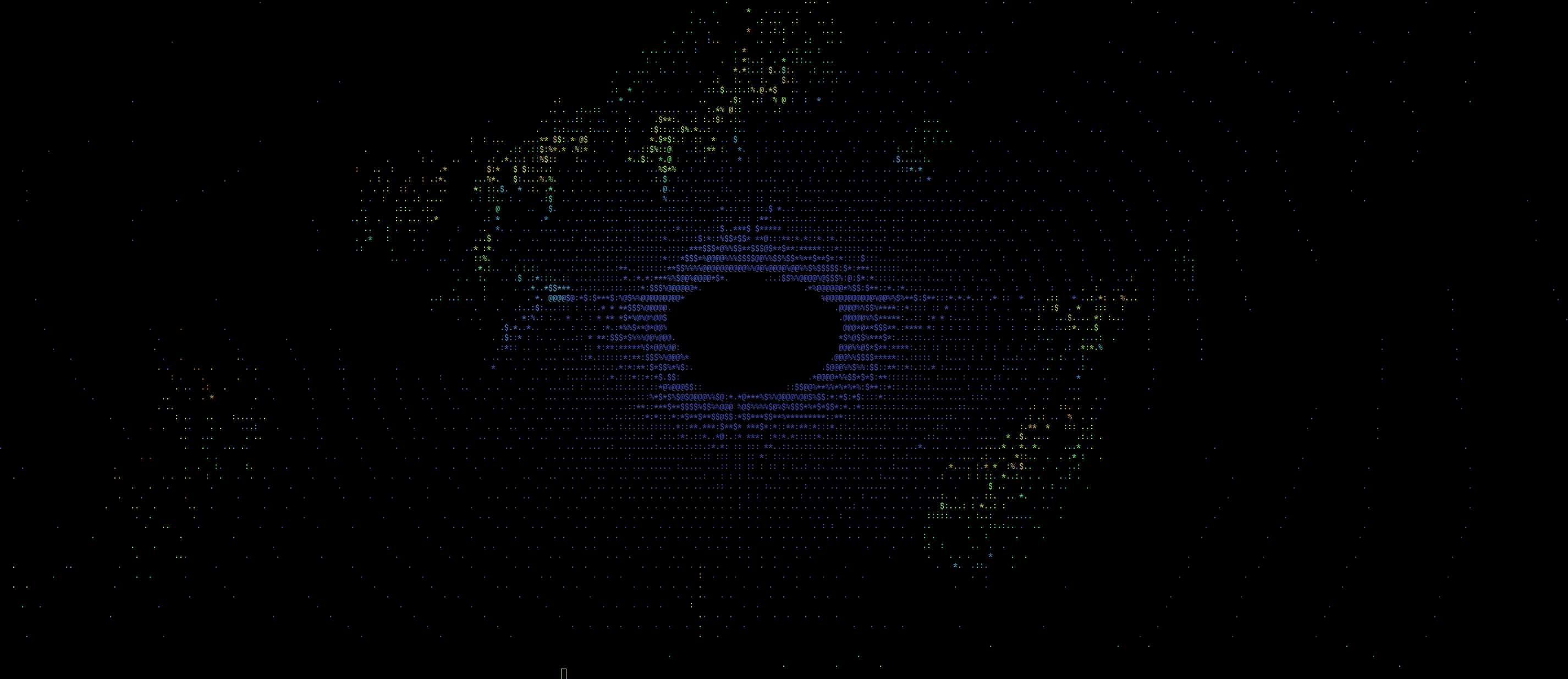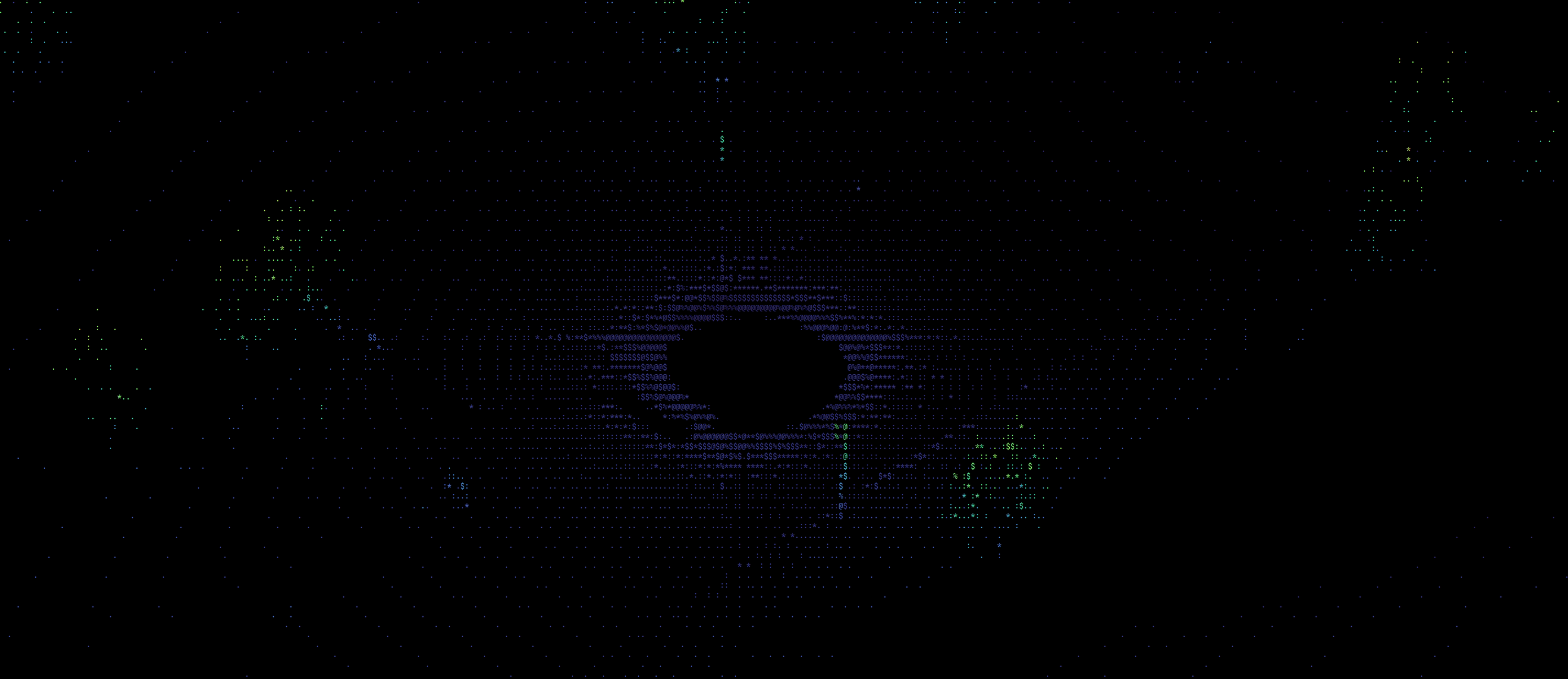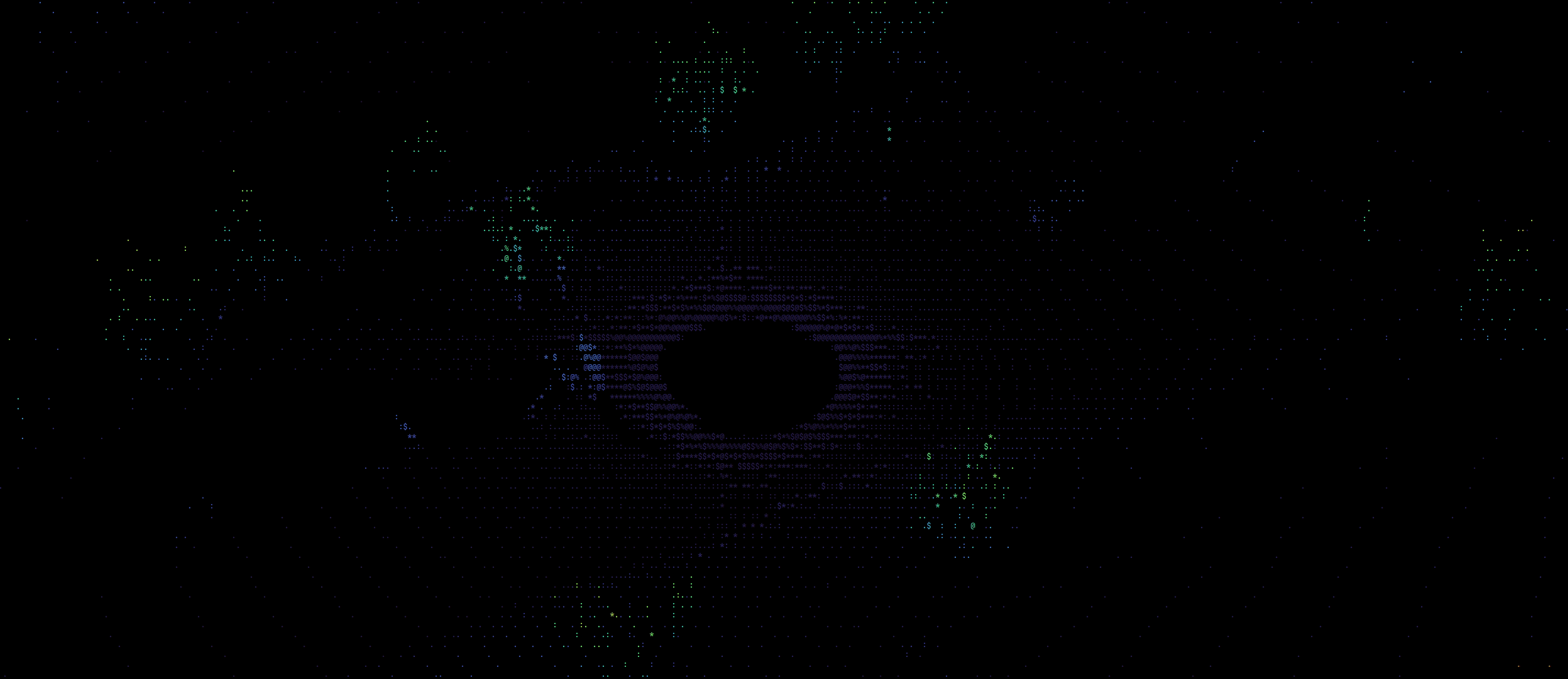
This should now start visualizing the point clouds that are streamed from the rosbag over the default topic : /simulator/lidar. The window should look something like this:

This node allows for some parameters to be changed as needed. See the ros_ws/src/roshell_graphics/launch/pcl2_visualizer.launch file for more details. For example, to change the camera focal distance (which controls the zoom level) and input topic, you should launch the node like this
roslaunch roshell_graphics pcl2_visualizer cam_focal_distance:=500 in_topic:=/lidar
With colormap turned on, the visualization looks something like this:
 To create line plots, we first need to have a publisher node that will publish random values to be plot on the line plot. To do that, launch the following
To create line plots, we first need to have a publisher node that will publish random values to be plot on the line plot. To do that, launch the following
roslaunch roshell_graphics float_visualizer.launch
This will start both a floating point publisher and a subscriber and start printing values to the scren.
 To test image functionality, make sure that the ROS bag you downloaded earlier is playing, then you can run the node.
To test image functionality, make sure that the ROS bag you downloaded earlier is playing, then you can run the node.
rosrun roshell_graphics image_viewer_nodeIf the images are being published on a different topic, or if you're using a different ROS bag, you can supply the topic to listen to using
rosrun roshell_graphics image_viewer_node _in_topic:=/wide_stereo/right/image_raw