An Autonomous UAV Assisted Communication is Remote Disaster Area using Imitation Learning (Behavioral Cloning)

You can find the Article related to this repository from IEEE.
Abstract: The damage to cellular towers during natural and man-made disasters can disturb the communication services for cellular users. One solution to the problem is using unmanned aerial vehicles to augment the desired communication network. The paper demonstrates the design of a UAV-Assisted Imitation Learning (UnVAIL) communication system that relays the cellular users’ information to a neighbor base station. Since the user equipment (UEs) are equipped with buffers with limited capacity to hold packets, UnVAIL alternates between different UEs to reduce the chance of buffer overflow, positions itself optimally close to the selected UE to reduce service time, and uncovers a network pathway by acting as a relay node. UnVAIL utilizes Imitation Learning (IL) as a data-driven behavioral cloning approach to accomplish an optimal scheduling solution. Results demonstrate that UnVAIL performs similar to a human expert knowledge-based planning in communication timeliness, position accuracy, and energy consumption with an accuracy of 97.52% when evaluated on a developed simulator to train the UAV.
- The sytem model and imitation model are based on experts data for Queues and UEs:
- os
- time
- copy
- keras
- pickle
- plotly
- scipy.io
- numpy
- sklearn
- random
- platform
- scipy.stats
- matplotlib.pyplot
- matplotlib.patches
- matplotlib.mplot3d.art3d
This code is run and tested on Python 3.6 on linux (Ubuntu 18.04) machine with no issues. All configurate data such as generated energy and location are saved in ConfigData Directory. All trained models, figures, and figure objects are saved in Output directory:
Repository/Output/
├──Figures
├── *.pdf
├──FigureObject
├── *.fig.pickle
├──Models
├── *.modelUser can change parameters such as Number of UEs, Number of Frames, CBR Rate, Number of Sectors, Number of simulation events, the Mode of the program, Packet Size, and all Flags in the config file (config.py). Seven different modes are considered for this implementation:
# ***** Modes ==> i) Demonstration: The expert shows his/her behavior
# ***** ii) Training: Supervised learning the clone expert's behavior after demonstration
# ***** iii) Classification: Evaluation of the imitated model on the classification problem
# ***** iv) Imitation: Getting action from the imitation model
# ***** v) Results_demonstration: Results of the expert
# ***** vi) Result_imitation: Result of the agent (Behavioral cloning)
# ***** vii) Result_imitation_newRate: Result of the agent (Behavioral cloning) for new arrival rates
Also, queues' lengths limitation and other parameters such as transmission and mobility energy consumption rates, Learning parameters such as Loss functions, Learning rate, Number of Epochs, and batch size are configurable as well in the config.py file.
- To run the simulator in ask expert for his/her knowledge, change Mode to 'Demonstration' in the config.py file and run main.py file (Change this):
Config_General = {..., 'Mode': "Demonstration", ...}
python3 main.py
- To train a DNN model based on the collected information from the expert, change Mode to 'Training' in the config.py file and run main.py file (Change this):
Config_General = {..., 'Mode': "Training", ...}
python3 main.py
- To evaluate the imitated and trained model from the previus section, change Mode to 'Classification' in the config.py file and run main.py file (Change this):
Config_General = {..., 'Mode': "Classification", ...}
python3 main.py
- To compare expert with Agent (the cloned model of behaviroal cloning) in the same scenario, change Mode to 'Imitation' in the config.py file and run main.py file (Like this):
Config_General = {..., 'Mode': "Imitation", ...}
python3 main.py
-
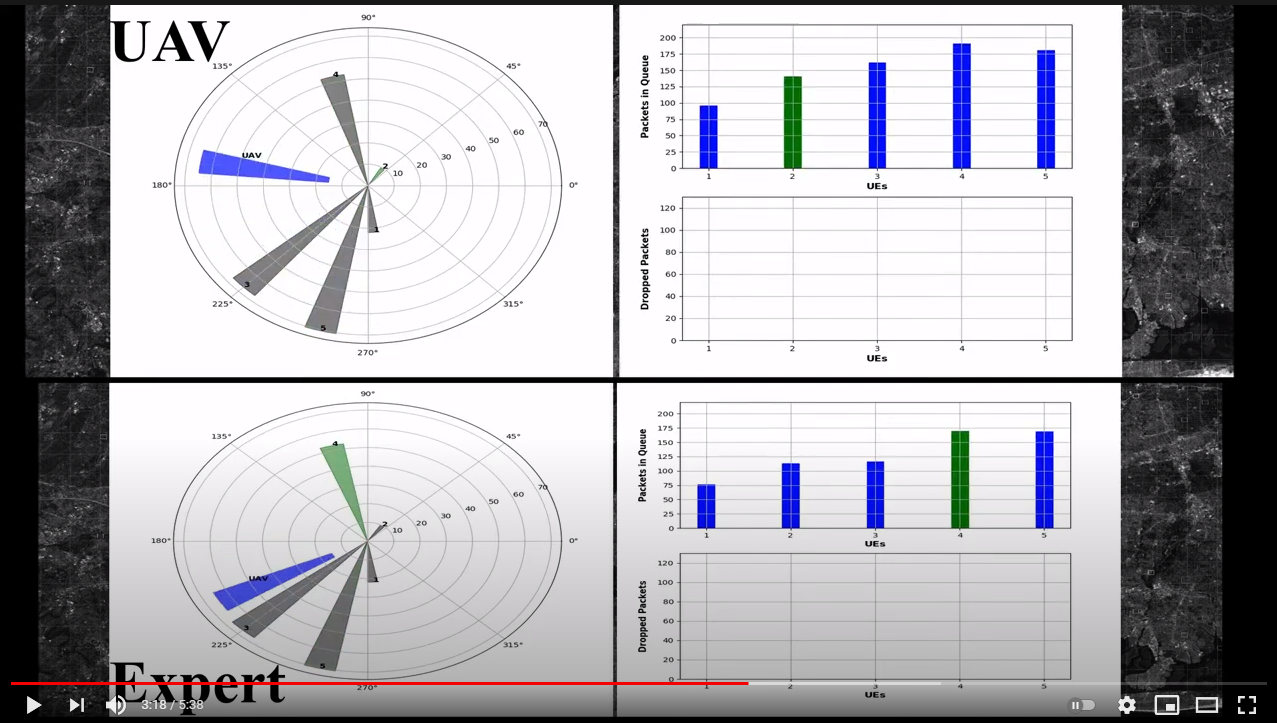
A short sample video of the simulator we designed is available on YouTube:
-
Performance evavluation (Accuracy and Loss) for Training, Vlidation, and Test sets:
-
Confusion matrix of true and predicted UEs during the test set for UnVAIL (Imitated Model):
- Performance comparison (EDT) for expert and the imitated model:
For more results please refer to our paper.
If you find the code or the article useful, please cite our paper using this BibTeX:
@article{shamsoshoara2021uav,
title={UAV-Assisted Communication in Remote Disaster Areas using Imitation Learning},
author={Shamsoshoara, Alireza and Afghah, Fatemeh and Blasch, Erik and Ashdown, Jonathan and Bennis, Mehdi},
journal={IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society},
year={2021},
publisher={IEEE}
}
For academtic and non-commercial usage