Implementation of the RRT algorithm with pygame interface for:
- Holonomic Robot
- Non-Holonomic Robot
A robot is to navigate a two dimensional space, avoiding known locations with obstacles, traveling from its initial location to a goal location. Given localization information (robot’s initial position, obstacle location, goal location), the task is to implement a path planning decision maker to drive the robot from its initial position to the desired location.
Specifically, the problem can be formed as follows: Consider a 2D grid instantiated with different kinds of obstacles (for instance, geometrical shapes like Rectangles, Circles, Triangles or a combination of any of the above 2/3).
-
The RRT Algorithm is a sampling-based path planning algorithm which randomly samples points in the environment and adds them to a tree based data structure.
-
They search high dimensional spaces by incrementally building random tree from random samples. The process of building a RRT and finding a path from starting to goal configuration can be broken down into simple steps:
- Sample a random point within the environment
- Find the node in the tree which is nearest to the random point and check for collisions with obstacles
- Extend the tree towards the random point
- Repeat steps 1 to 3. Stop iteration on reaching goal or within a threshold of the goal
- Install PyGame 1.9.4 module in Python 3
- run python3 <filename.py> and choose the filename accordingly
- Holonomic robot with fixed obstacles - run RRT_holonomic.py / RRT-Holonomic-Robot.ipynb
- Holonomic robot with hand drawn obstacles - RRT_holonomic_drawn.py
- Non Holonomic robot with fixed obstacles - run RRT_nonholonomic.py / RRT-Non-Holonomic-Robot.ipynb
- Non Holonomic robot with hand drawn obstacles - RRT_nonholonomic_drawn.py
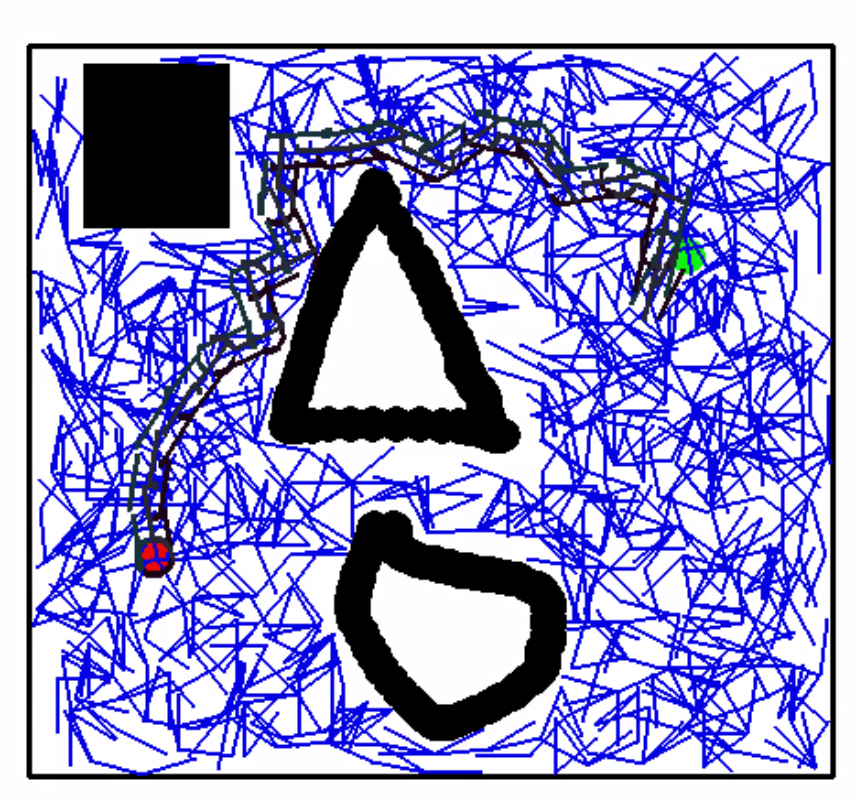
- When the UI window opens, click on the buttons and place the start, finish point and the draw the obstacles
- Then view the RRT graph evolution of the robot along with the center and wheel trajectories
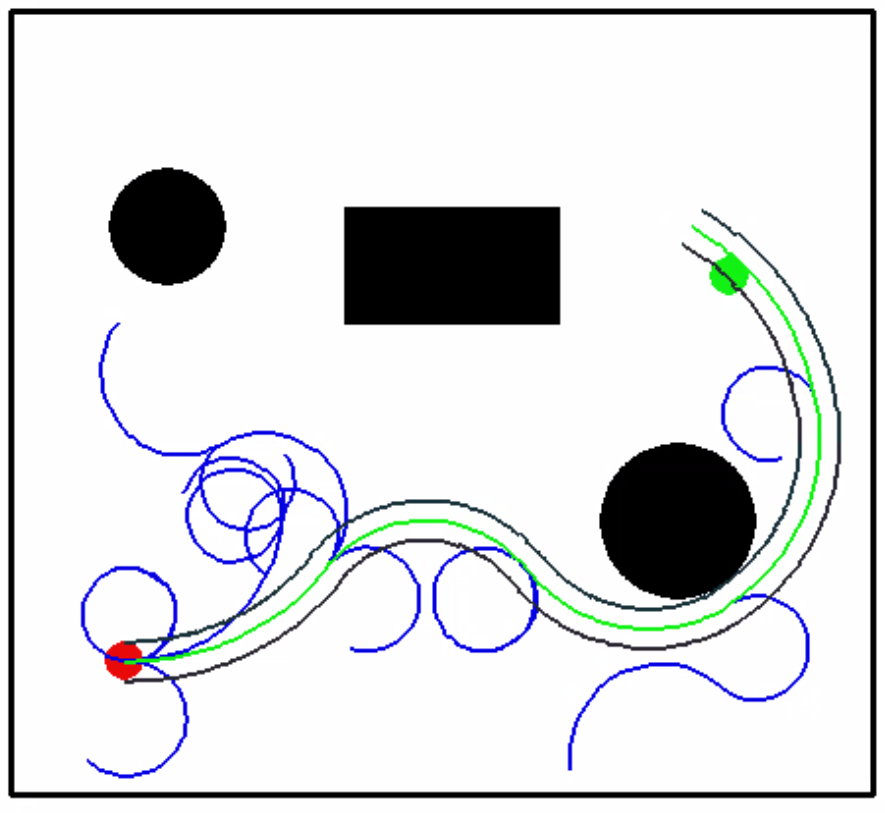
- We used a three wheeled omnidirectional robot for implementing RRT algorithm for the holonomic case. The robot with a radius of 8 units and has three wheels aligned at an angle of 120 degrees from each other.
- We used pygame interface to for custom selection of start and goal points.
- For obstacle detection, we checked the intensity of all points in the RRT path and did not add the node to the RRT tree if black in color(obstacle).
- Additionally, we also make sure the node is within the boundary
- To find the RRT path, we used backtracking of all the parent nodes in the tree structure.
- We also find the wheel trajectories for all three wheels of the robot by following the RRT path.
-
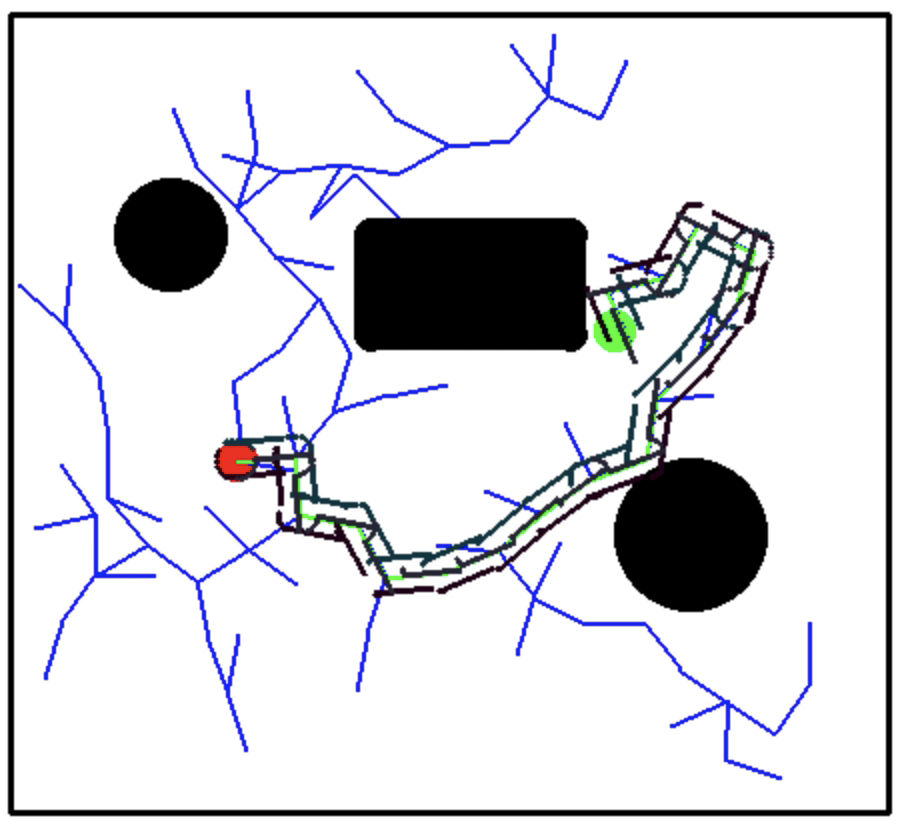
We used a differential drive robot for implementing RRT algorithm for the holonomic case. The robot with a length of 20 units and has two wheels aligned at an angle of 180 degrees from each other. Differential Drive
-
These robots have two wheels and the controllable parameters are velocity v and angular velocity omega
-
Velocities v_x and v_y are not decoupled. They are coupled through the robot's instantaneous direction theta
-
Differential Drive Equations
- v_cx(t) = v*cos(omega * t)
- v_cy(t) = v*sin(omega * t)
- v_cy(t) = v_cx(t)*tan(omega * t)
-
We used pygame interface to for custom selection of start and goal points.
-
For obstacle detection, we checked the intensity of all points in the RRT path and did not add the node to the RRT tree if black in color(obstacle).
-
Additionally, we also make sure the node is within the boundary
-
To find the RRT path, we used backtracking of all the parent nodes in the tree structure.
-
We also find the wheel trajectories for the two wheels of the robot by following the RRT path.