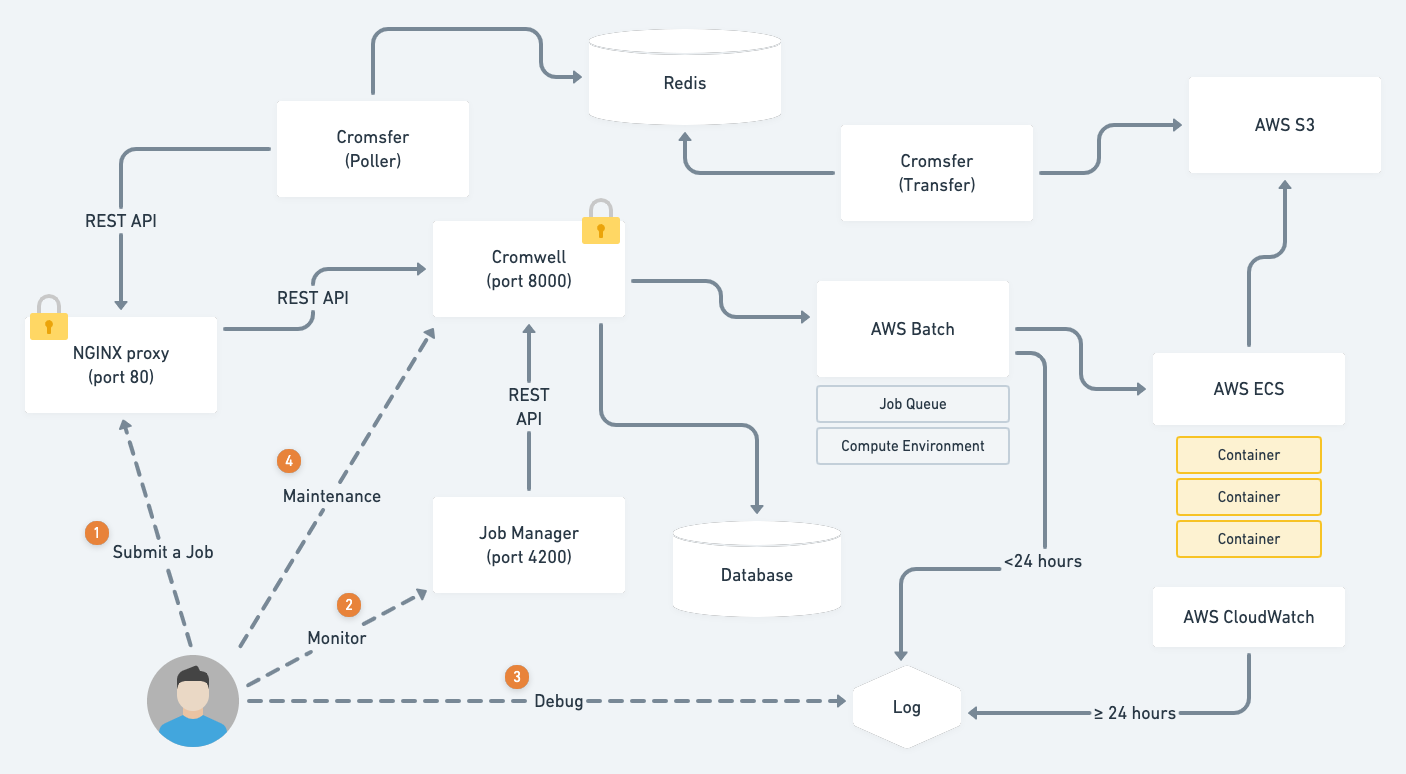
Setting Up AWS GWF (Genomics Workflows) + Cromwell
Create a new VPC using the CloudFormation template here: https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home?#/stacks/new?stackName=GenomicsVPC&templateURL=https://aws-quickstart.s3.amazonaws.com/quickstart-aws-vpc/templates/aws-vpc.template.yaml
Create a Genomics Workflow Core using the CloudFormation templete here: https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home?#/stacks/new?stackName=gwfcore&templateURL=https://aws-genomics-workflows.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/templates/gwfcore/gwfcore-root.template.yaml
Follow the instructions in the section called Deployment of Genomics Workflow Core into an existing VPC which can be found here.
The pre-downloaded template can be found in the cloudformation directory.
Create a Cromwell server instance and and and RDS Aurora Serverless database cluster using the CloudFormation template here: https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/home?#/stacks/new?stackName=cromwell-resources&templateURL=https://aws-genomics-workflows.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/templates/cromwell/cromwell-resources.template.yaml
- Make sure that the value for
GWFCoreNamespaceyou put in this template must be matched with the value you set when you created a Genomics Workflow Core in the section above. - If you are deploying multiple instances of GWF/Cromwell, make sure that the value for
Namespaceyou put in this template is unique across all regions (us-east-1, us-west-1, ...)
Follow the instructions in the section called Deploy Cromwell Resources which can be found here.
The pre-downloaded template can be found in the cloudformation directory.
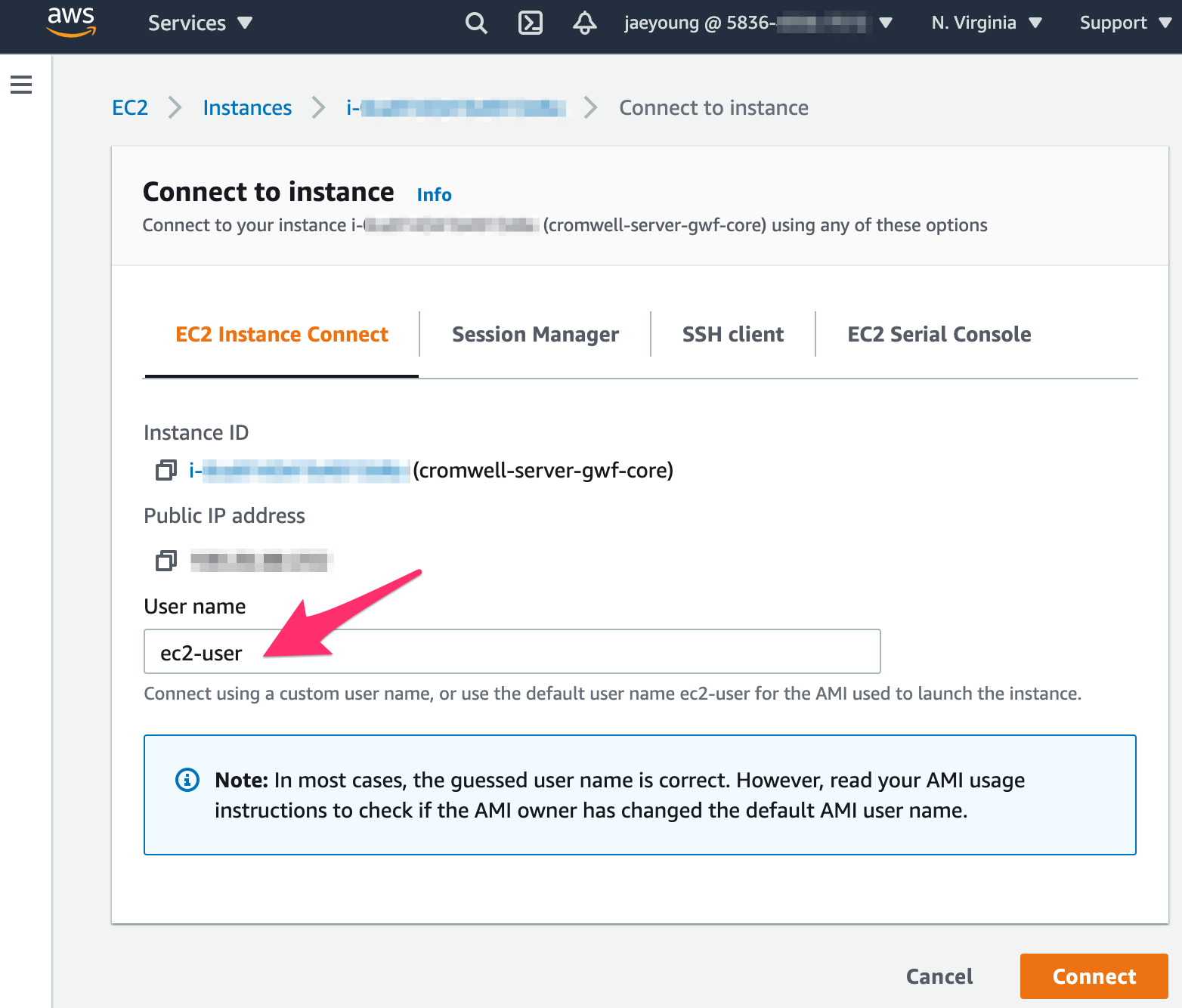
Once the Cromwell server EC2 instance is created, SSH into it using the web-based "EC2 Instance Connect" tool in the AWS Management Console. Use the username ec2-user (no password required). This is the only way to connect at the moment because CloudFormation does not associate a key pair when creating the Cromwell server instance.
To use your existing key pair (.pem) to connect to this instance, first retrieve the public key for your key pair: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ec2-key-pairs.html#retrieving-the-public-key
Then, SSH into the Cromwell server instance and add the public key to the authorized keys ():
$ echo 'ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAA...PLE' >> /home/ec2-user/.ssh/authorized_keys
Helpful article: https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/user-data-replace-key-pair-ec2/
SSH into the Cromwell server instance and install the following software.
Skip this section if the recent AMI comes with Python 3.
$ sudo yum install python36
$ cd /usr/bin/
$ sudo ln -s pip-3.6 pip3$ sudo yum install -y docker
$ sudo service docker start
$ sudo usermod -a -G docker ec2-userLog out, log back in. Check Docker is properly installed by running:
$ dockerInstall docker-compose (https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/#install-compose):
$ sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.1/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-composeCheck Docker Compose is properly installed by running:
$ docker-composeThe latest version can be found here: https://github.com/DataBiosphere/job-manager/releases
You will be asked a series of questions. Enter v1.5.7 for the Job Manager version (latest as of April 2021). You can use default values for the rest of the questions.
$ cd ~
$ curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DataBiosphere/job-manager/master/deploy/quickstart/quick_start.py > /tmp/jmui.py && python3 /tmp/jmui.py
>> Select a version [ v0.3.0 ] > v1.5.7
>> Select an installation directory [ /home/ec2-user/jmui ] >
Using: /home/ec2-user/jmui
Creating directory: /home/ec2-user/jmui
That directory already exists... I can...
1. Default: Re-use the existing directory which might leave behind some old files
2. Delete the entire directory and all of its contents - and then remake it, completely empty
Re-use or replace? (1/2) [ 1 ] > 2
Removing /home/ec2-user/jmui and its subdirectories
Creating a new directory at /home/ec2-user/jmui
Creating directory: /home/ec2-user/jmui/bin
Creating directory: /home/ec2-user/jmui/config
>> Select a shim to use (Cromwell/dsub) [ Cromwell ] >
Using: Cromwell
>> Enter the Cromwell URL [ http://addr:172.17.0.1:8000/api/workflows/v1 ] >
>> Setting up for single-instance or against Caas? (instance/caas) [ instance ] >
Using: instance
To start, run:
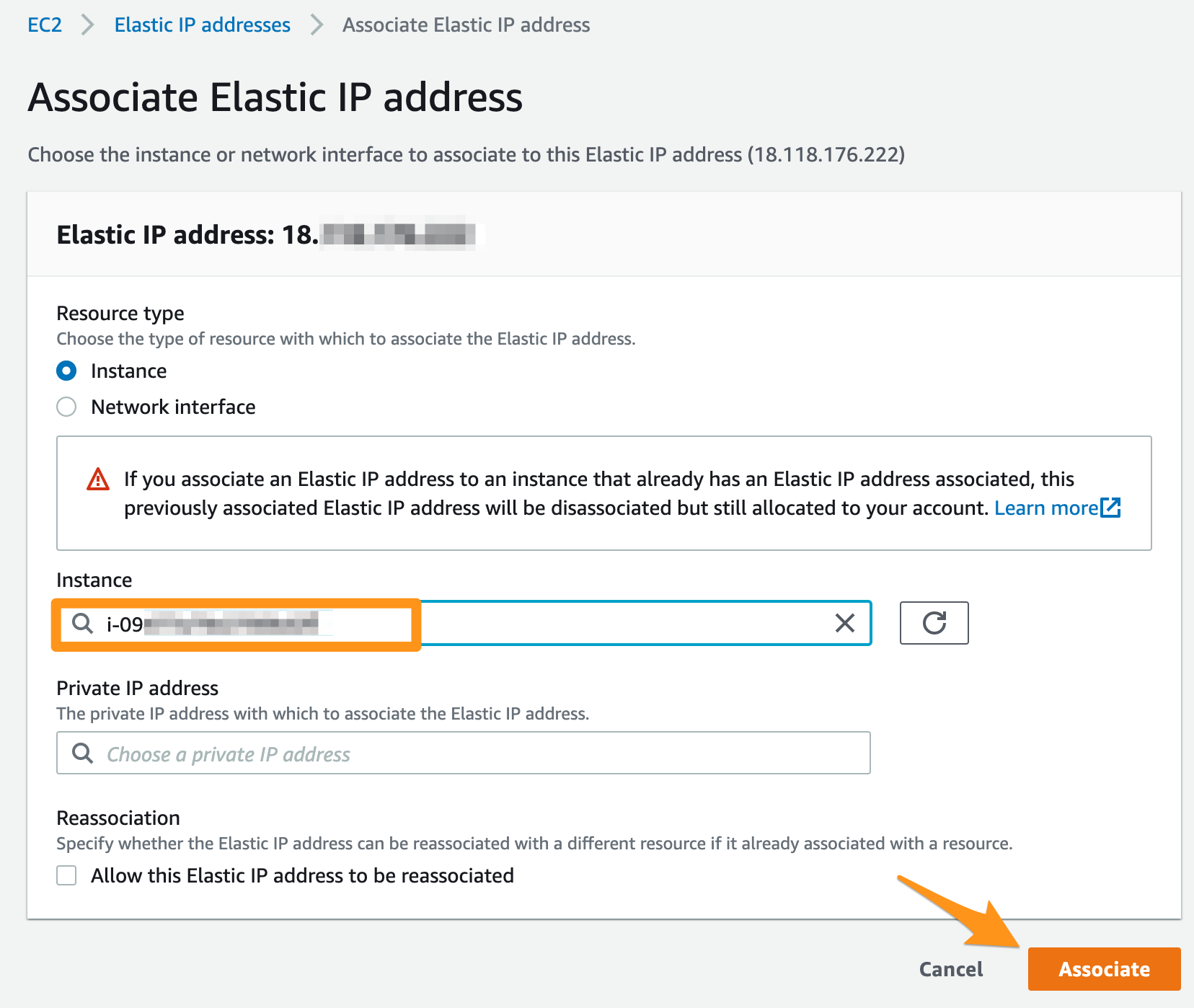
> /home/ec2-user/jmui/bin/jmui_start.shAssign an Elastic IP address to the Cromwell server instance. The IP address assigned here will be used in the later section.
Make sure the listening port is set to 8000 and the server binds to all interfaces (i.e. 0.0.0.0).
$ nano ~/cromwell.confBEFORE:
webservice {
interface = localhost
port = 8000
}
AFTER:
webservice {
interface = 0.0.0.0
port = 8000
}
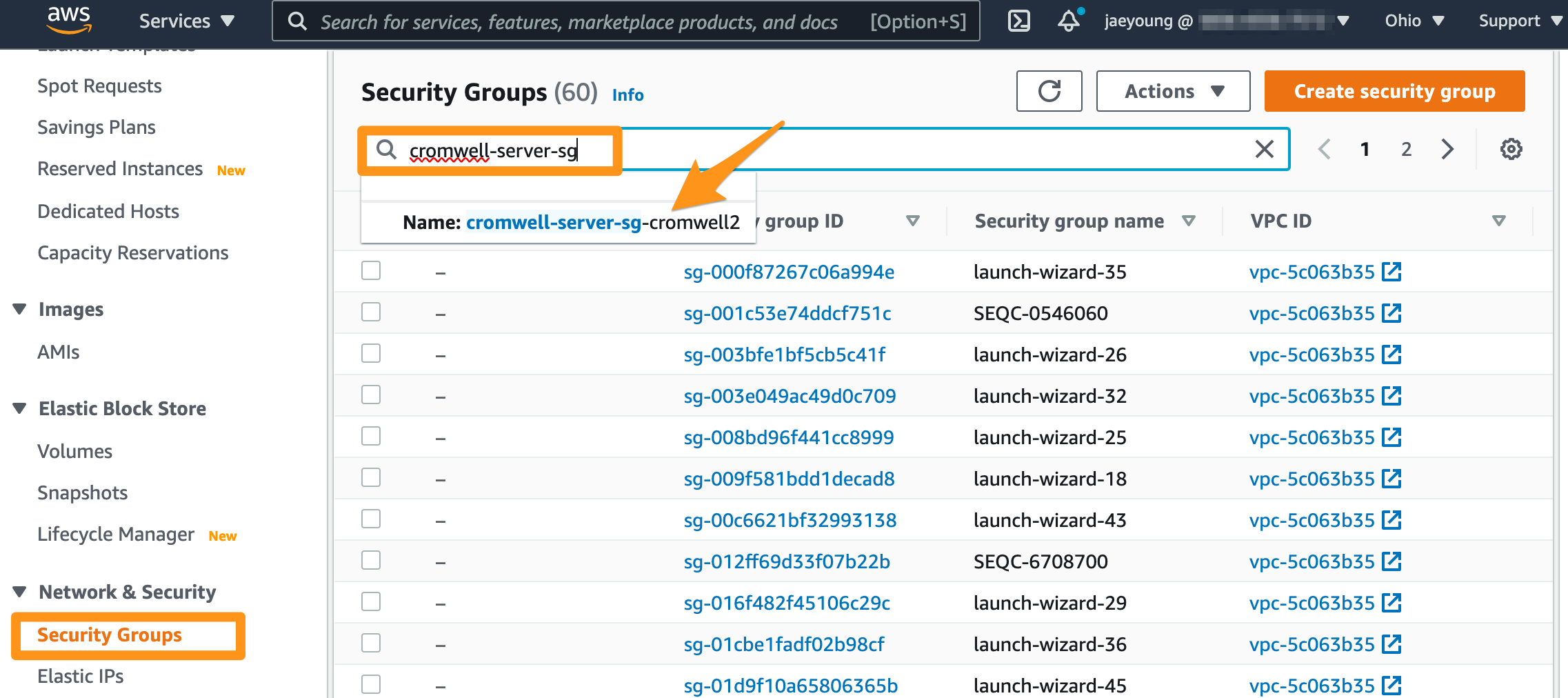
Choose Security Groups, start tyyping cromwell-server-sg in the search box, and choose the security group whose name starts with cromwell-server-sg.
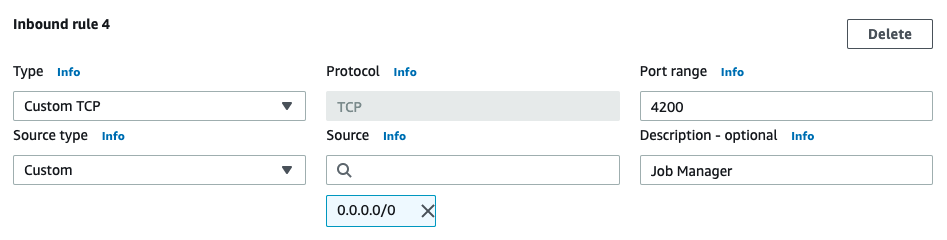
Add TCP port 4200 to the cromwell-server security group to allow inbound traffic for Job Manager.
Make sure the listening port is set to 80, and turn off SSL by commenting out the three lines as shown below:
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.confBEFORE:
...
listen 80 default_server;
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
# redirect all non-ssl traffic to ssl
if ($ssl_protocol = "") {
rewrite ^ https://$host$request_uri? permanent;
}
...
AFTER:
...
listen 80 default_server;
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
# redirect all non-ssl traffic to ssl
# if ($ssl_protocol = "") {
# rewrite ^ https://$host$request_uri? permanent;
# }
...
To add basic authentication, please refer to this article: https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/security-controls/configuring-http-basic-authentication/
Replace user2, user3, ... to actual user names.
$ sudo yum install httpd-tools
$ sudo mkdir /etc/apache2
$ sudo htpasswd -c /etc/apache2/.htpasswd user1
$ sudo htpasswd /etc/apache2/.htpasswd user2
$ sudo htpasswd /etc/apache2/.htpasswd user3Configure the NGINX to use Basic Authentication:
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.confAFTER:
...
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
auth_basic "restricted area";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/apache2/.htpasswd;
}
...
Reload the modified NGINX configuration:
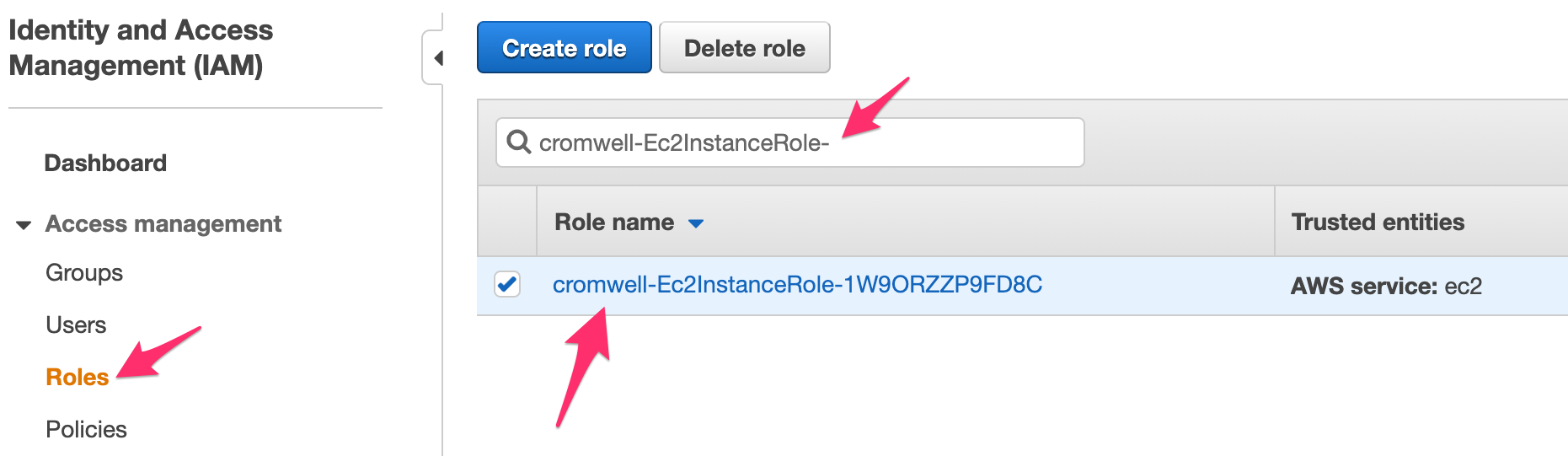
$ sudo systemctl reload nginxLook for IAM role whose name starts with cromwell-Ec2InstanceRole-.
Give all S3 permission to every bucket. This is necessary if your input files to workflow is stored in other S3 buckets.
BEFORE:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"s3:*"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::dp-lab-gwf-core",
"arn:aws:s3:::dp-lab-gwf-core/*"
],
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::gatk-test-data/*",
"arn:aws:s3:::broad-references/*"
],
"Effect": "Allow"
}
]
}AFTER:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"s3:*"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
],
"Effect": "Allow"
},
{
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::gatk-test-data/*",
"arn:aws:s3:::broad-references/*"
],
"Effect": "Allow"
}
]
}Open cromwell.conf and change job-queue/default-gwf-core to job-queue/priority-gwf-core. Using the priority queue will ensure that jobs submitted to AWS Batch will not use spot instances.
...
backend {
default = "AWSBATCH"
providers {
AWSBATCH {
actor-factory = "cromwell.backend.impl.aws.AwsBatchBackendLifecycleActorFactory"
config {
numSubmitAttempts = 10
numCreateDefinitionAttempts = 10
root = "s3://dp-lab-gwf-core/cromwell-execution"
auth = "default"
default-runtime-attributes { queueArn = "arn:aws:batch:us-east-1:583643567512:job-queue/priority-gwf-core" , scriptBucketName = "dp-lab-gwf-core" }
filesystems {
s3 {
auth = "default"
duplication-strategy: [
"hard-link", "soft-link", "copy"
]
}
}
}
}
}
}
...
SSH into the Cromwell server EC2 instance. Run the following command to download the setup package (requires jq):
curl -Ls https://api.github.com/repos/hisplan/cromwell-gwf-setup/releases/latest | jq -r .tarball_url | xargs wget -O - | tar -xz --strip-components=1Run the following command to install Redis and Cromsfer:
$ ./install.sh$ mkdir -p ./cromsfer
$ cp ./config/cromsfer/config.template.yaml ./cromsfer/config.yamlOpen the ./cromsfer/config.yaml file and replace ec2-w-x-y-z.compute-1.amazonaws.com with the actual public IPv4 DNS name of the Cromwell server EC2 instance. The user1 password must match with the password you set up for NGINX Basic Authentication.
cromwell:
url: http://ec2-w-x-y-z.compute-1.amazonaws.com
username: user1
password: 123
redis:
host: ec2-w-x-y-z.compute-1.amazonaws.com
port: 6379$ cp ./config/job-manager/capabilities-config.json ./jmui/bin/capabilities-config.jsonThe default CloudFormation does not come up with larger EC2 instance types. To add additional larger EC2 instance types, refer to this document here.
If this is the first time, manually stop the Cromwell server instance and use the following command to start the server again.
To bring up the server, run the following from your local machine:
$ ./server.sh -u -i i-09477a79e2700bd2f -k ~/mykey.pem -r us-east-1{
"StartingInstances": [
{
"CurrentState": {
"Code": 0,
"Name": "pending"
},
"InstanceId": "i-0ca914341b4913d6c",
"PreviousState": {
"Code": 80,
"Name": "stopped"
}
}
]
}
Cromwell server address: ec2-w-x-y-z.compute-1.amazonaws.com
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start docker.service
Starting up Redis...
Backing up Cromwell Server Log...
Starting up Cromwell Server...
Waiting for Cromwell Server to be up and running...
Waiting for Cromwell Server to be up and running...
Starting up Job Manager...
DONE.
Cromwell/Job Manager is available at http://ec2-w-x-y-z.compute-1.amazonaws.com:4200
To bring down the server, run the following from your local machine:
$ ./server.sh -d -i i-09477a79e2700bd2f -k ~/mykey.pem -r us-east-1Follow the instructions here and submit a test workflow.