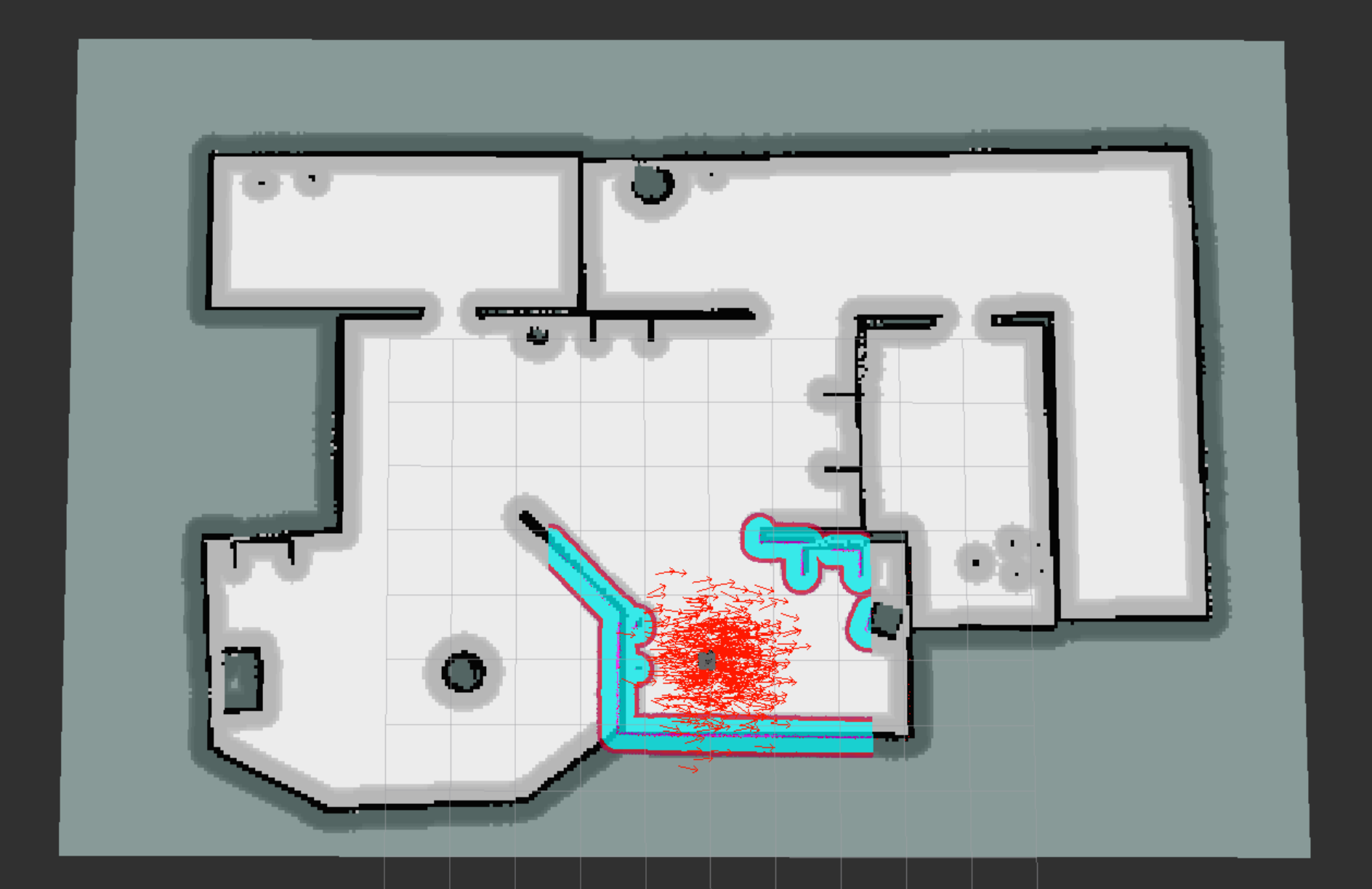
Final project for Udacity's Robotics Software Engineer Nanodegree.
A Home Service Robot simulated in ROS and Gazebo. The service-robot performs SLAM to map an indoor environment, localizes itself and autonomously navigates to pick up and place objects around the house. The aim is to navigate to a pick-up location to collect a virtual object and then navigate to a specified drop-off zone to deposit it.
The turtlebot3 (Waffle Pi) robot is used.
The project consists of the following parts:
- Design an indoor environment with the Building Editor in Gazebo.
- Create a 2D occupancy grid map of the environment by teleoperating the robot and performing SLAM using the
gmappingpackage (utilizing odometry and laser scan data). - Use Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization (AMCL) to localize the robot inside the environment with the
amclpackage (by utilizing odometry and laser scan data). - Test the navigation stack and send a goal for the robot to navigate to via the 2D Nav Goal button in Rviz.
- Write a pick_objects node that commands the robot to navigate to the desired pick-up and drop-off zones.
- Write an add_markers node that subscribes to the robot odometry and publishes markers to Rviz to simulate the object pick-up and drop-off.
There are three packages in this project:
- home_service: This package holds the Gazebo world, the amcl parameters, the rviz configurations, the generated map, the launch files to interface with all the packages and scripts to automatically run them.
- pick_objects: This package is responsible for commanding the robot to navigate to the desired pick-up and drop-off locations.
- add_markers: This package publishes markers to rviz to simulate the object pick-up and drop-off.
The directory structure is depicted below:
. RoboticsND-Home-Service-Robot
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── add_markers # Publishes markers to Rviz to simulate the object pick-up and drop-off
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── package.xml
│ └── src
│ └── add_markers_node.cpp
├── home_service
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── config # amcl parameters
│ │ ├── base_local_planner_params.yaml
│ │ ├── costmap_common_params.yaml
│ │ ├── global_costmap_params.yaml
│ │ └── local_costmap_params.yaml
│ ├── launch
│ │ ├── amcl_demo.launch # Launches the amcl package for localization
│ │ ├── gmapping_demo.launch # Launches the gmapping package for performing SLAM & creating a 2D map
│ │ ├── home_service_world.launch # Launches the home environment
│ │ ├── robot_description.launch # Launches the robot
│ │ └── view_navigation.launch # Launches Rviz with saved config
│ ├── map # The map of the environment
│ │ ├── home_service_map.pgm
│ │ └── home_service_map.yaml
│ ├── package.xml
│ ├── rviz
│ │ └── rvizconfig_home_service.rviz
│ ├── scripts
│ │ ├── add_markers.sh
│ │ ├── home_service.sh # To run the home service robot
│ │ ├── pick_objects.sh
│ │ ├── test_navigation.sh
│ │ └── test_slam.sh
│ └── worlds
│ └── home_service.world
├── images # Simulation images
│ ├── home.png
│ ├── home_service.gif
│ ├── home_service_map.png
│ └── rviz.png
└── pick_objects # Commands the robot to navigate to the desired pick-up and drop-off zones
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── package.xml
└── src
└── pick_objects_node.cpp
The project was developed on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with:
- ROS Noetic
- Gazebo 11.11.0
The following dependencies need to be installed:
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
$ sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-turtlebot3
$ sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-teleop-twist-keyboard
$ sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-openslam-gmapping
$ sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-navigationThe scripts to run multiple packages utilize the xterm terminal which can be installed via:
$ sudo apt-get install xtermTo run this project, you must have ROS and Gazebo installed.
$ mkdir -p /catkin_ws/src/
$ cd catkin_ws/src/
$ catkin_init_workspace$ git clone https://github.com/elena-ecn/RoboticsND-Home-Service-Robot.git
$ sudo mv RoboticsND-Home-Service-Robot/* ./$ cd /catkin_ws/
$ catkin_make$ source devel/setup.bash$ cd src/home_service/scripts
$ sudo chmod +x *.shOptional: If you would like to test the SLAM algorithm and create a new map of the environment, run:
$ ./test_slam.shTeleoperate the robot through your keyboard to explore the environment and see the map appear in Rviz. Once the house is fully explored, save the map with:
$ rosrun map_server map_saver -f ../map/home_service_mapOptional: If you would like to test the navigation algorithm, run:
$ ./test_navigation.shNow you will be using the already generated map and localize with AMCL. Press the 2D Nav Goal button in Rviz and click somewhere on the map to command the robot to navigate there.
To simulate the full home service robot, run:
$ ./home_service.shThe robot will be using the generated map and will localize itself with the acml package. It will navigate to a virtual object (indicated by a green cube in Rviz), pick-up the object (the cube will disappear to simulate the pick-up) and then the robot will navigate to a drop-off zone and deliver the object (the cube will re-appear once the robot reaches the drop-off location).
The contents of this repository are covered under the MIT License.