- TubeRenderer ($10) by Sixth Sensor
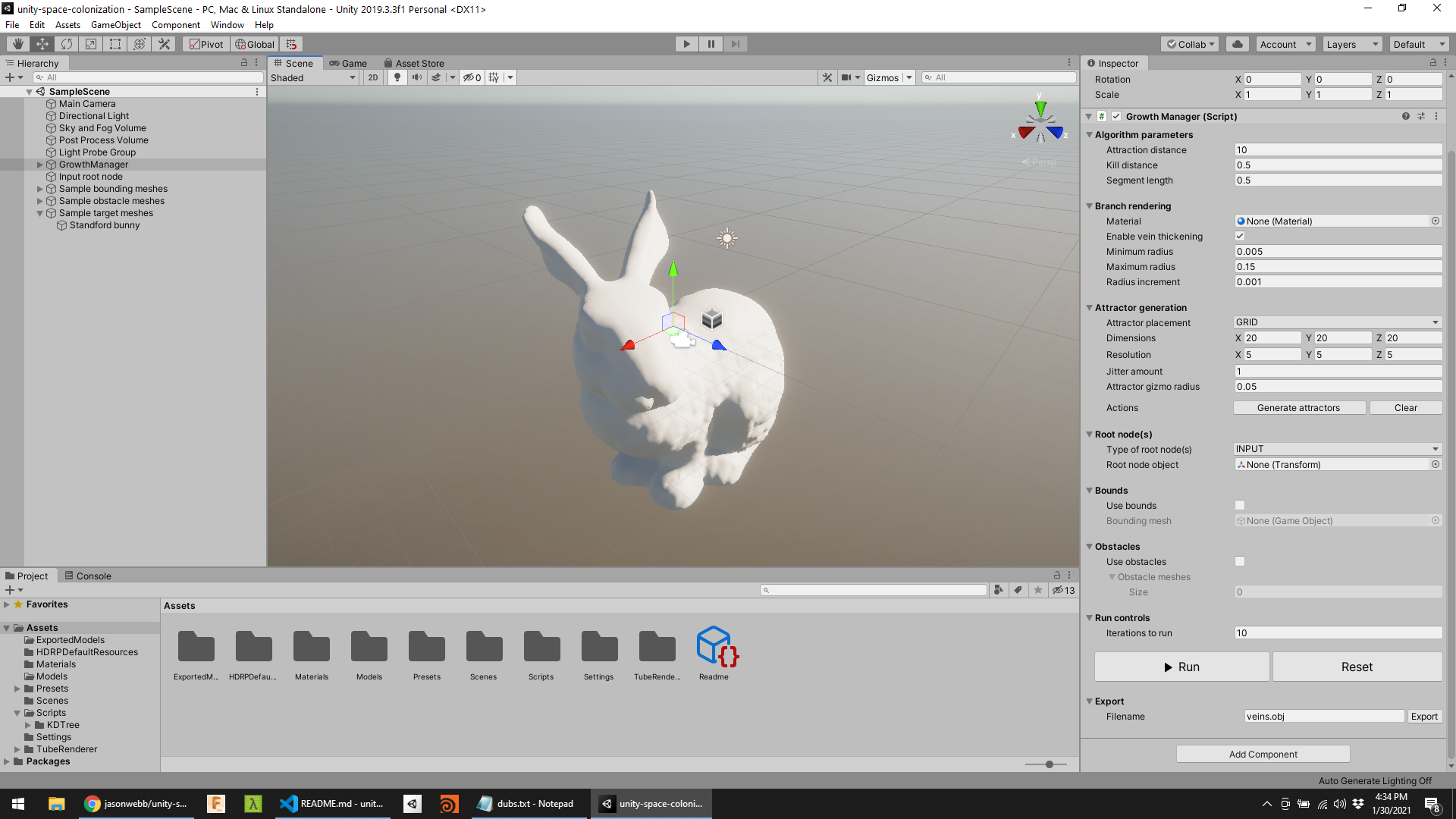
- Attraction distance - branches that are within this distance (and outside the kill distance) of an attractor will grow towards that attractor.
- Kill distance - how close branches can grow to attraction nodes before stopping.
- Segment length - length of each branch segment of the generated structure. In each iteration of the simulation, one segment is added to the tips of each branch that is not within a kill distance of an attractor.
- Material - reference to a material object that is applied to each individual branch segment.
- Enable vein thickening - progressively increase the radius of each branch segment starting from the tip (smallest) to the root node (largest).
- If enabled ...
- Minimum radius - smallest thickness that a branch can get.
- Maximum radius - largest thickness that a branch can get.
- Radius increment - rate at which the radius changes across each branch segment from tip to root.
- If disabled ...
- Radius - constant radius for all branch segments.
- If enabled ...
- Attractor placement - dropdown with the following options:
- SPHERE
- Radius - radius of sphere.
- Attractor count - number of attractors to scatter.
- GRID - evenly spaced attractors on a grid.
- Dimensions - length, width, height of grid.
- Resolution - number of attractors per axis.
- Jitter - amount of random displacement per attractor to make them less uniform.
- MESH - scatter attractors on the surface or inside of a custom mesh.
- Target mesh - reference to the mesh you want to use.
- Raycasting attempts - number of times to try casting a random ray. Unity's collision detection is not perfect, so the actual number of attractors that are generated will be much less than this number.
- Raycasting direction - direction to fire random rays for attractor placement.
- INWARDS - casts random rays from outside the mesh towards the origin. Scatters points on the surface.
- OUTWARDS - casts random rays from the origin to the outside. Scatters points on inner surface.
- DOME - casts random rays in a hemisphere around the mesh.
- SPHERE
- Attractor gizmo radius - size of the editor gizmos that indicate the position of each attractor.
- Actions
- Generate attractors - attempt to place attractors using the parameters chosen above. This may take a while depending on the parameters chosen and the complexity of the mesh.
- Clear - remove all attractors from the scene, like a reset.
- Type of root node(s) - dropdown with the following options:
- INPUT
- Root node object - reference to the point object you want to use as a root node.
- MESH
- Target mesh - reference to the mesh you want to randomly place root nodes on.
- Number of root nodes - how many randomly-placed root nodes you want.
- INPUT
- Use bounds - enable or disable restriction of branch growth to a chosen bounding volume.
- If enabled ...
- Bounding mesh - reference to a mesh object you want to use to constrain growth inside of.
- If enabled ...
- Use obstacles - enable or disabled the use of obstacle objects that branch growth cannot occur in.
- If enabled ...
- Size - how many obstacles you want to use.
- Element [n] - reference to a mesh object that the branch growth must avoid.
- If enabled ...
- Iterations to run - number of times to run the simulation. Start small until you know what you're doing!
- Run - press to run the simulation for the number of times chosen above.
- Reset - press to remove any previously-generated branches so growth can start over.
- Filename - name of the file you want to export. Be sure to provide a file extension.
- Export - press to export the generated branches on the screen to a file with the name provided above.