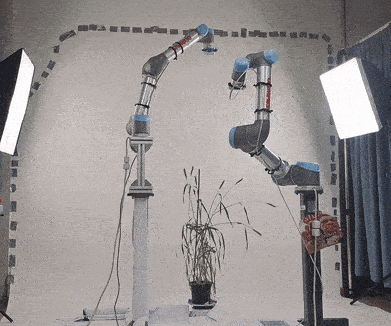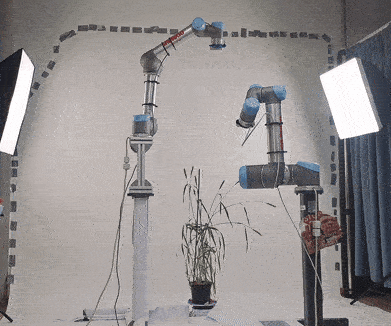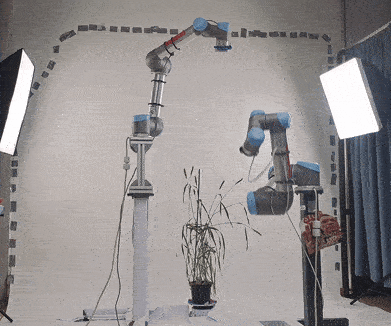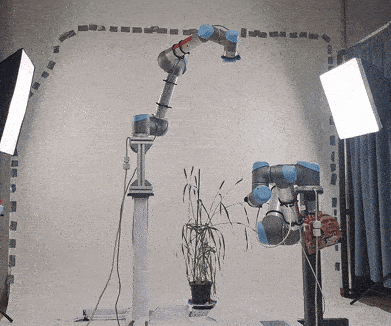UR5s, and other robot arms, are extremely useful for performing a wide range of complex tasks with high precision. However, controlling these arms can be extremely difficult, with most provided software not providing the enough functionality for dynamic tasks. Meanwhile, MoveIt is an extremely advanced path planning framework that can calculate trajectories for various robots in a wide range of environments. MoveIt also supports control using different programming languages, such as Python and C++, allowing integration into advanced scripts. Overall, MoveIt provides much better functionality than traditional software that comes packaged with the majority of these robot arms.
But, configuring MoveIt to work with customised setups can be challenging, often requiring expertise to configure for each individual setup. This becomes even more challenging when multiple robots are introduced; collision avoidance and parallel path planning becomes even more difficult to configure.
In this repo, we provide all files for our duel UR5 setup. Each UR5 arm is attached to a customised pedestal and has an attached RealSense camera. The joints of each robot start from the base of the pedestal, and finish at the camera lens, allowing for manipulation of the camera lens in relation to the robot base. Both arms support parallel path planning and collision avoidance. Furthermore, each robot has an attached camera, which can be loaded using a ROS topic (currently supports RealSense cameras in real life). Finally, we provide Gazebo launch files, which allow this setup to be launched in a simulation as well as real life.
The original purpose of this setup was for creating a new imaging setup for capturing various plants for 3D reconstruction. Our main repo for this experiment can be found here: https://github.com/Lewis-Stuart-11/3D-Plant-View-Synthesis
The commands to execute these different setups are:
- Arm 1: roslaunch ur5_control ur5_arm1_bringup.launch
- Arm 2: roslaunch ur5_control ur5_arm2_bringup.launch
- Duel Arms: roslaunch ur5_control ur5_duel_bringup.launch
This installation is designed for running on Ubuntu operating systems. While this setup might work on other operating systems, we recommend running this setup on Ubuntu 20.04.6.
Python 3.8.10 can be installed from the Python website: https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-3810/
While our configuration will probably work on other versions, this is the version that we employed for controlling our robots
Next, it is important to install the Robot Operating System (ROS) package. This is the underlying framework that is utilised by MoveIt to communicate with the UR5 robot effectively.
Ros Noetic can be installed from the ROS website: http://wiki.ros.org/noetic/Installation/Ubuntu
We have not tested our setup with any other version of ROS, while other versions may work, we recommend using Noetic.
Remember to source the noetic setup filepath and add this to your bashrc file (to ensure these files are sourced on launch). Example: echo "source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
It is important to also install Catkin, which manages ROS packages and is used for creating a workspace. If this has not already been installed, then install via the following command: sudo apt-install python3-catkin-tools ros-noetic-catkin
If you already have a catkin workspace, then skip this part.
Next, create a catkin workspace at the top-level directory:
mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
rosdep install -y --from-paths . --ignore-src --rosdistro melodic
cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin config --extend /opt/ros/${ROS_DISTRO} --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
catkin build
Remember to source the catkin setup filepath and add this to your bashrc file: echo "source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bach" >> ~/.bashrc
The src directory will contain the ROS packages needed for controlling the UR5. These will need to be built, using catkin, in order to the executed.
For more info, please visit: http://wiki.ros.org/catkin/workspaces
MoveIt is the framework that can control a variety of different robots.
MoveIt can be installed from the MoveIt website: https://moveit.ros.org/install/
Or by executing the following command: sudo apt install ros-noetic-moveit
We utilised the Trac-IK kinematric solver for calculating the path planning for the robots. This needs to be installed seperately to function.
TRAC-IK Kinematics Solver can be installed on the ROS website: https://docs.ros.org/en/kinetic/api/moveit_tutorials/html/doc/trac_ik/trac_ik_tutorial.html
Or by executing the following command: sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-trac-ik-kinematics-plugin
Gazebo is a software package that can simulate robots virtually. If you plan on only using these config files on a real UR5, this can be skipped.
Gazebo can be installed via the Gazebo website: https://classic.gazebosim.org/tutorials?tut=install_ubuntu
In order to control the Ur5 robots, the universal robot moveit package must be installed. These contain all the config, controller and kinematic files required for running the robots.
Make sure that you are in the correct directory: cd ~/catkin_ws/src
Next, use clone the repo: git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/universal_robot
Make sure to rebuild: cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin build
In order to communicate with the UR5, the robot driver package needs to be installed.
Make sure that you are in the correct directory: cd ~/catkin_ws/src
Next, use clone the repo: git clone https://github.com/UniversalRobots/Universal_Robots_ROS_Driver.git
Make sure to rebuild: cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin build
Make sure to install the URCAP on the UR5 robot, to ensure that commands are correctly recieved: https://github.com/UniversalRobots/Universal_Robots_ExternalControl_URCap/releases
Each UR5 arm in this setup has an attached camera at the end of the UR5 TCP. Each camera has been modelled to match the specifications of the real life RealSense D345i camera. There are two main transforms for the camera:
- camera_controller: used for repositioning the camera; this acts as the end of the kinematic chain, so any movements map from the base of each robot to this transform.
- camera_predicted_colour_lens: the transform for the predicted position of the camera lens. This is used for generating camera poses (e.g. for 3D reconstruction information)
There are two arms in this setup. Each of these arms can be executed seperately, or together in the same scene. Arm1 is attached to a pedestal of height 1.2 and arm2 is on a pedestal of height 0.85. The duel arm setup has both arms in the scene. Arm 1 is positioned (0.35 -0.45 0) from the origin, and arm 2 is positioned (0.85 0.45 0) from the origin.
We provide bringup files for executing the different robot setups for arm1, arm2 and duel arms.
Each file has the following options:
- sim: If true, launch the MoveIt config as a simulation (and launch Gazebo).
- robot_ip: The IP address of the robot on the network. It is important to change this for it to work on your real life setup.
- robot_kinematics_config: the kinematics calibration file for the robot that you will be connecting to. A new version will need to be generated for your real life robots.
- world: the Gazebo world to load into a simulation.
- use_ros_realsense: If true, launch the ROS camera drivers for the real life cameras (currently supports realsense cameras).
Every robot setup is unique and it is important that these configuration files can be altered to match a variety of different arrangements. Ultimately, the main changes will be performed in the robot URDF files, which determine the position/configuration of each joint in the robot chain.
Firstly, ensure that the robots IP addresses have been correctly set on the bringup file.
Any joint changes can be made in the gazebo.xacro and gazebo_macro.xacro files for each of the arms. We recommend keeping the joints directly related to the UR5 robots the same, but alter attached joints (such as the pedestal, camera, etc...) to match your setups correctly. Any changes made directly to the TCP (camera lens) will mean that a new MoveIt package will need to be generated to ensure the kinematic chain correctly accounts for these alterations. To ensure that each joint accurately represents its real life counterpart, make sure that all joints are correctly measured and calibrated (otherwise there could be issues such as collisions).
If extra robots need to be added to the setup, then a new set of controllers will need to be added for that robot and a new MoveIt package will need to be generated. For more information on how to generate new MoveIt packages, visit: http://docs.ros.org/en/kinetic/api/moveit_tutorials/html/doc/setup_assistant/setup_assistant_tutorial.html